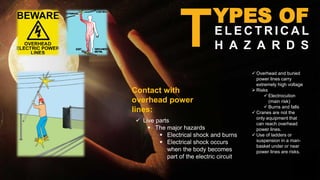
This document discusses electrical safety and precautions for working with electricity. It defines key electrical terms like current, resistance, and voltage. The main electrical hazards are burns, electrocution, shock, arc flash, fire, and explosions. Precautions include inspecting tools and cords for damage, keeping cords away from heat and moisture, using lockout/tagout procedures for live equipment, wearing proper PPE like insulating gloves and blankets, and only allowing qualified personnel to install or repair electrical systems. Safety signs and barriers should also be followed to keep areas near energized equipment clear.