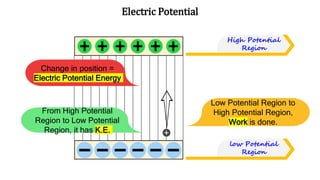
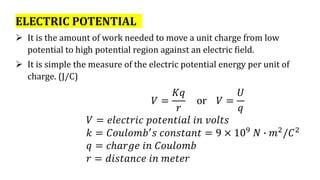
This document discusses electric potential energy and electric potential. It aims to help readers understand the concepts of electric potential, differentiate it from electric potential energy, and solve problems involving electric potential. It provides examples of calculating electric potential energy and electric potential using the equations U=kq1q2/r and V=kq/r, where U is electric potential energy, V is electric potential, k is Coulomb's constant, q1 and q2 are charges, r is distance. It also gives several practice problems for readers to calculate electric potential energy and electric potential using the provided values and equations.