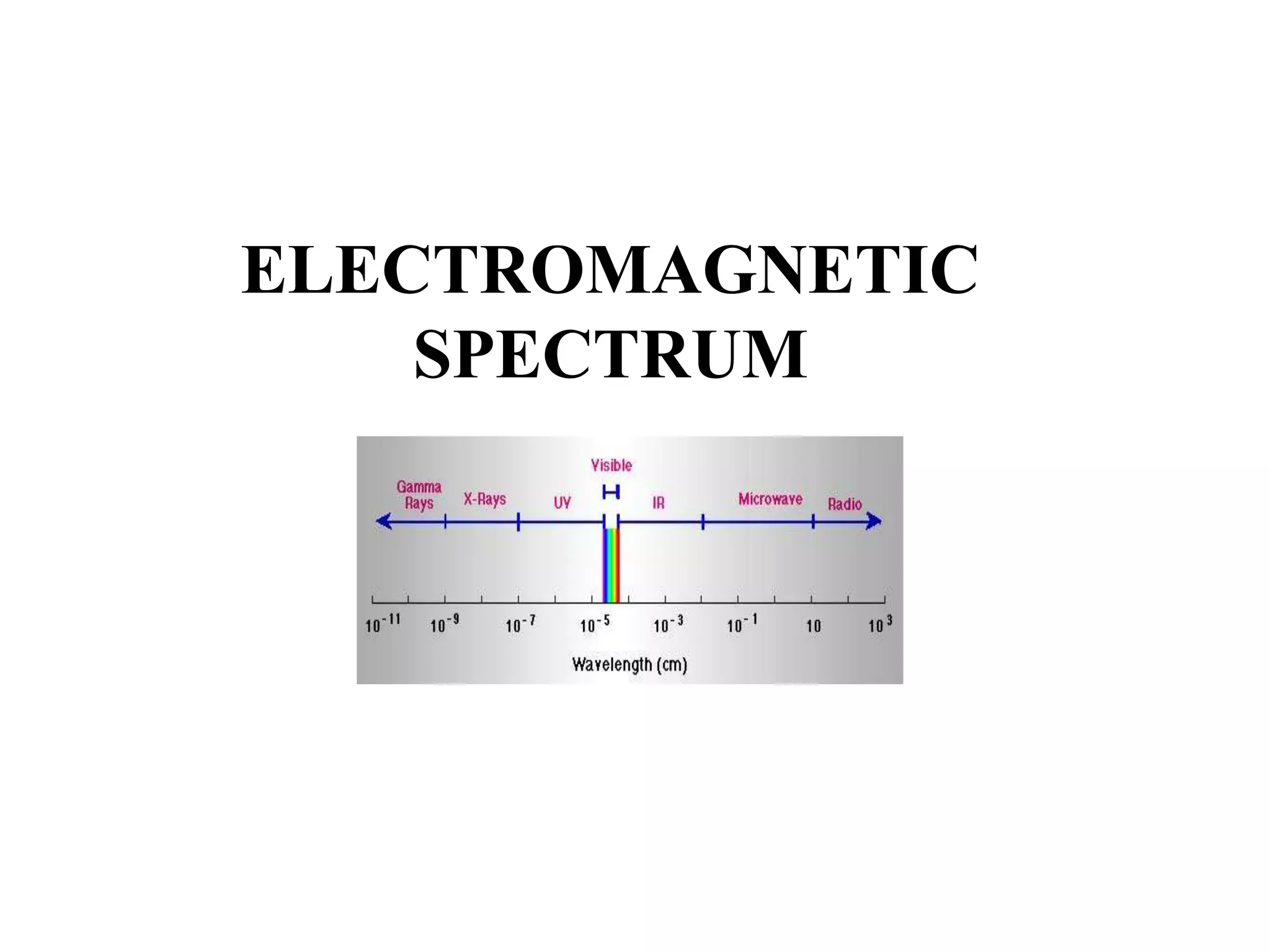
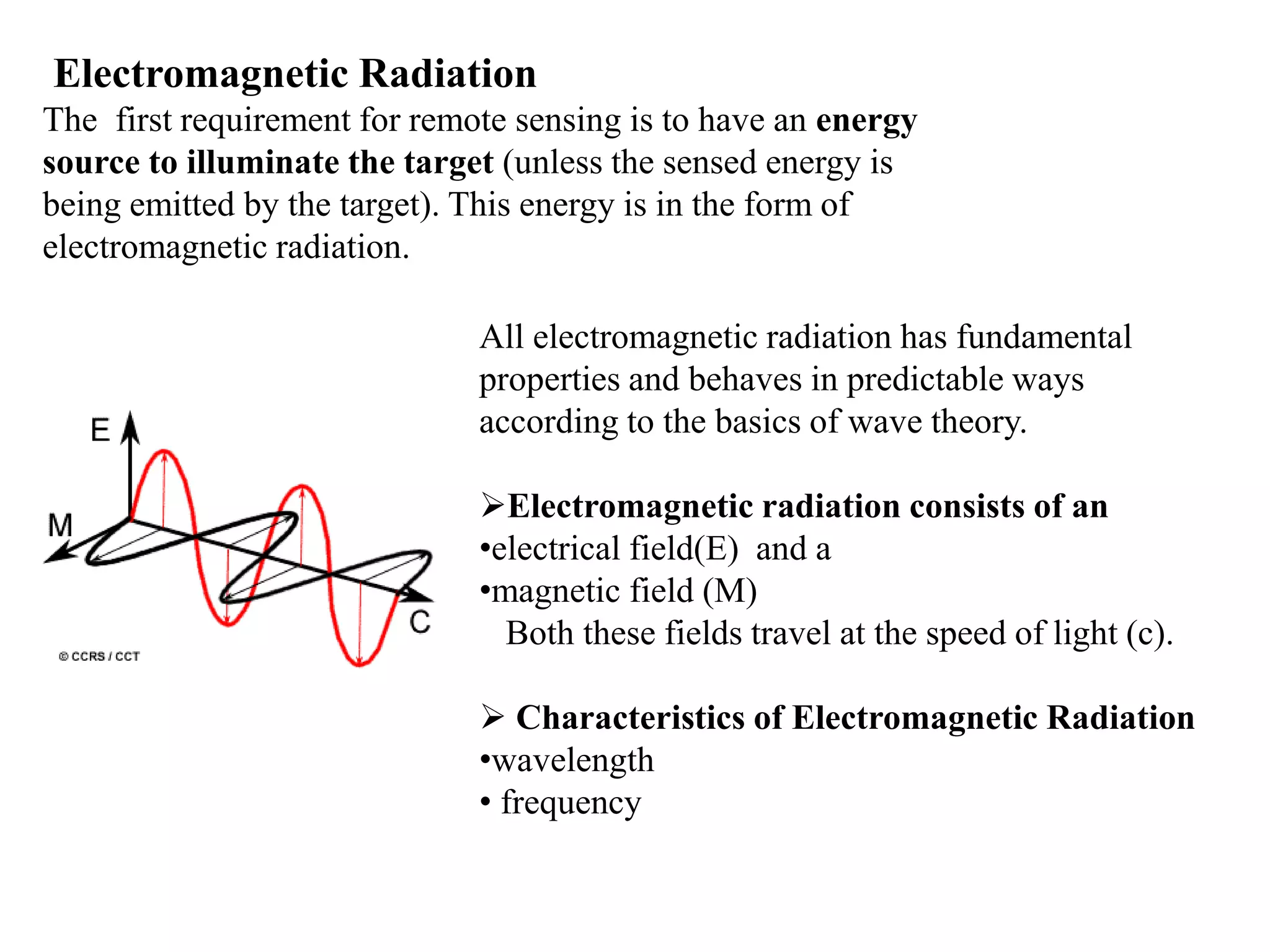
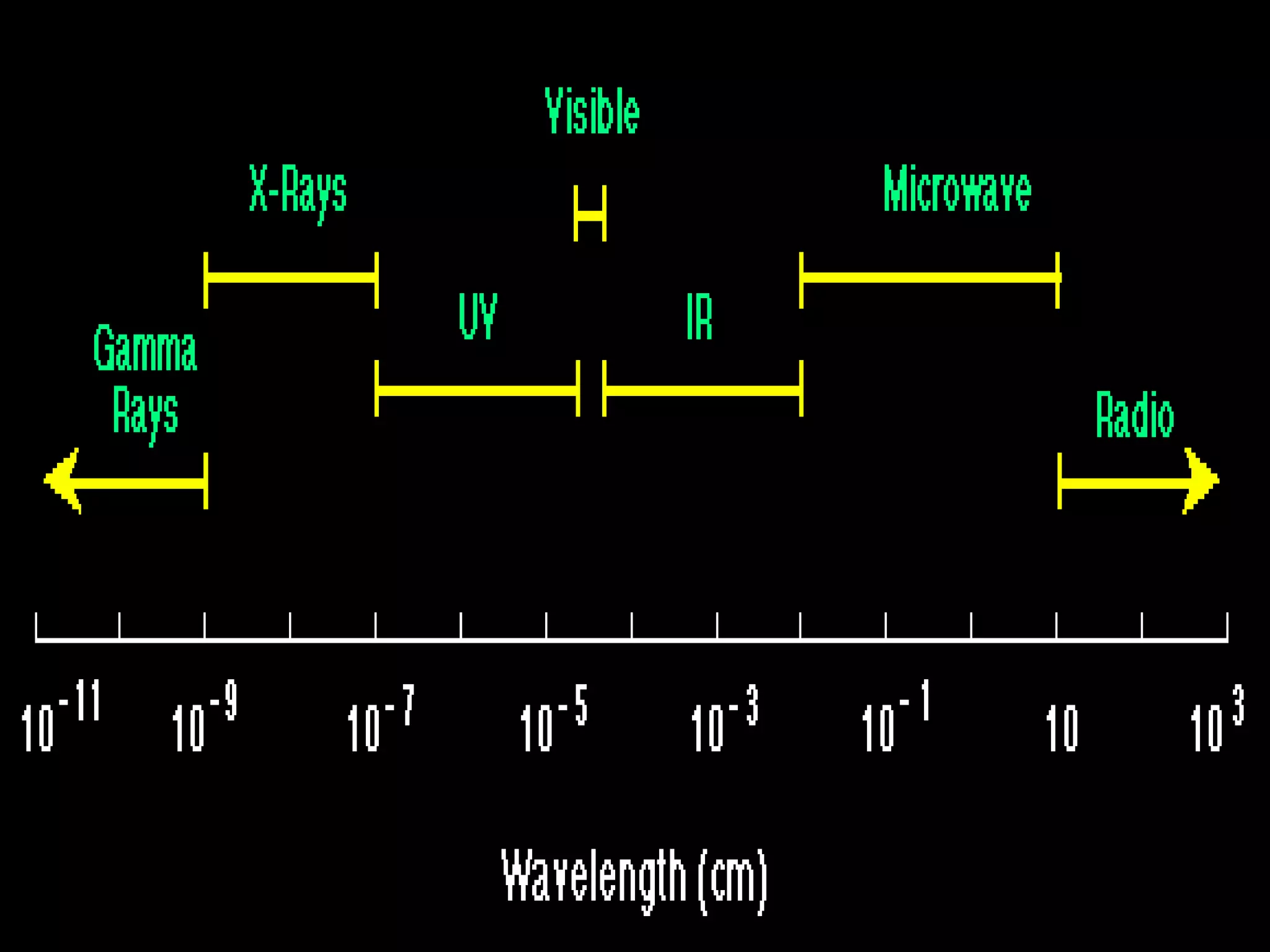
