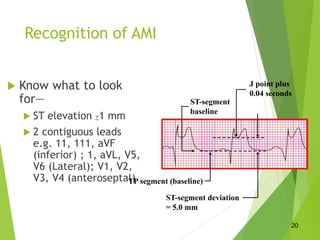
The document discusses acute coronary syndrome (ACS), which includes STEMI, NSTEMI, and unstable angina representing varying degrees of coronary artery occlusion. A 12-lead ECG within 10 minutes of arrival is central to diagnosis and risk stratification. STEMI shows ST elevation and elevated enzymes, while NSTEMI shows ST depression/T-wave inversion and elevated enzymes. The primary goals are early reperfusion for STEMI patients via fibrinolysis within 30 minutes or PCI within 90 minutes. Treatment involves oxygen, aspirin, nitroglycerin, morphine and reperfusion therapies like fibrinolytics or PCI, with important timelines to maximize outcomes for ACS patients.