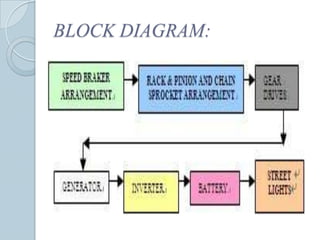
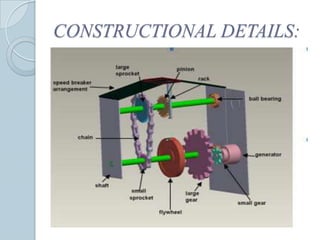
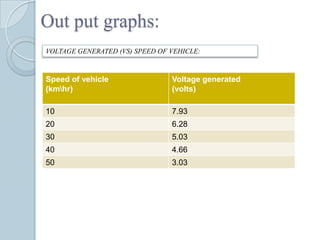
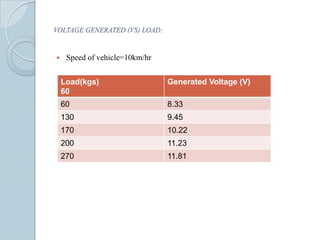
This document describes a project to generate electricity from speed breakers. Speed breakers cause wasted energy through vehicle friction that passes over them. The project aims to convert this mechanical energy through a rack and pinion gear arrangement connected to a generator. As vehicles pass over the speed breaker, the up and down motion is converted to rotational motion to generate electricity. The electricity could then be used to power street lights or charge batteries. Tests showed increased voltage generation with higher vehicle speeds and loads. The system provides a low-cost way to capture wasted kinetic energy.