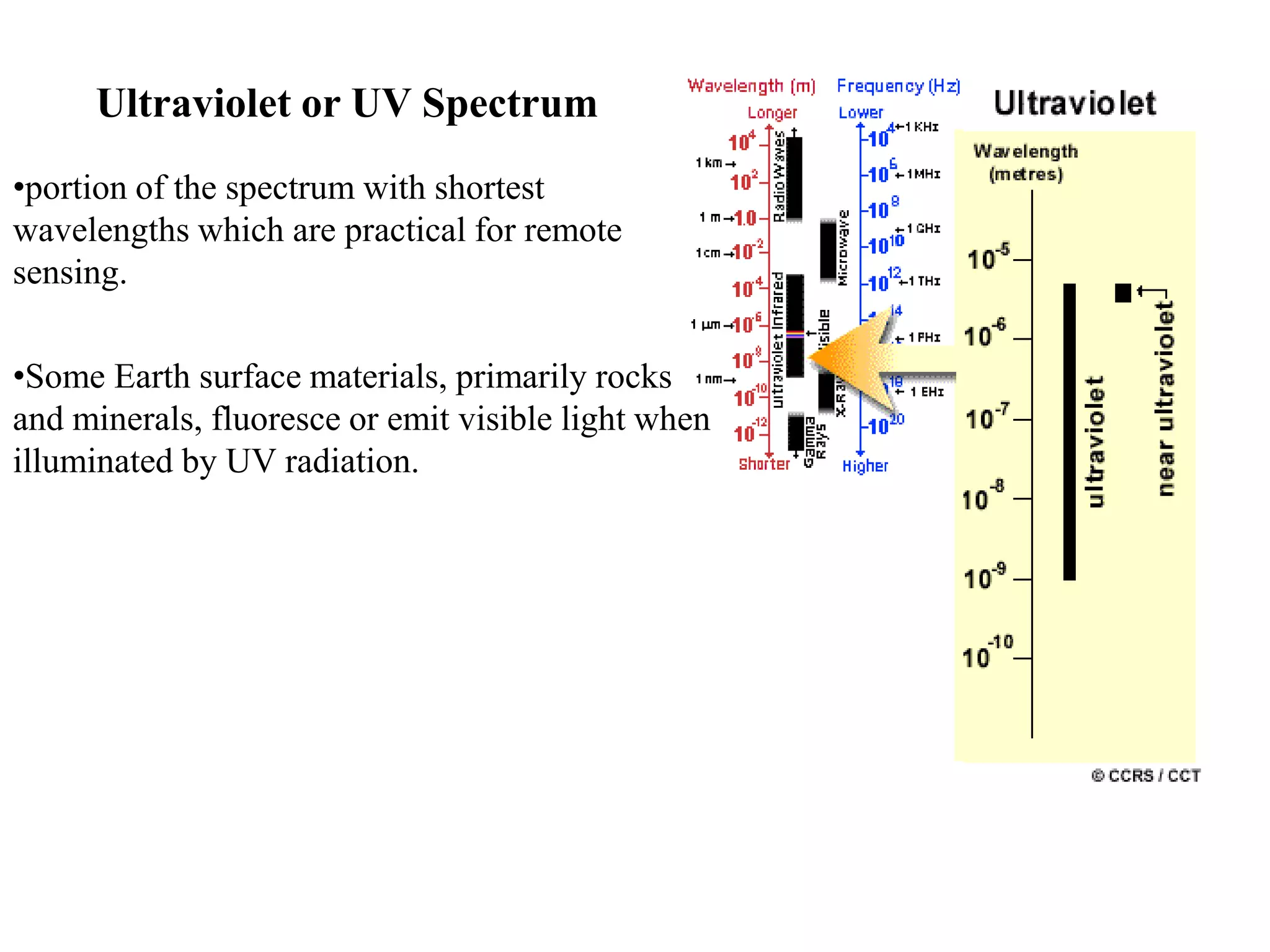
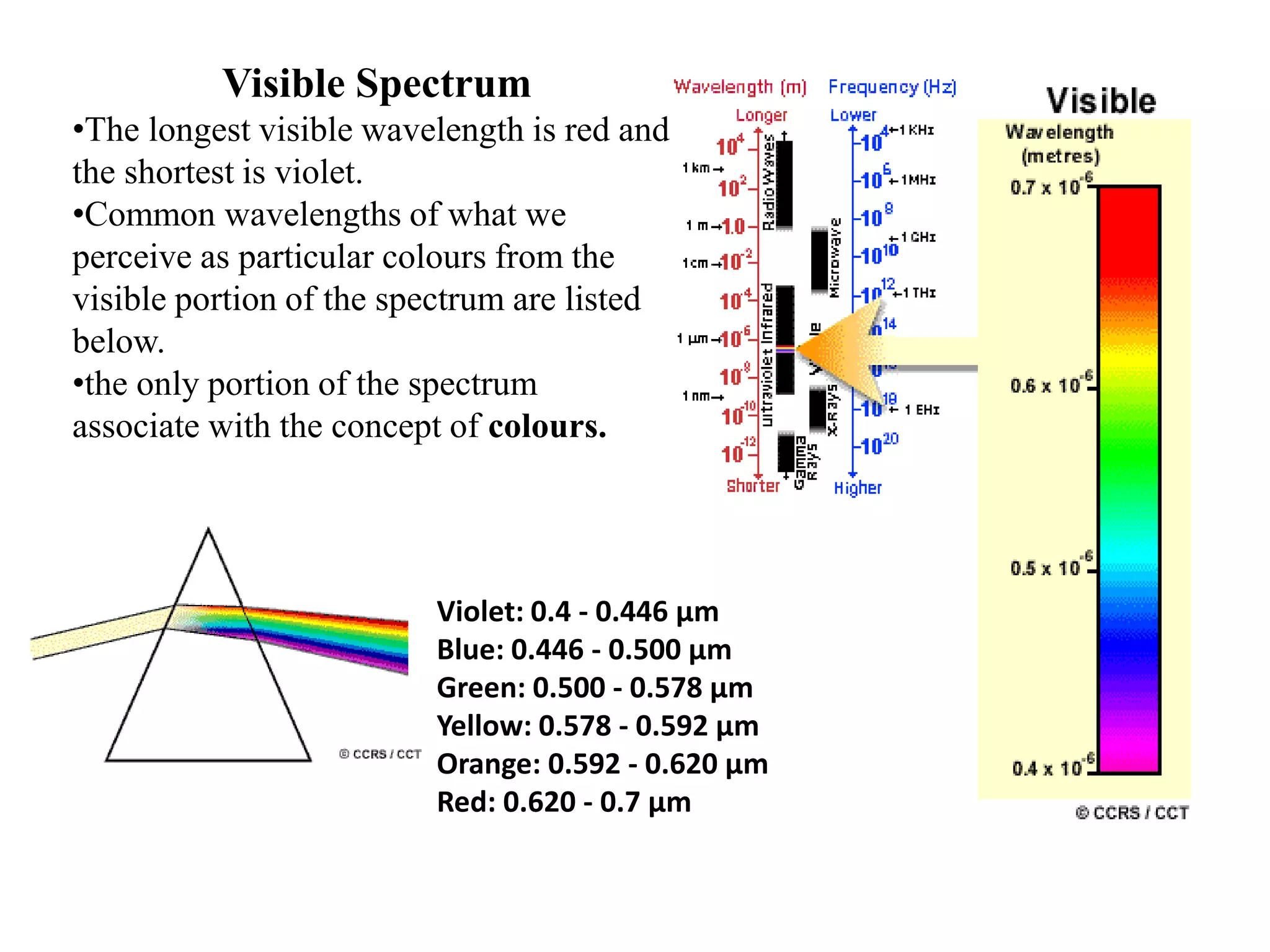
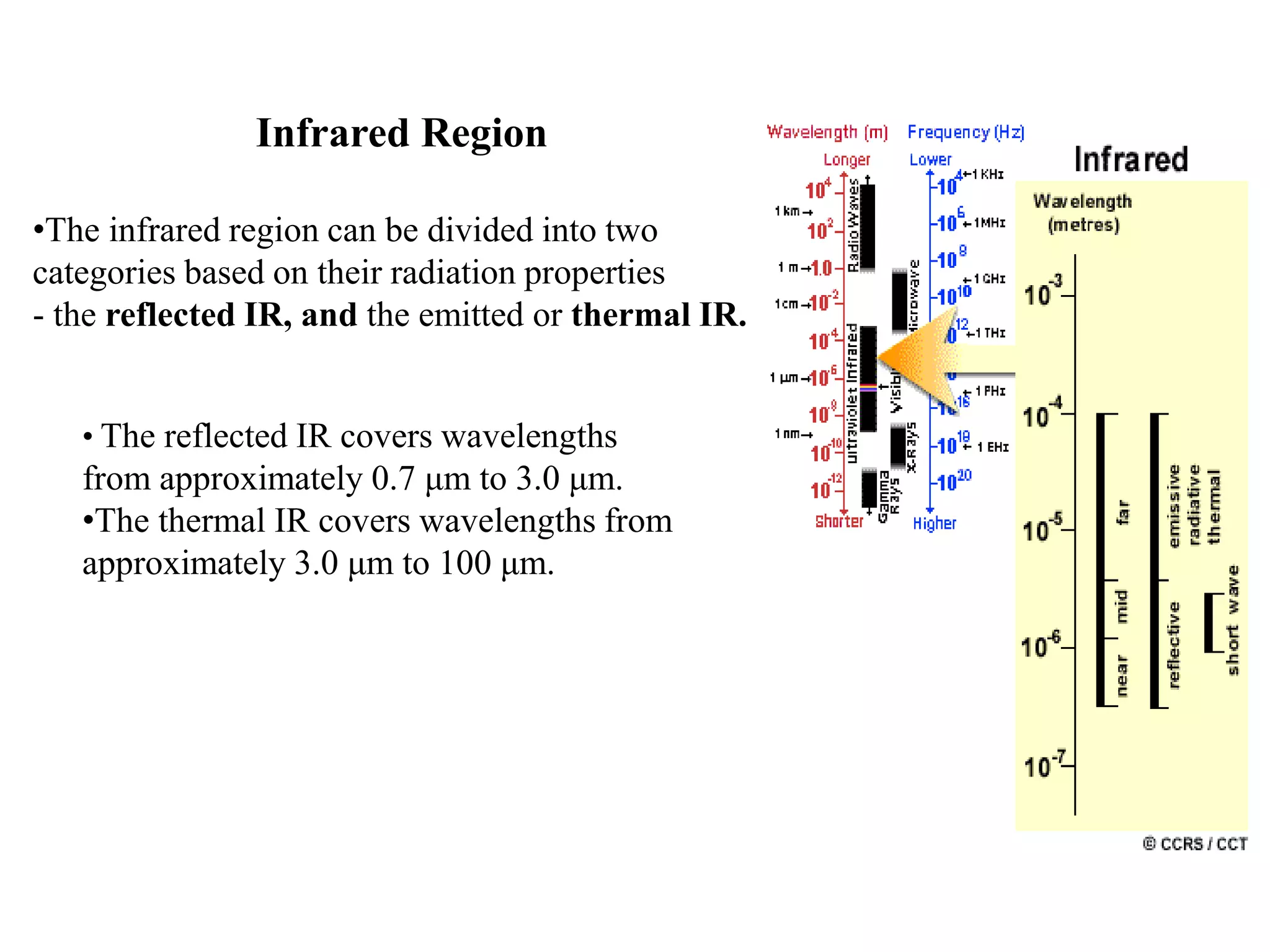
