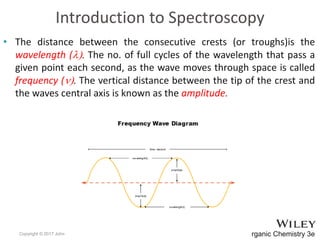
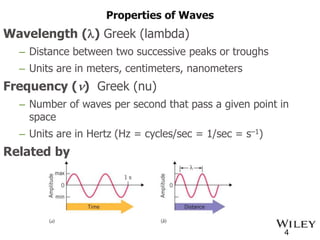
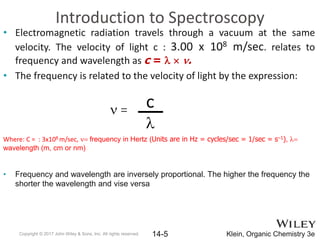
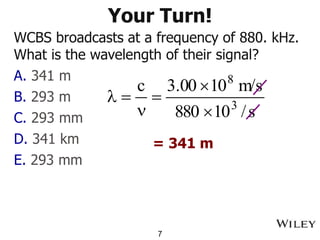
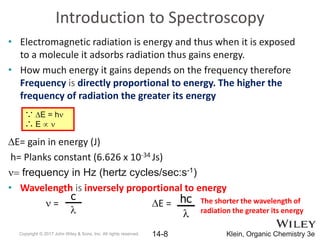
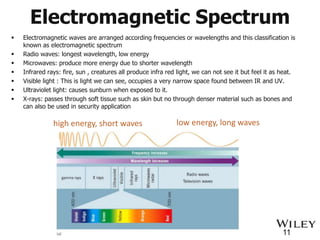
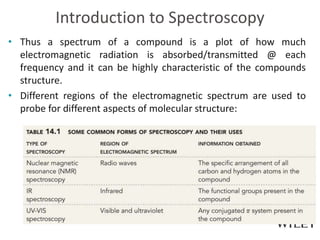
The document provides an introduction to the electromagnetic spectrum and spectroscopy. It discusses how electromagnetic radiation exhibits wave-like properties with a wavelength and frequency. The wavelength is the distance between peaks and troughs, while frequency is the number of waves passing a point per second. Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional and related by the velocity of light. Higher frequency radiation has higher energy. Spectroscopy studies how electromagnetic radiation interacts with atoms and molecules. Different regions of the spectrum probe different molecular structures.