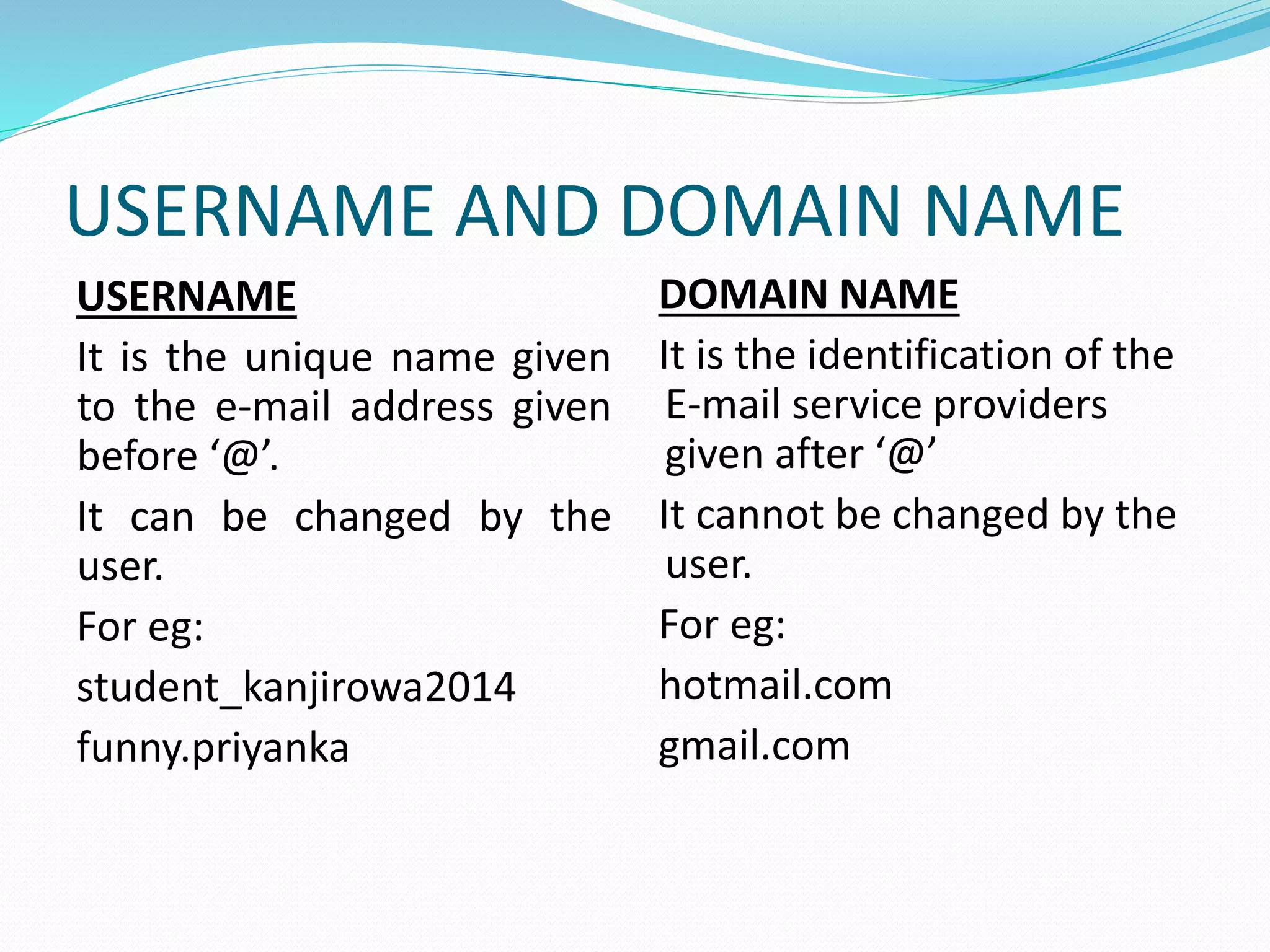
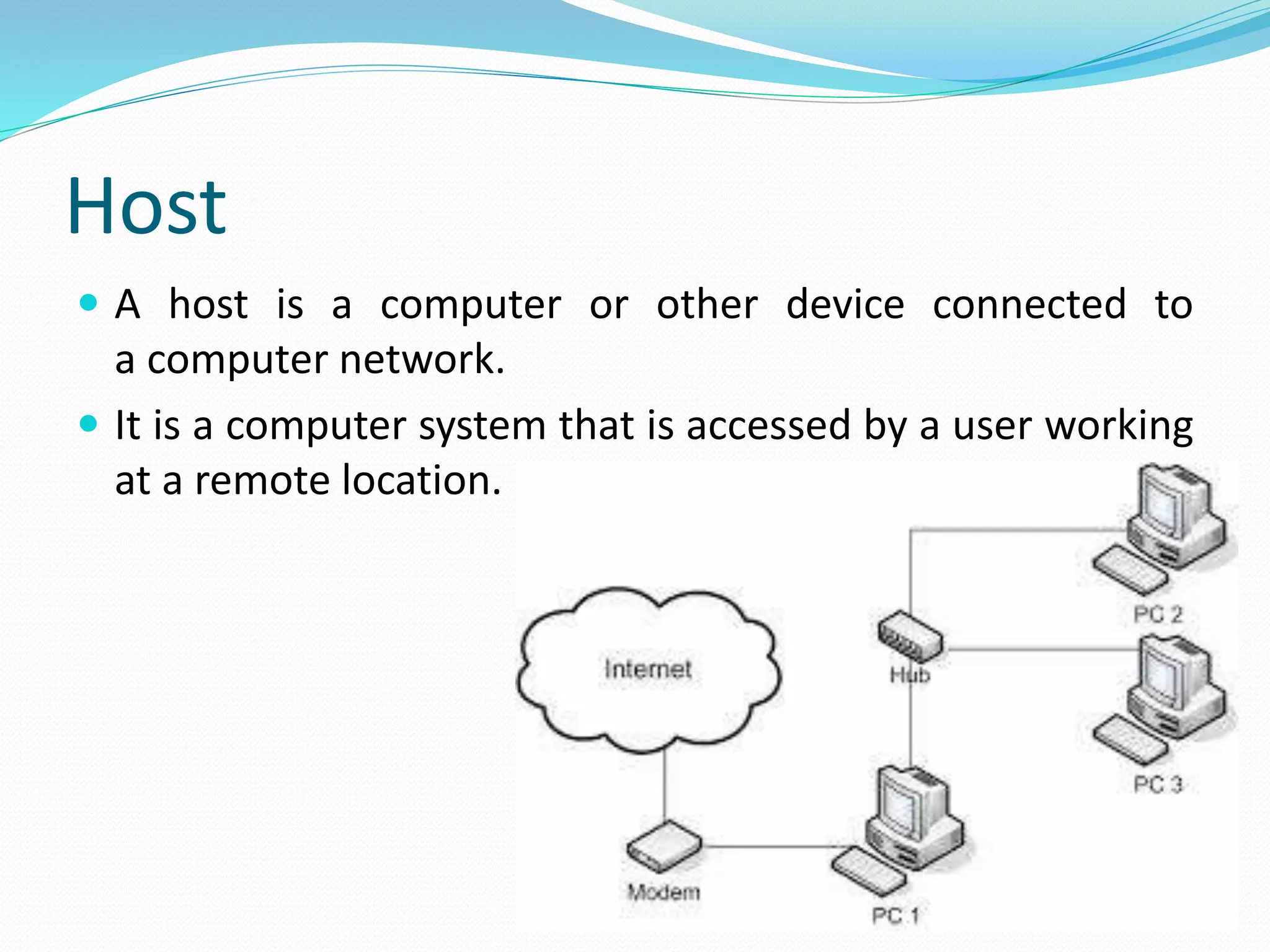
E-mail is a method for exchanging digital messages electronically between an author and recipients. It allows transmission of text, files, photos, audio and video. Major email providers include Gmail, Hotmail, Yahoo, and AOL. E-mail works on a store-and-forward model, with the sender's message stored on a mail server and forwarded through internet and satellite links to the recipient's mail server. Key aspects of e-mail include the address format of username@domain, mail servers that act as electronic post offices, and advantages like low cost and speed versus disadvantages like potential for viruses and spam.