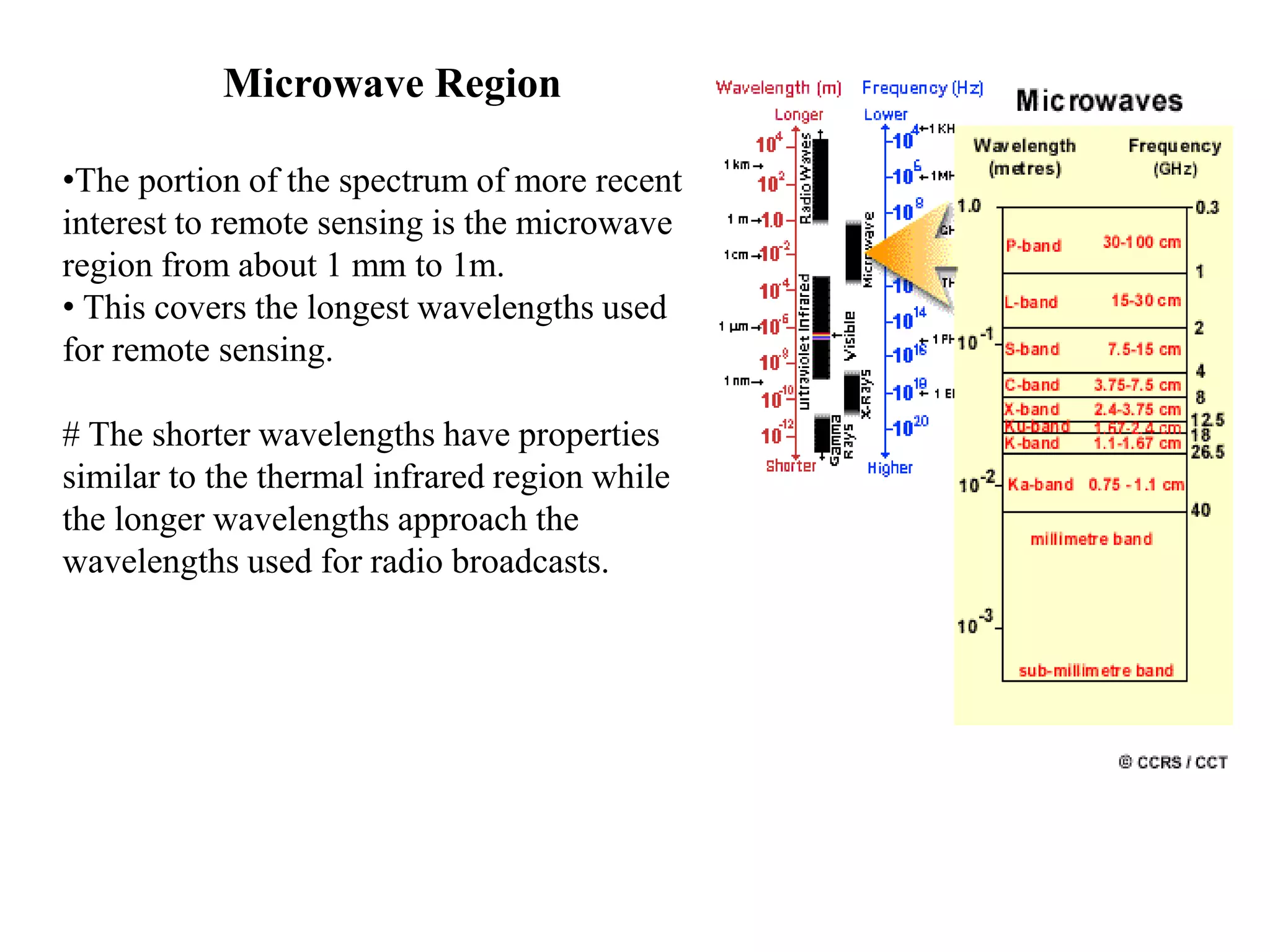
1. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from gamma rays to radio waves, with different types of radiation having different wavelength ranges. Several regions of the spectrum are useful for remote sensing including ultraviolet, visible, infrared, and microwaves.
