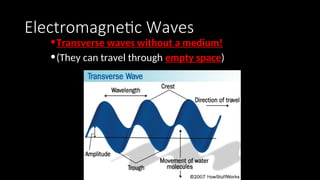
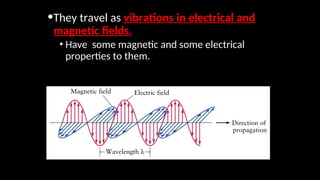
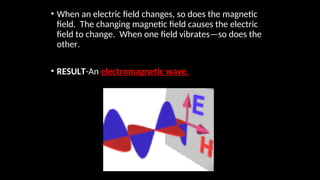
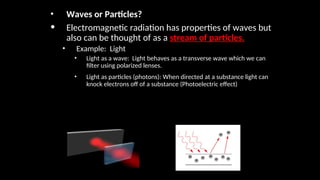
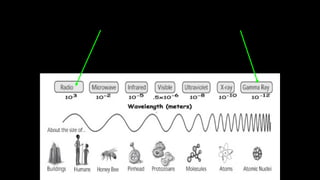
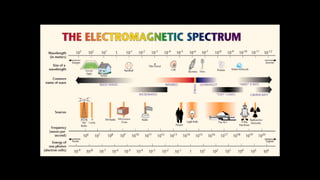
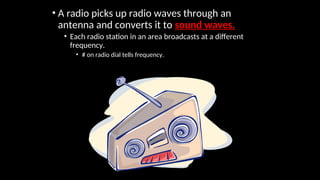
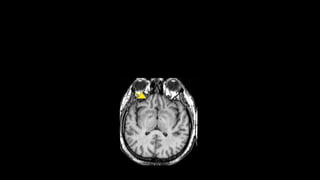
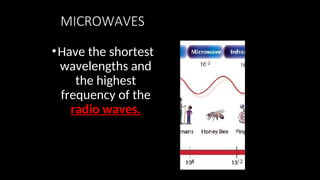
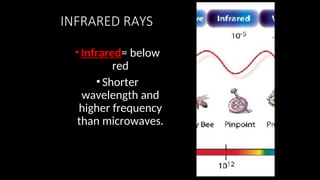
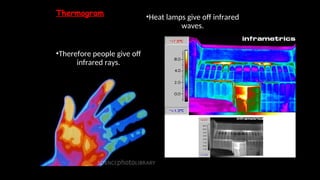
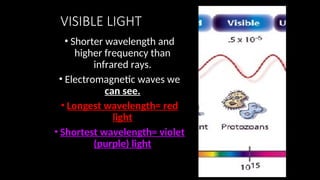
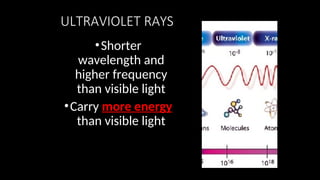
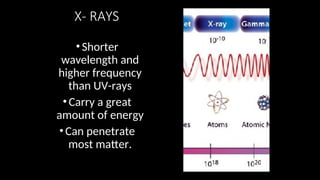
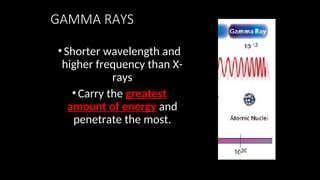
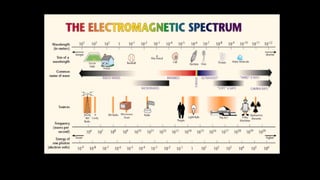
Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves that can travel through empty space, moving at the speed of light (300,000 km/s). The electromagnetic spectrum includes various types of waves, ordered by increasing frequency, from radio waves to gamma rays, each with unique properties and applications. Key uses range from GPS and microwaves to medical imaging (MRI) and radiation treatment, highlighting their diverse impact on technology and health.