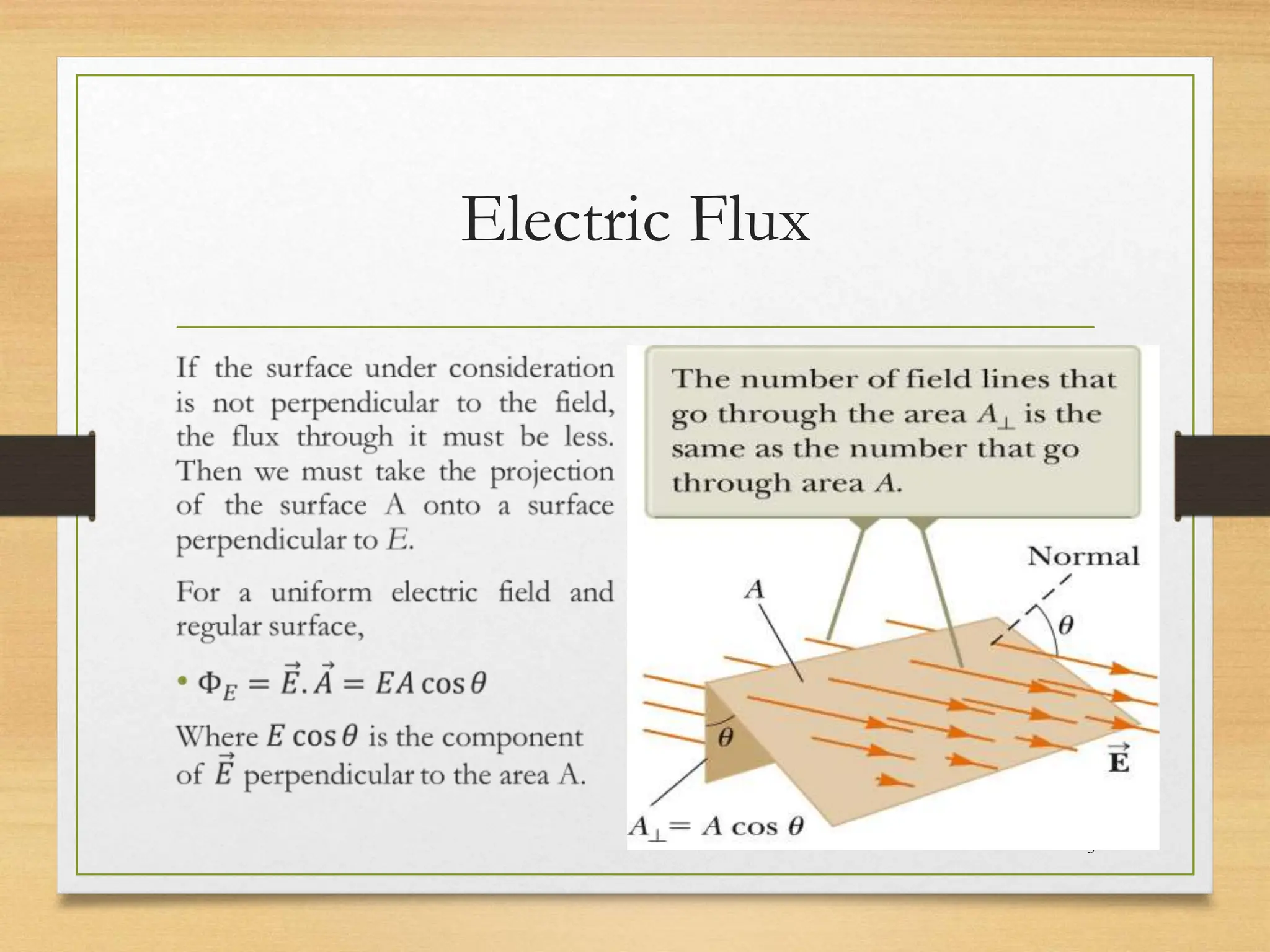
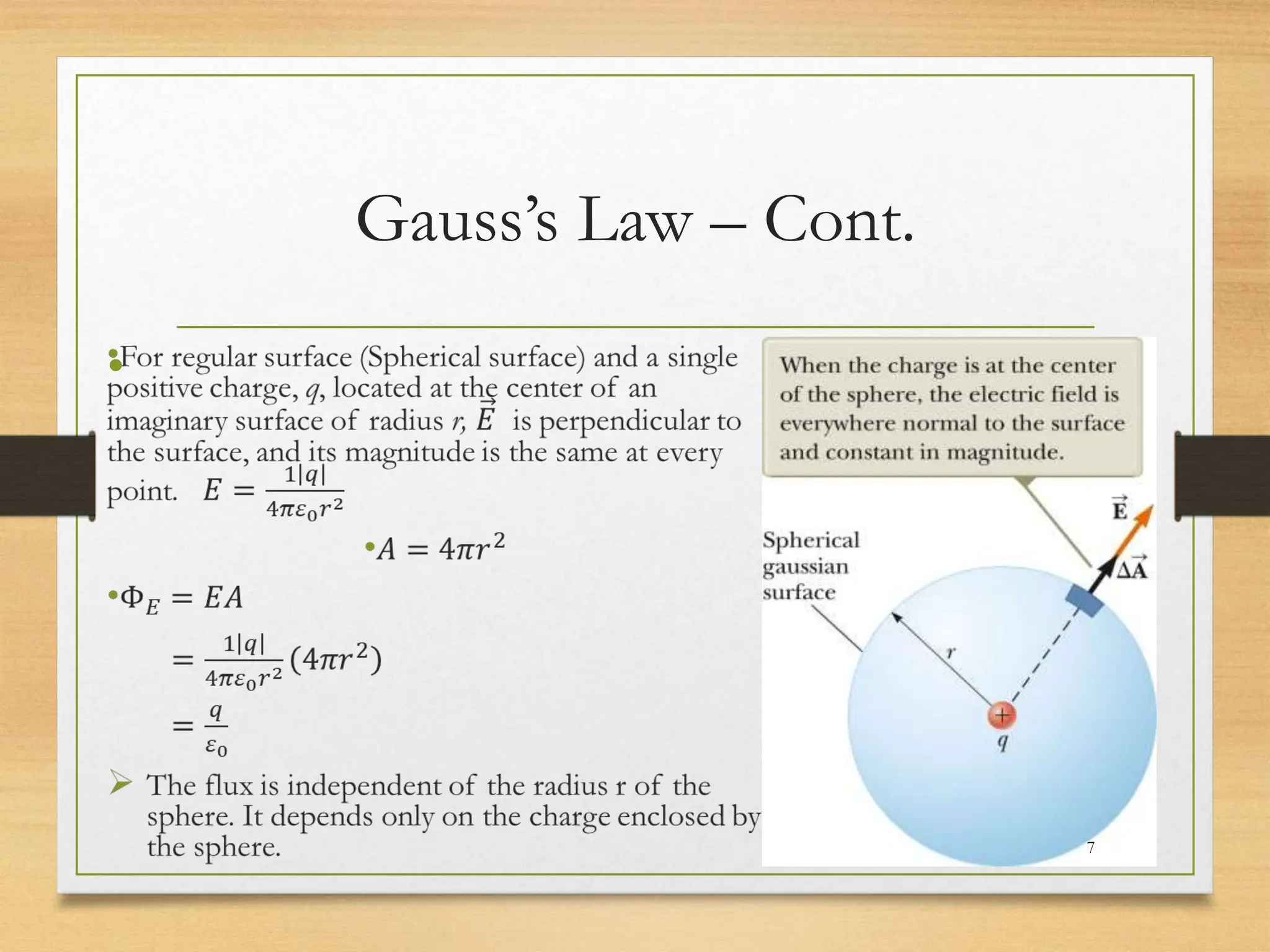