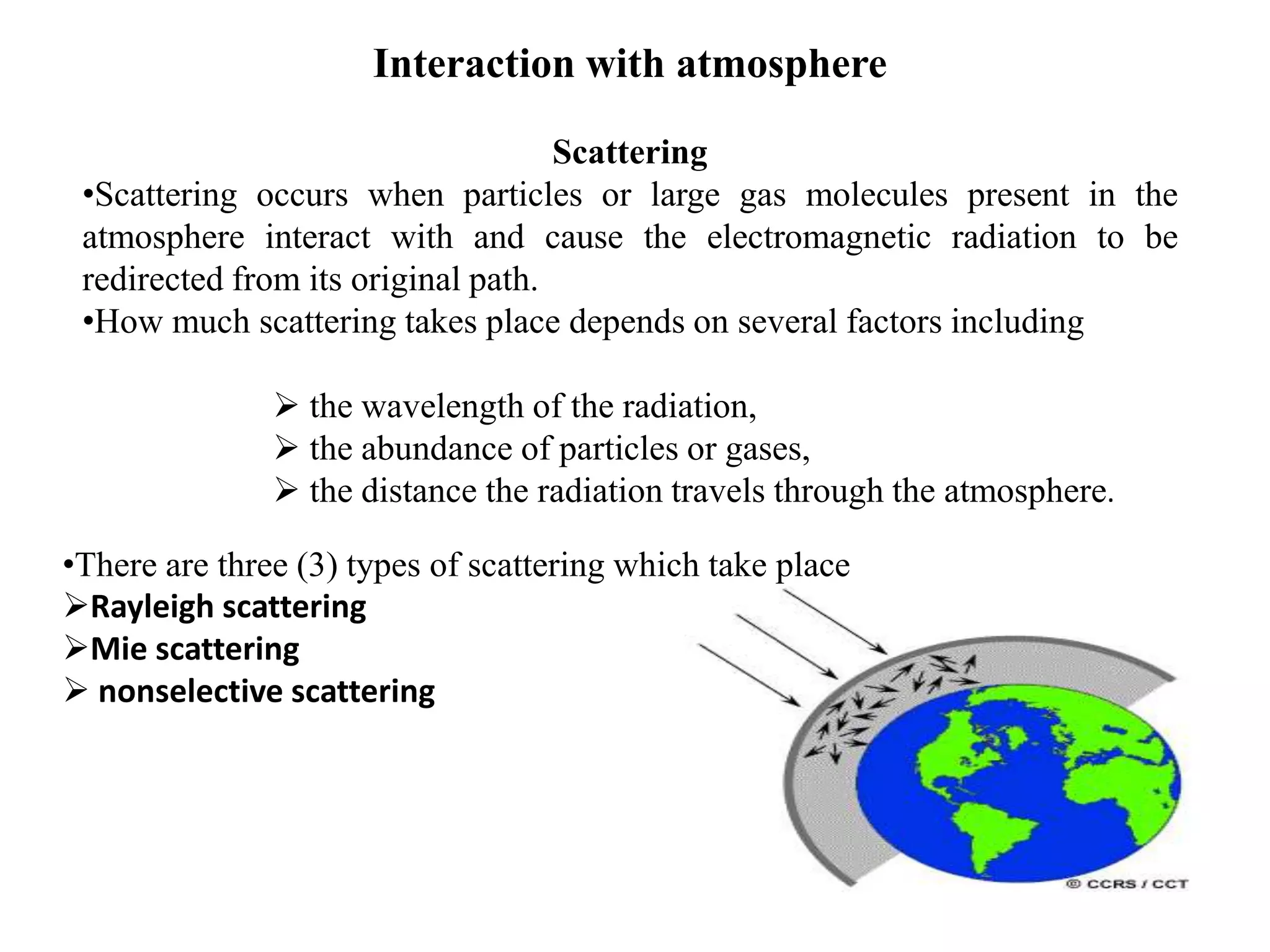
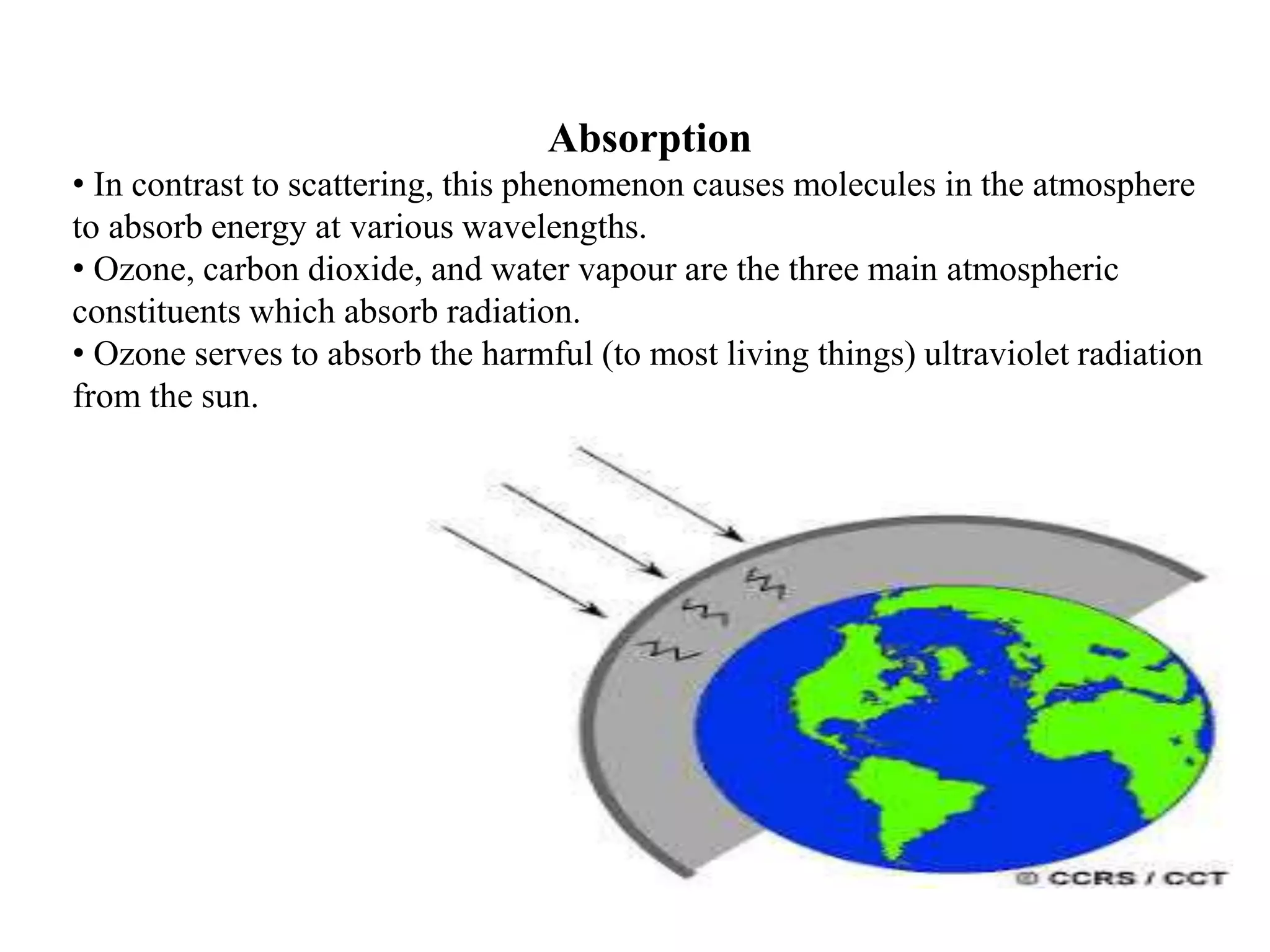
2. When electromagnetic radiation interacts with the atmosphere, it can be scattered, absorbed, or pass through. Scattering