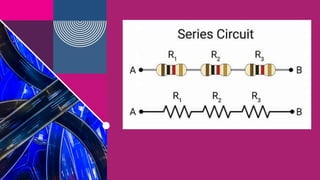
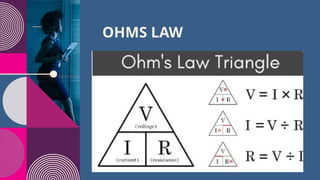
The document discusses the differences between series and parallel resistors in electric circuits, focusing on their configurations, current flow, and equivalent resistance calculation. It explains that in series circuits, resistors are connected in a sequence, summing up resistance values, while in parallel circuits, resistors are connected side by side, reducing total resistance. Ohm's law is also highlighted to assist in calculations involving voltage, current, and resistance in circuits.














![REFERENCES
James, A. (2020). 12 simple electrical circuits [PowerPoint slides]. SlideShare.
https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/12-simple-electrical-circuits/238342671
Owino, D. (2017). Electric circuits [PowerPoint slides]. SlideShare.
https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/electric-circuits-38340844/38340844
Nontsikiza, S. (2022). Electric circuits [PowerPoint slides]. SlideShare.
https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/electric-circuitspptx-253889687/253889687
Thomas, S. (2010). 20 Electric Circuits[PowerPoint slides]. SlideShare.
https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/ch-20-electric-circuits-online/5950181
Proenca P. (2008). P5 Electric Circuits[PowerPoint slides]. SlideShare.
https://www.slideshare.net/slideshow/p5-electric-circuits-presentation/615982](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electriccircuits-240821201700-28ccde3c/85/Electric-circuits-Series-and-Parallel-pptx-21-320.jpg)