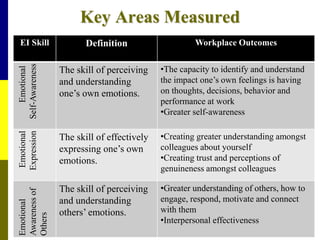
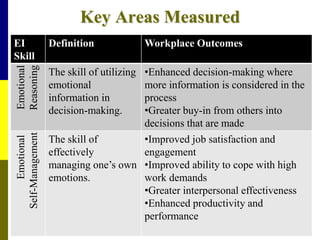
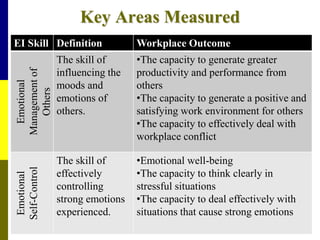
The document discusses the significance of emotional intelligence (EQ) in nursing, distinguishing it from cognitive intelligence (IQ) and highlighting its role in effective patient care and workplace relationships. It outlines how high EQ contributes to lower stress levels, improved decision-making, and greater job satisfaction, while addressing the importance of training in emotional competencies for better healthcare outcomes. Additionally, the document emphasizes that EQ is a crucial quality for nurse leaders to foster a supportive work environment and enhance overall team performance.







































![ Nurses who pretended to have unfelt feelings were more
burned out than nurses who did not pretend to have
unfelt emotions. And, ...nurses who covered up their true
feelings were more burned out than nurses who did not
cover up such emotional experiences. Nurses who
covered up their true feelings were more burned out than
nurses who did not cover up such emotional
experiences.
Increasing recognition of the emotional experiences and
demands that constitute an essential facet of the nursing
work environment is the first step to providing younger
nurses with the support they need...[to] reduce their rates](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emotionalintelligenceeq-copy-copy-210315175647/85/Emotional-intelligence-53-320.jpg)