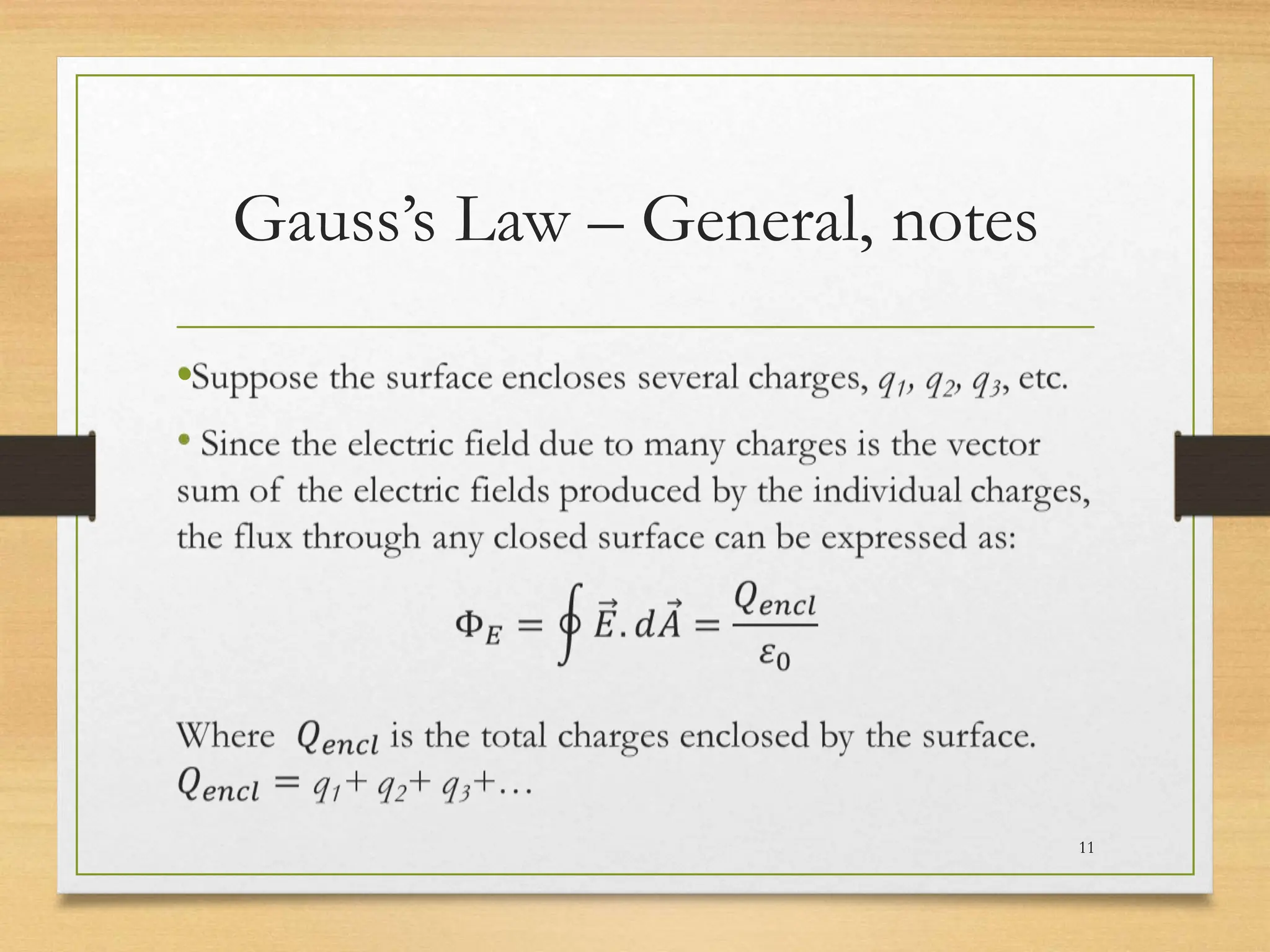
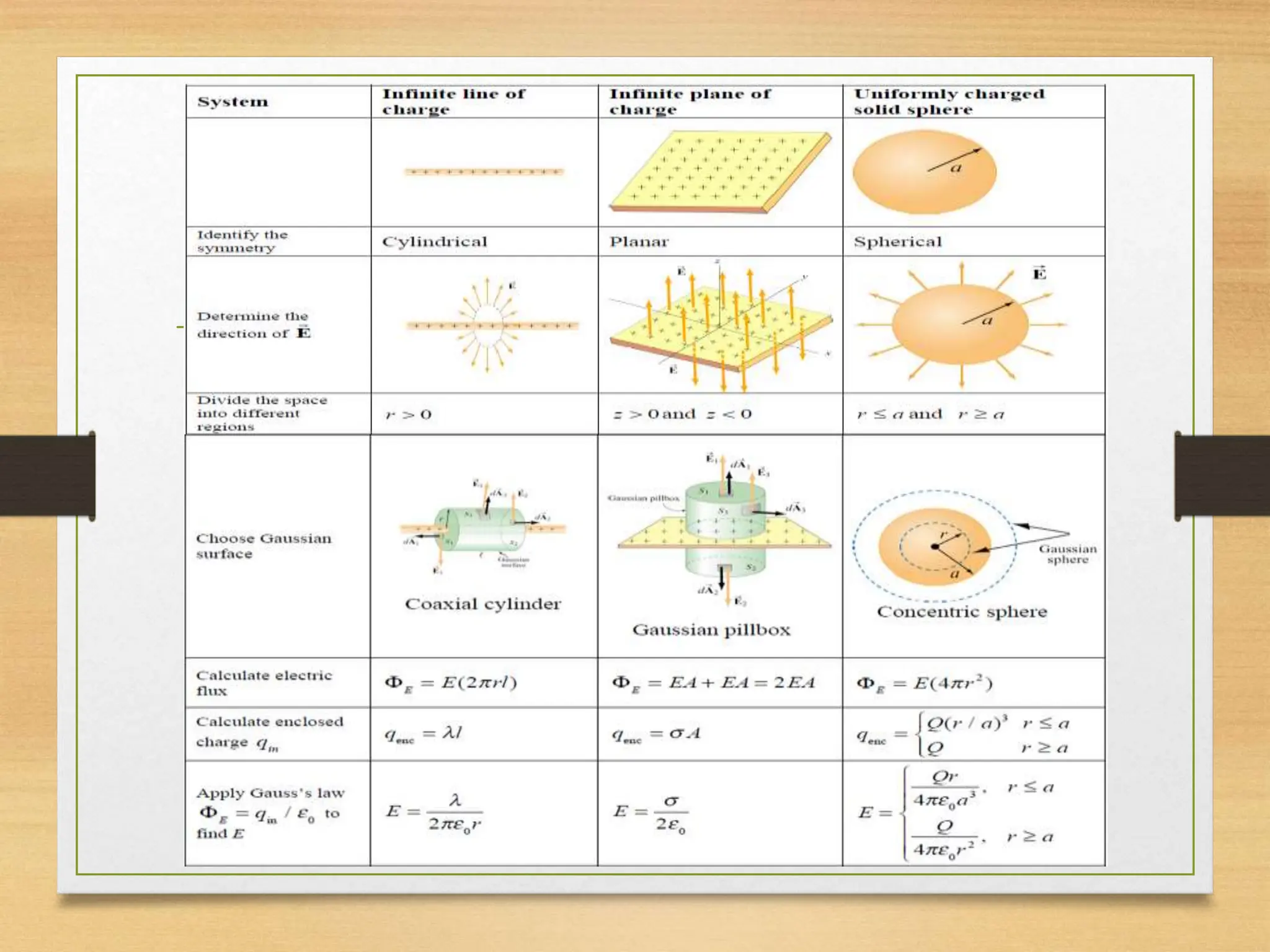
