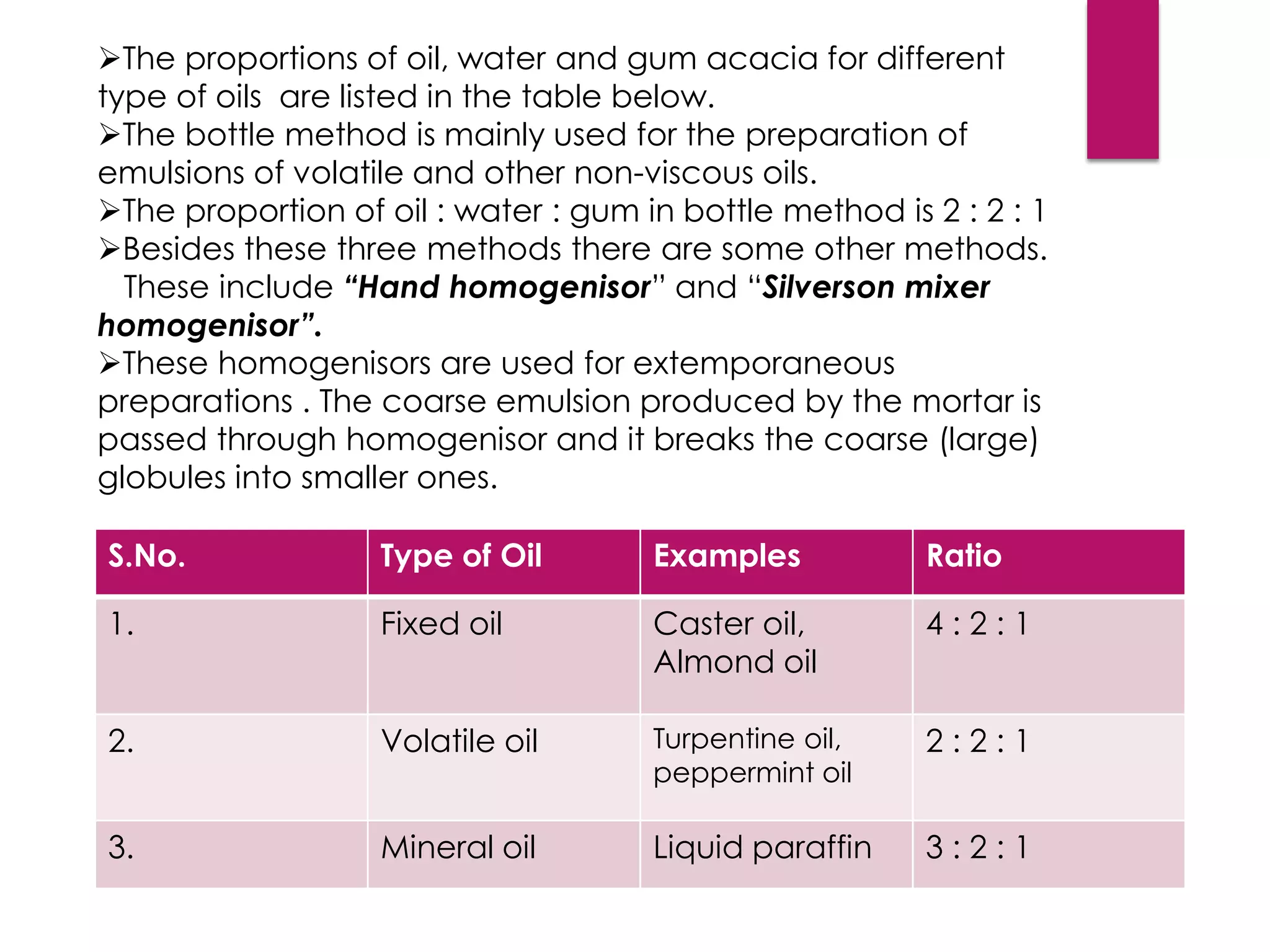
This document discusses emulsions, which are biphasic liquid dosage forms containing two immiscible phases, one dispersed within the other. The dispersed phase is known as the internal or dispersed phase, while the phase it is dispersed in is the continuous or external phase. The two main types are oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions, with water as the continuous phase, and water-in-oil (W/O) emulsions, with oil as the continuous phase. Tests can identify the emulsion type based on conductivity, dye interaction, or stability on dilution. Emulsions require emulsifying agents to reduce interfacial tension and allow formation. Common methods to prepare emulsions include using a mortar