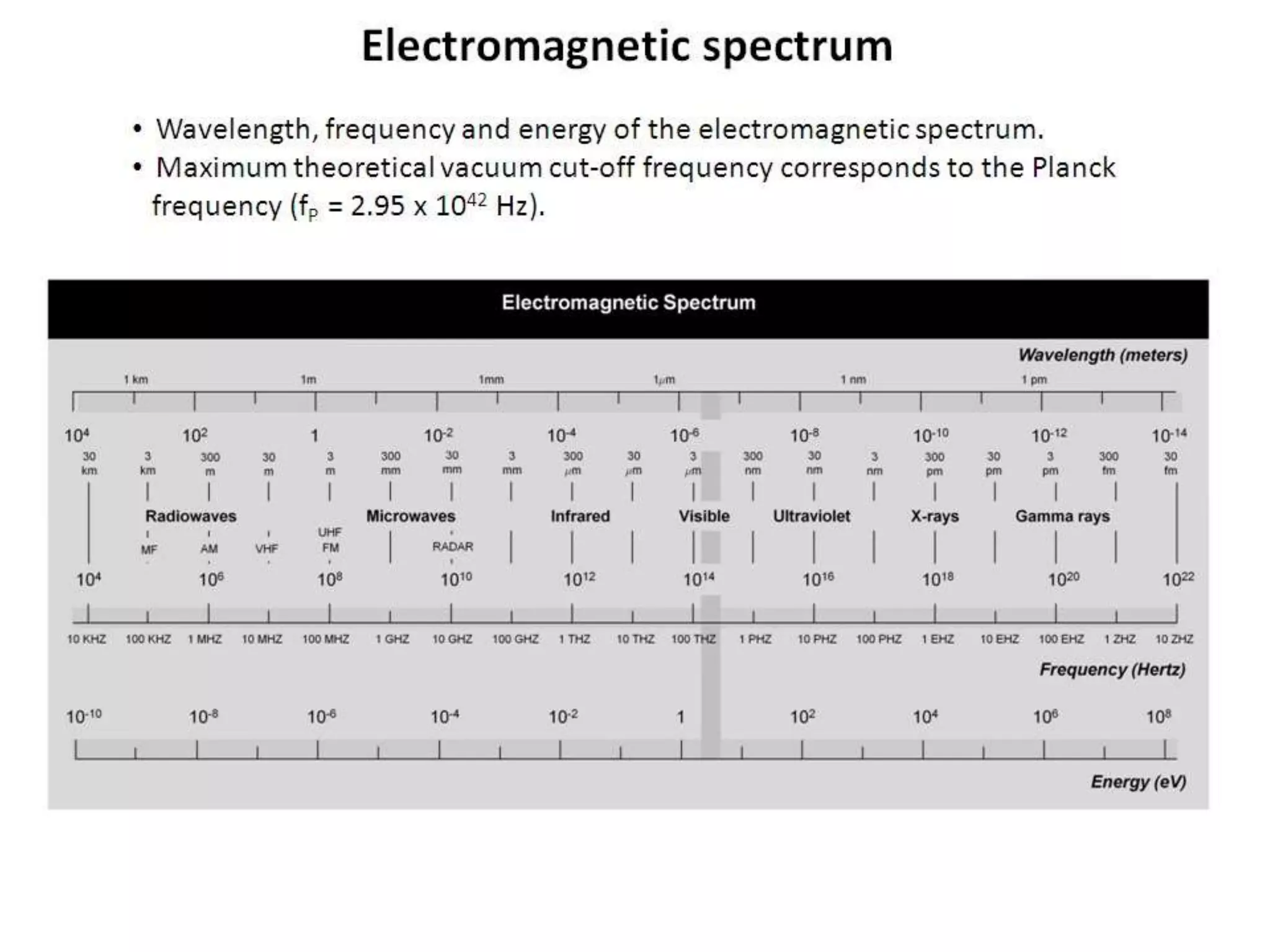
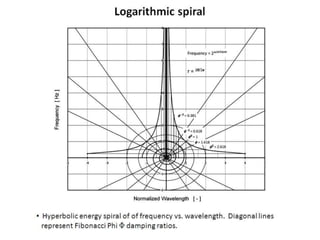
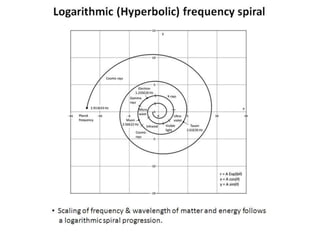
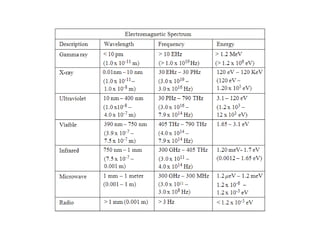
The document discusses the electromagnetic spectrum, which spans over 140 octaves from low frequencies like microwaves up to a theoretical maximum frequency called the Planck frequency of 2.95 x 1042 Hz. It follows a logarithmic spiral pattern with wavelength inversely proportional to frequency. The visible light spectrum detectable by the human eye ranges from 430-770 THz. The highest measured gamma cosmic ray had a frequency of around 1023 Hz.