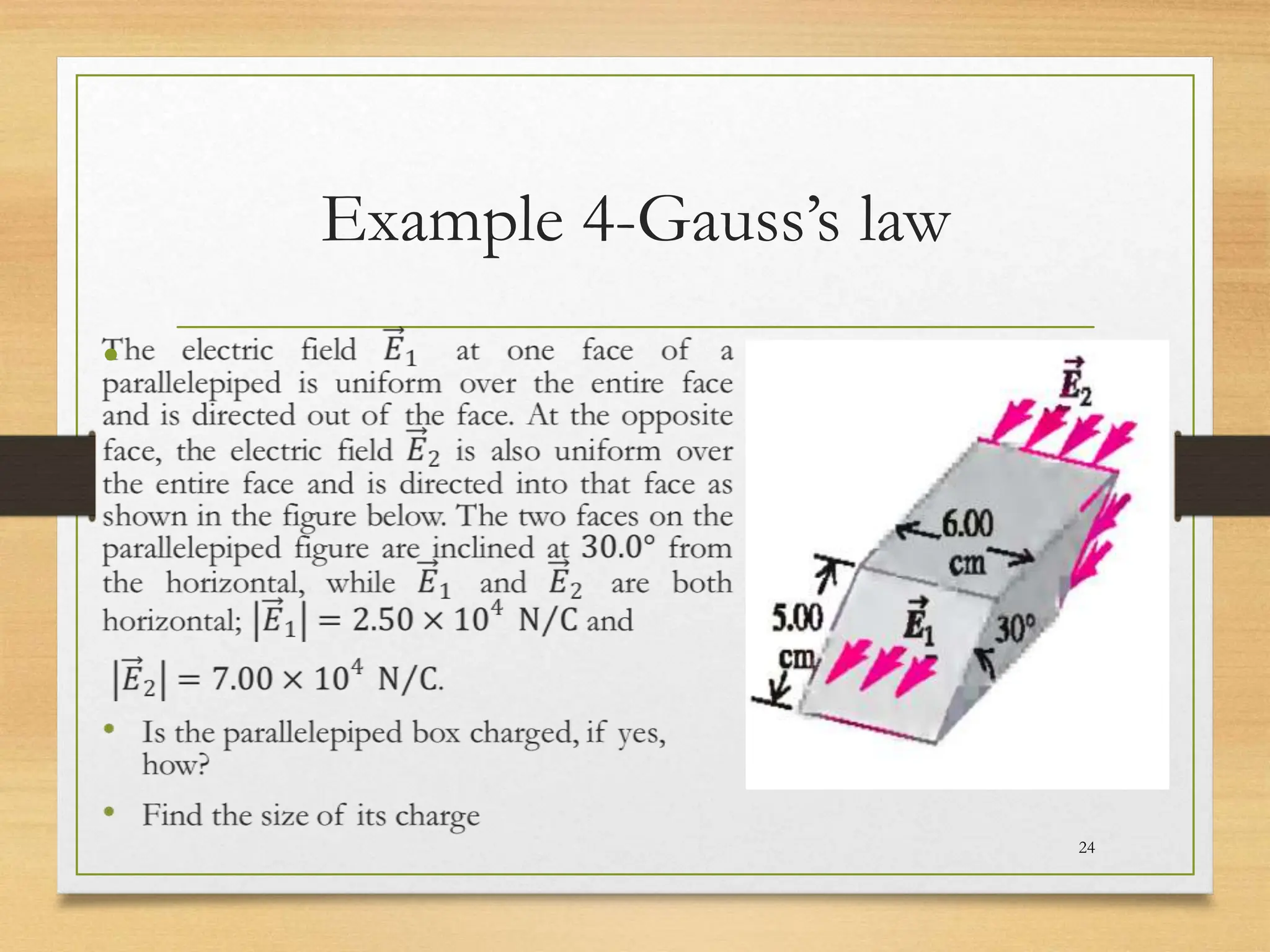
1) Gauss's law relates the electric flux passing through a closed surface to the electric charge enclosed by the surface. It states that the total electric flux is proportional to the total enclosed charge.
