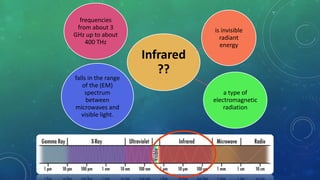
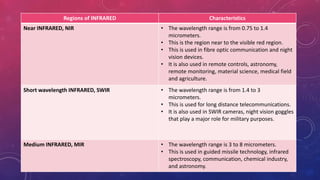
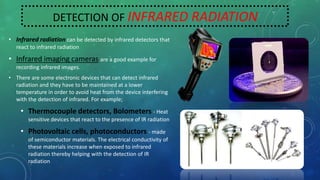
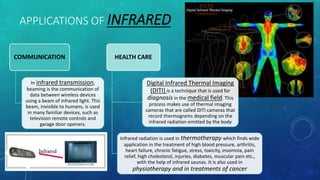
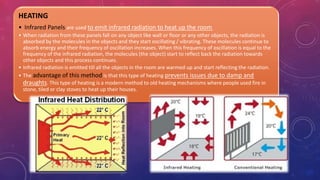
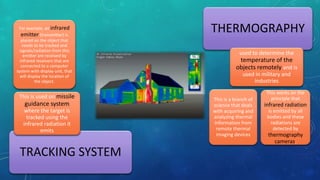
The document discusses infrared radiation, highlighting its properties, history, and applications across various fields such as medical, military, and communication. Infrared radiation, which is invisible electromagnetic energy, is emitted by all warm objects and can be divided into regions based on wavelength, including near, medium, and far infrared. Key uses include night vision devices, medical imaging, and climate monitoring, as well as several sophisticated detection technologies.