is affected by the wavelength and atmospheric particles, while absorption is caused mainly by ozone, carbon dioxide, and water vapor.
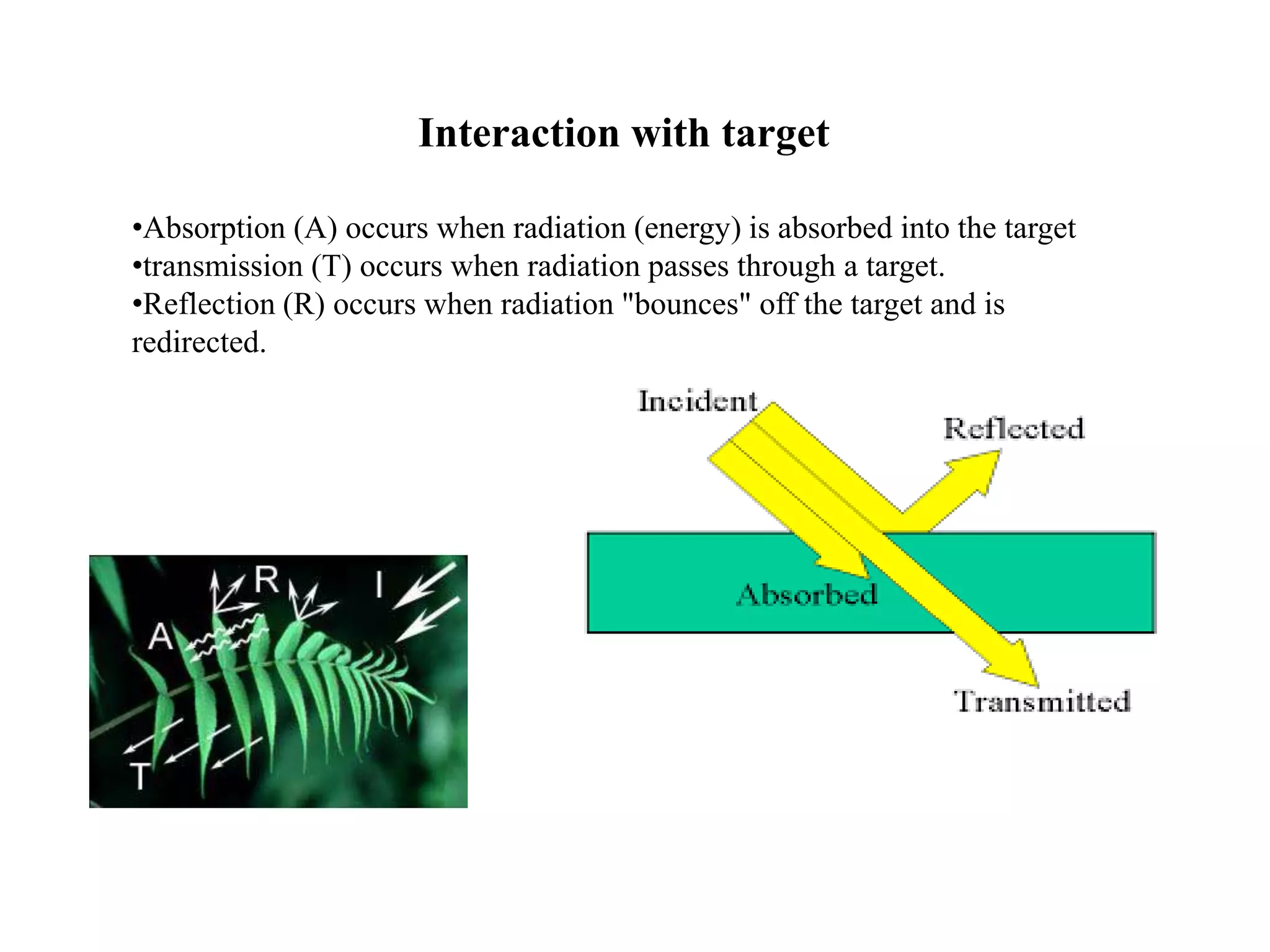
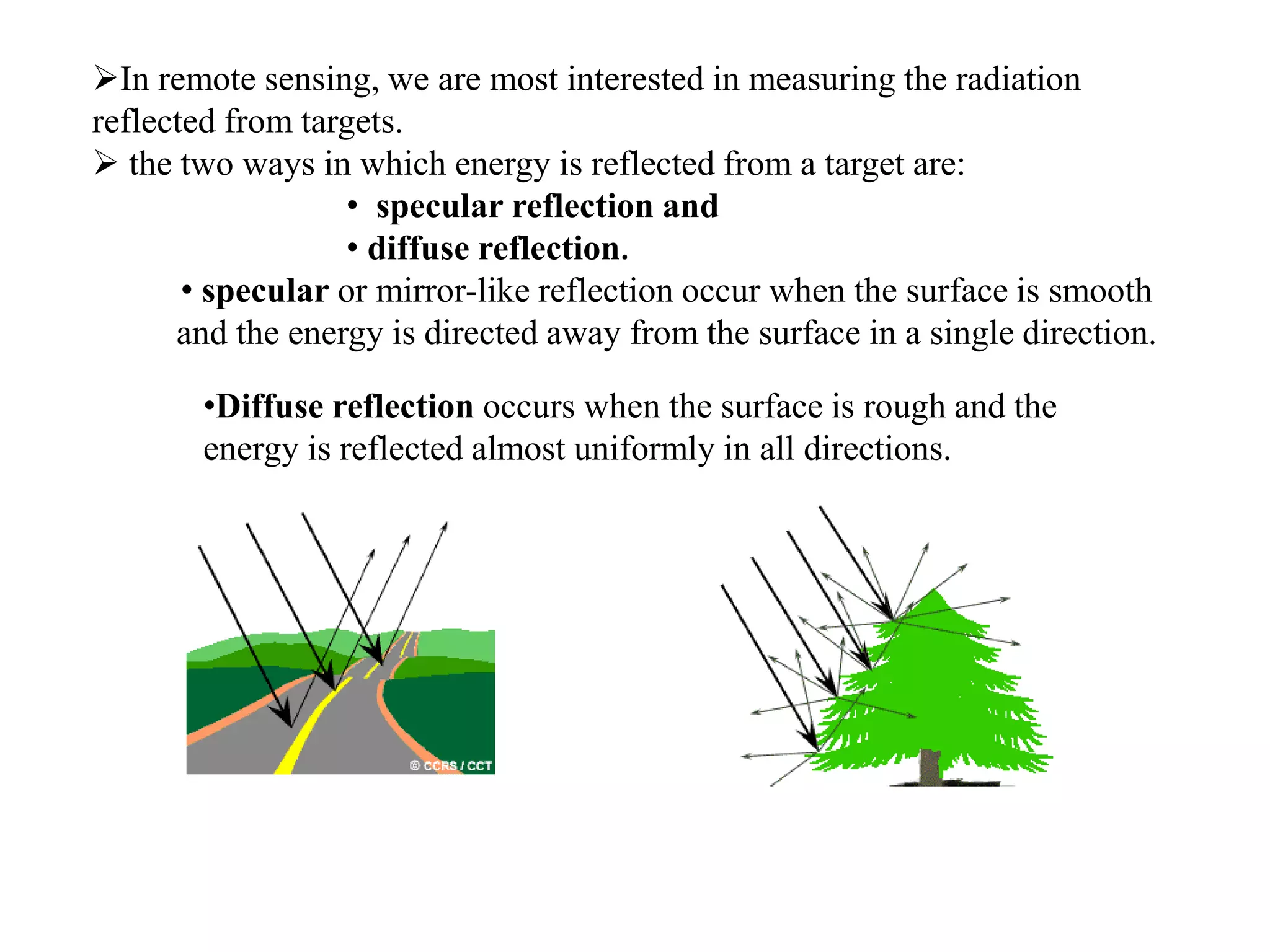
3. At the Earth's surface, radiation can be absorbed, transmitted, or reflected. Reflection is important for remote sensing and can be specular or diffuse depending on the surface smoothness.