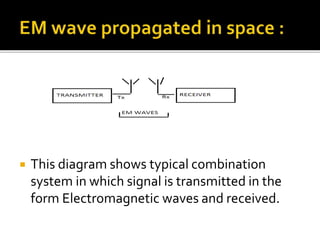
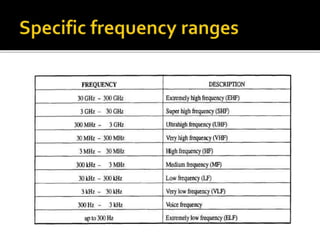
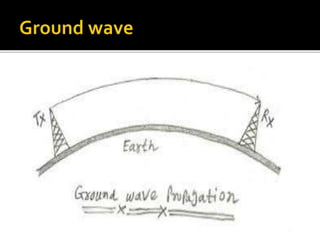
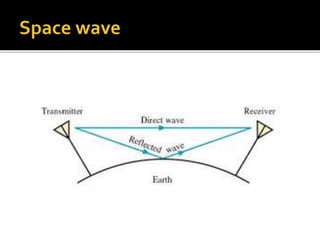
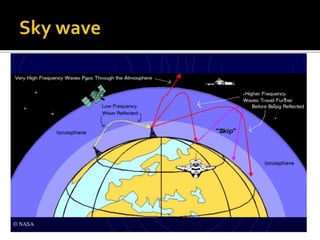
This document discusses different methods of electromagnetic wave propagation through space. There are three basic paths: ground waves which follow the Earth's curvature for lower frequencies; space waves which travel line-of-sight; and sky waves which are reflected by ionized layers in the atmosphere, allowing higher frequency signals to travel farther than line-of-sight. The ionosphere, located 30-240 miles above the Earth, plays a key role in sky wave propagation by reflecting radio signals back to Earth, enabling long-distance HF radio communications.