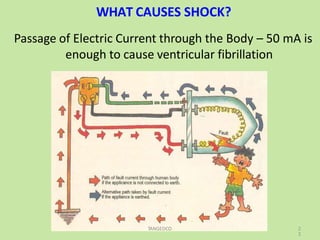
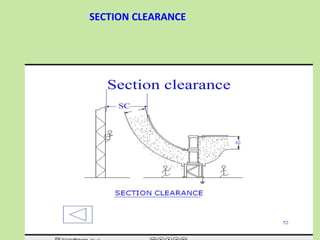
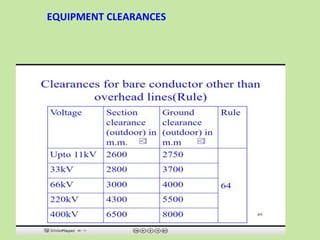
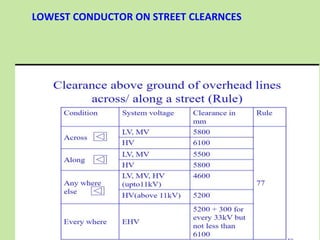
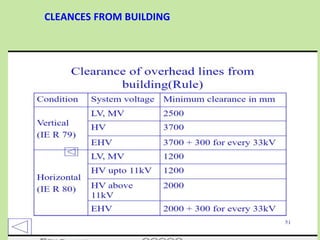
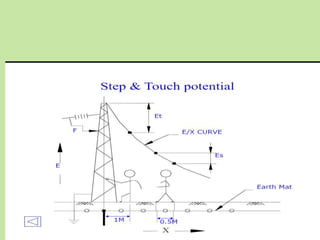
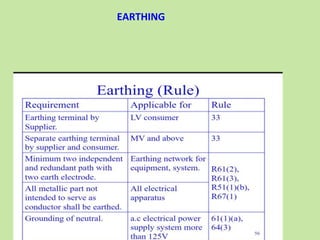
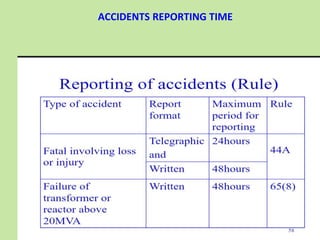
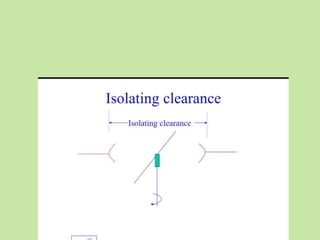
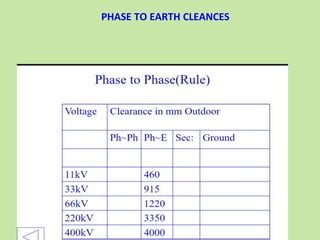
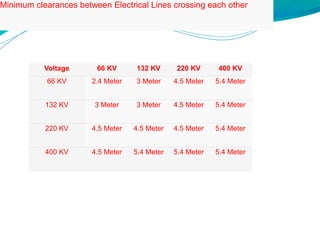
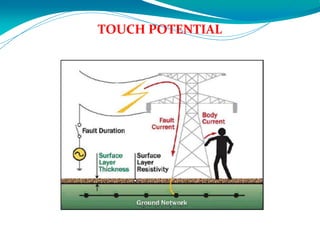
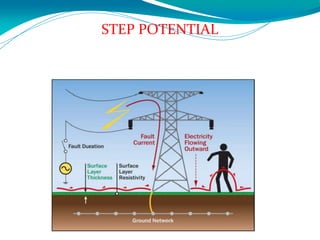
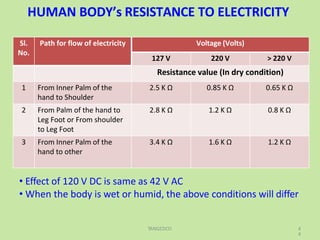
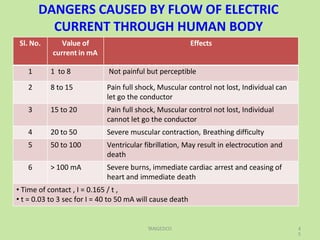
Electrical safety is important to prevent accidents and protect lives. The document discusses several key points:
1. Electrical accidents are common in India, causing 15-16 deaths per day from electrocution. Improper electrical safety also causes fires and loss of production.
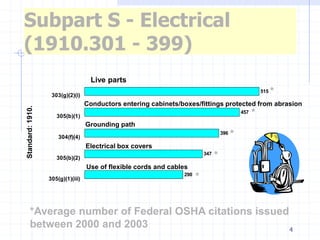
2. Federal OSHA regulations in the US (1910.301-399) address electrical safety topics like live parts, grounding, electrical box covers, and flexible cord protection which have resulted in hundreds of citations each year.
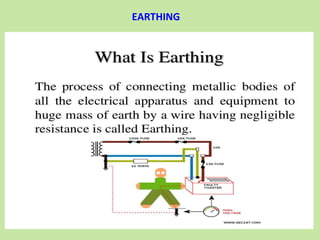
3. Proper electrical safety involves protecting operating personnel, equipment, electrical components, and property from emergencies through compliance with regulations and safety practices.