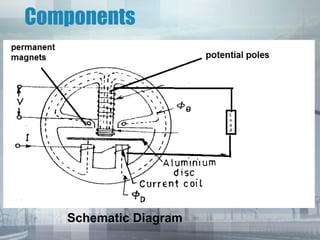
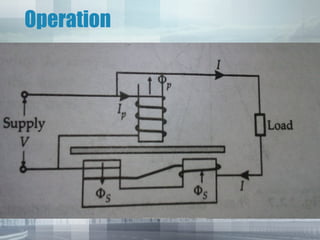
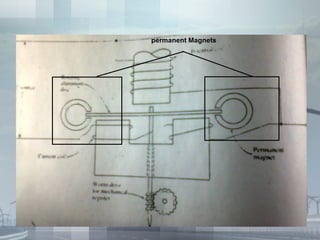
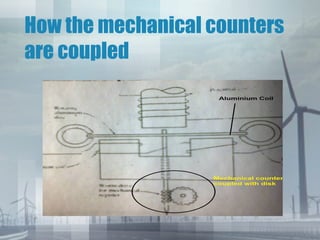
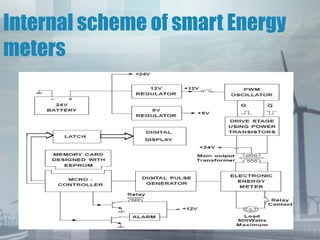
An energy meter measures the amount of electrical energy consumed. It works by using magnetic fields to rotate an aluminum disk, whose rotation is proportional to energy usage. The disk's rotation is retarded by permanent magnets to prevent over-rotation. Its movement is registered by mechanical counters displaying the energy consumed. Traditional meters have drawbacks like friction and flux inaccuracies over time. Smart meters provide more accuracy, longer life, and digital displays to address these issues.