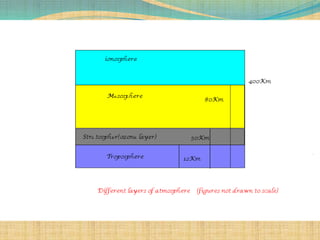
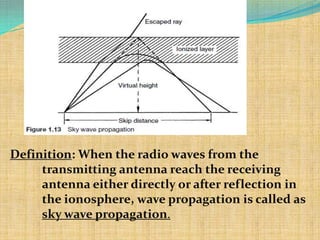
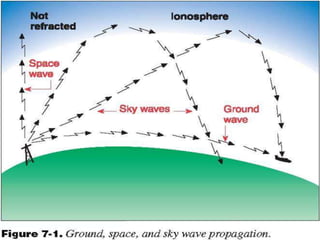
The document discusses three modes of electromagnetic wave propagation:
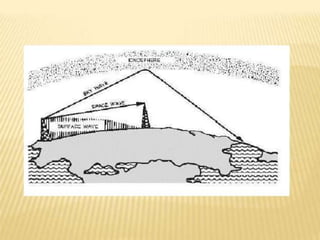
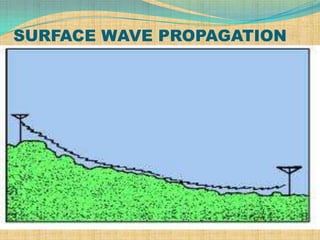
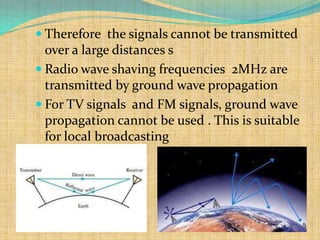
1) Surface wave propagation involves waves traveling along the Earth's surface and is suitable for local broadcasting up to 2MHz.
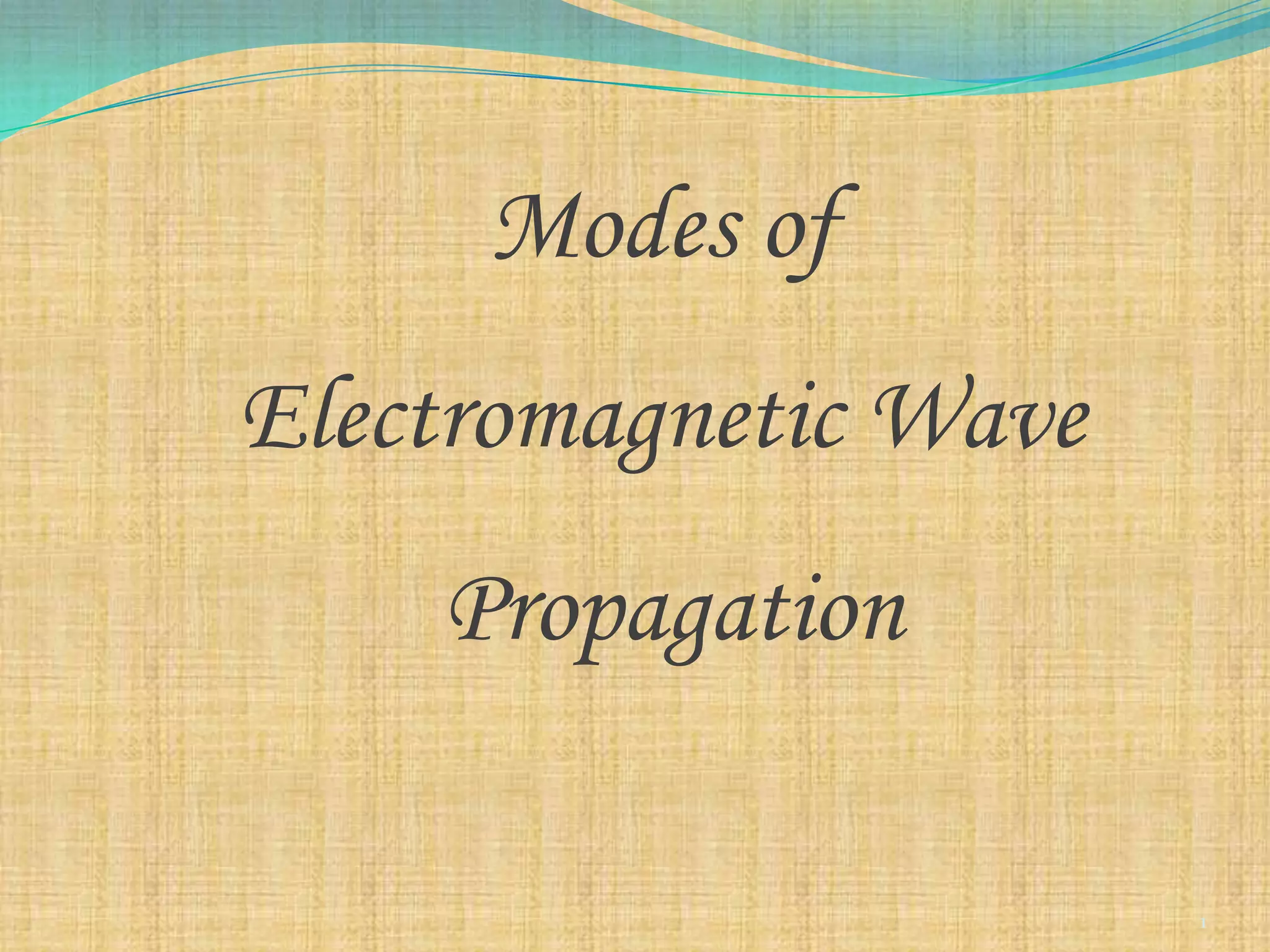
2) Space wave propagation includes direct, ground-reflected, and tropospheric waves not subjected to ground absorption. It is used for FM radio and TV signals over line-of-sight distances.
3) Sky wave propagation uses reflection from the ionosphere to transmit signals from 3-30MHz over long distances but is unreliable due to weather variations.