2) Gauss's law is useful for calculating electric fields of highly symmetric charge distributions. It allows choosing a Gaussian surface where the surface integral can be easily evaluated.
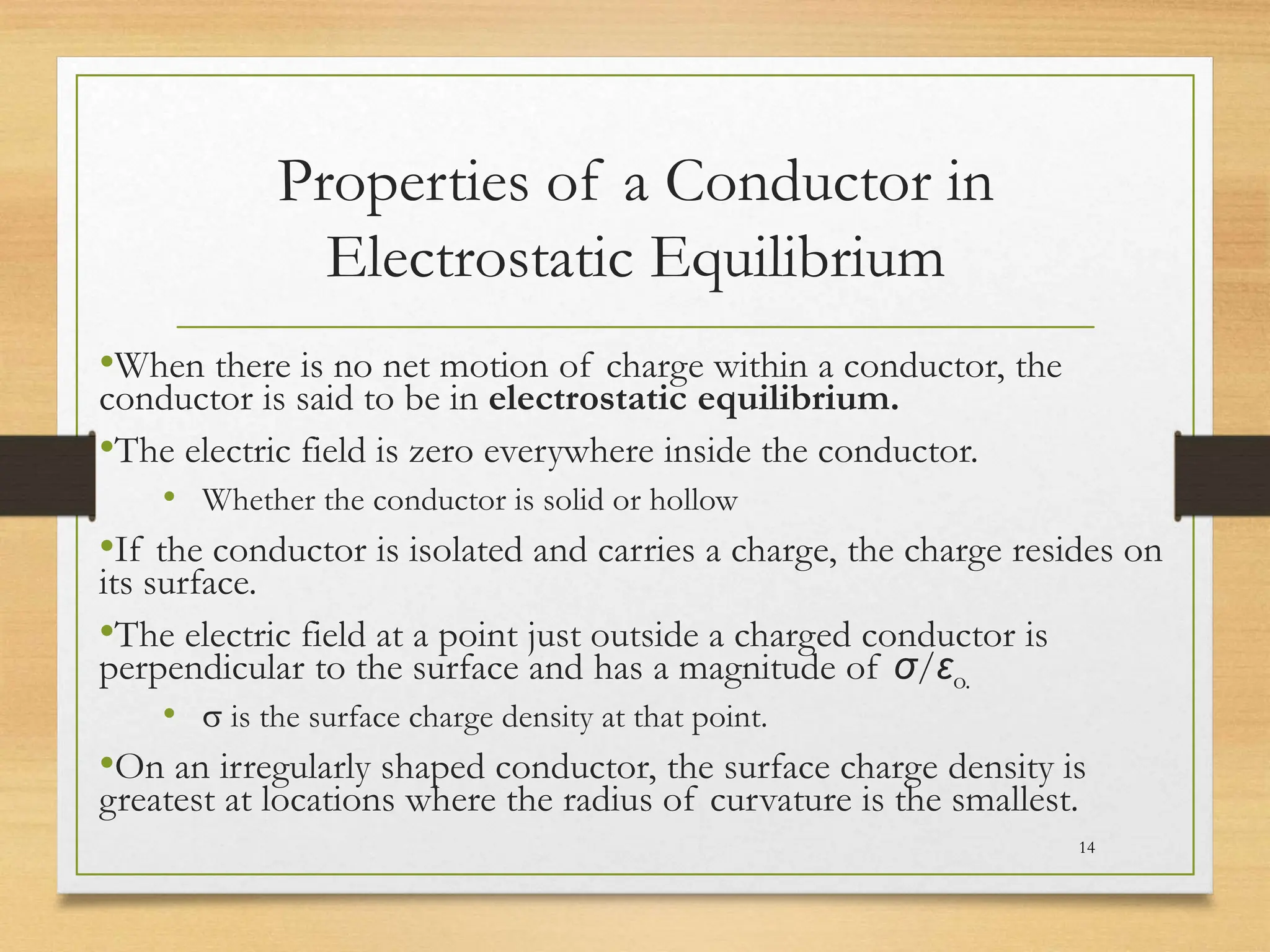
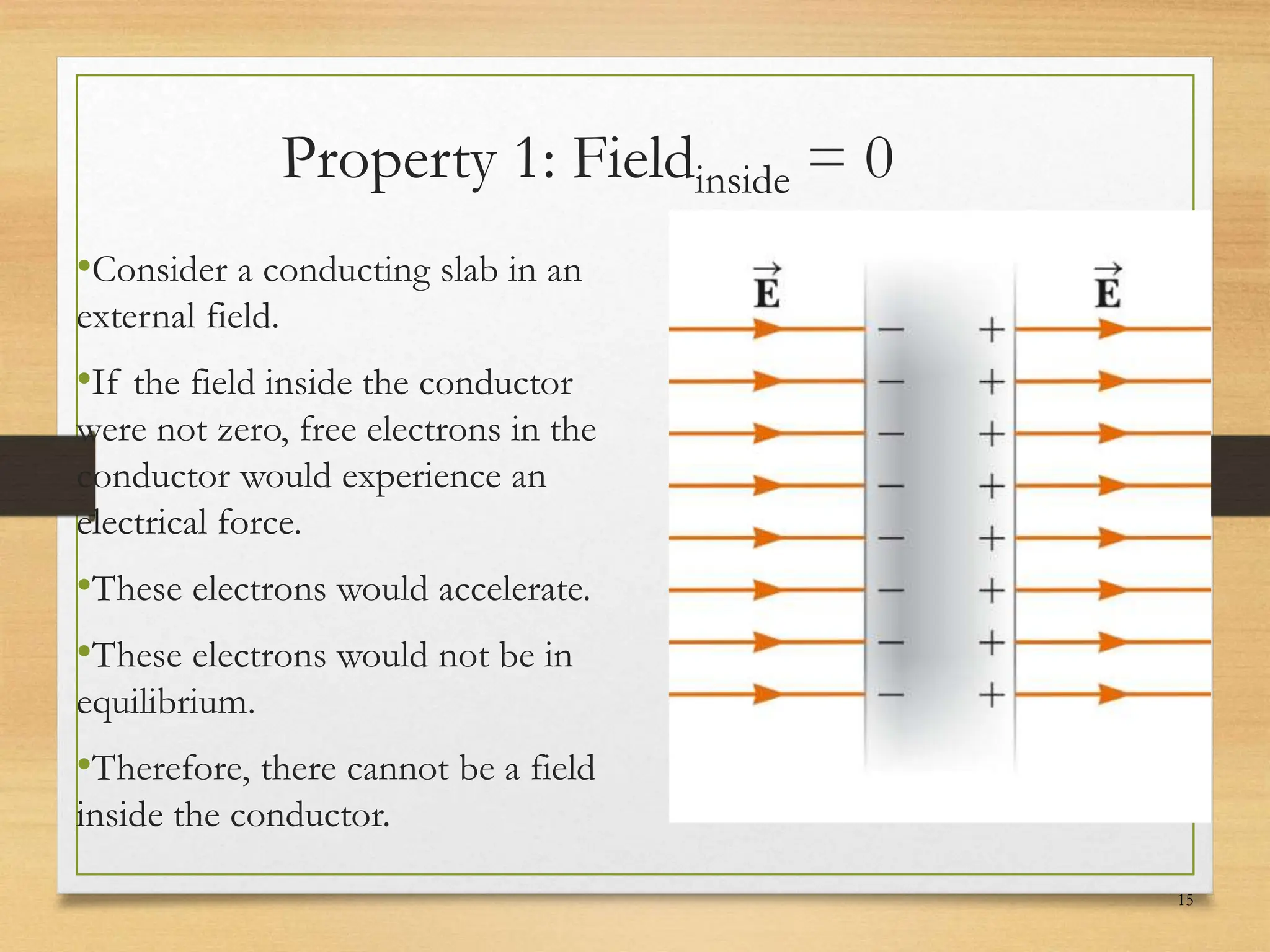
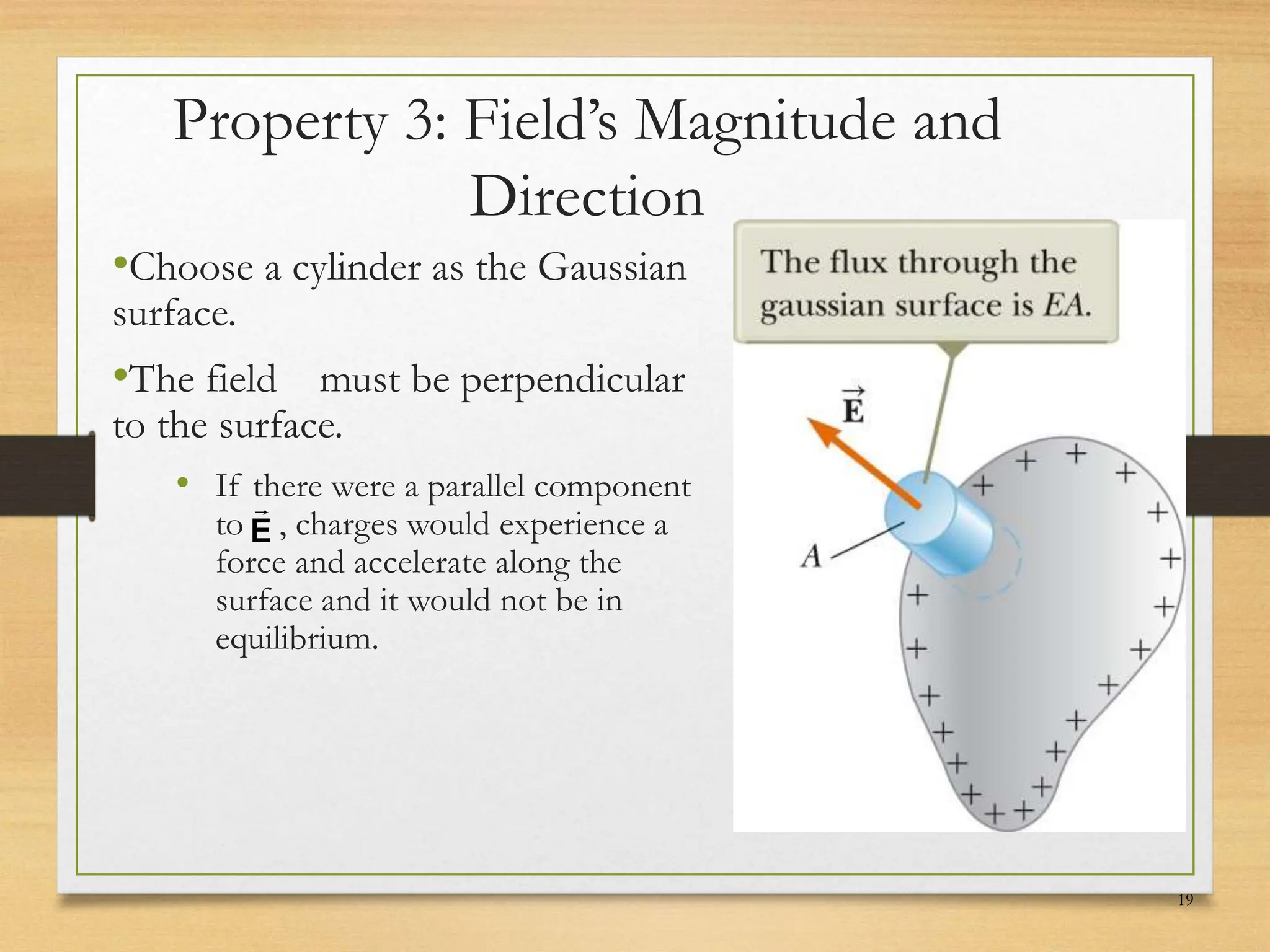
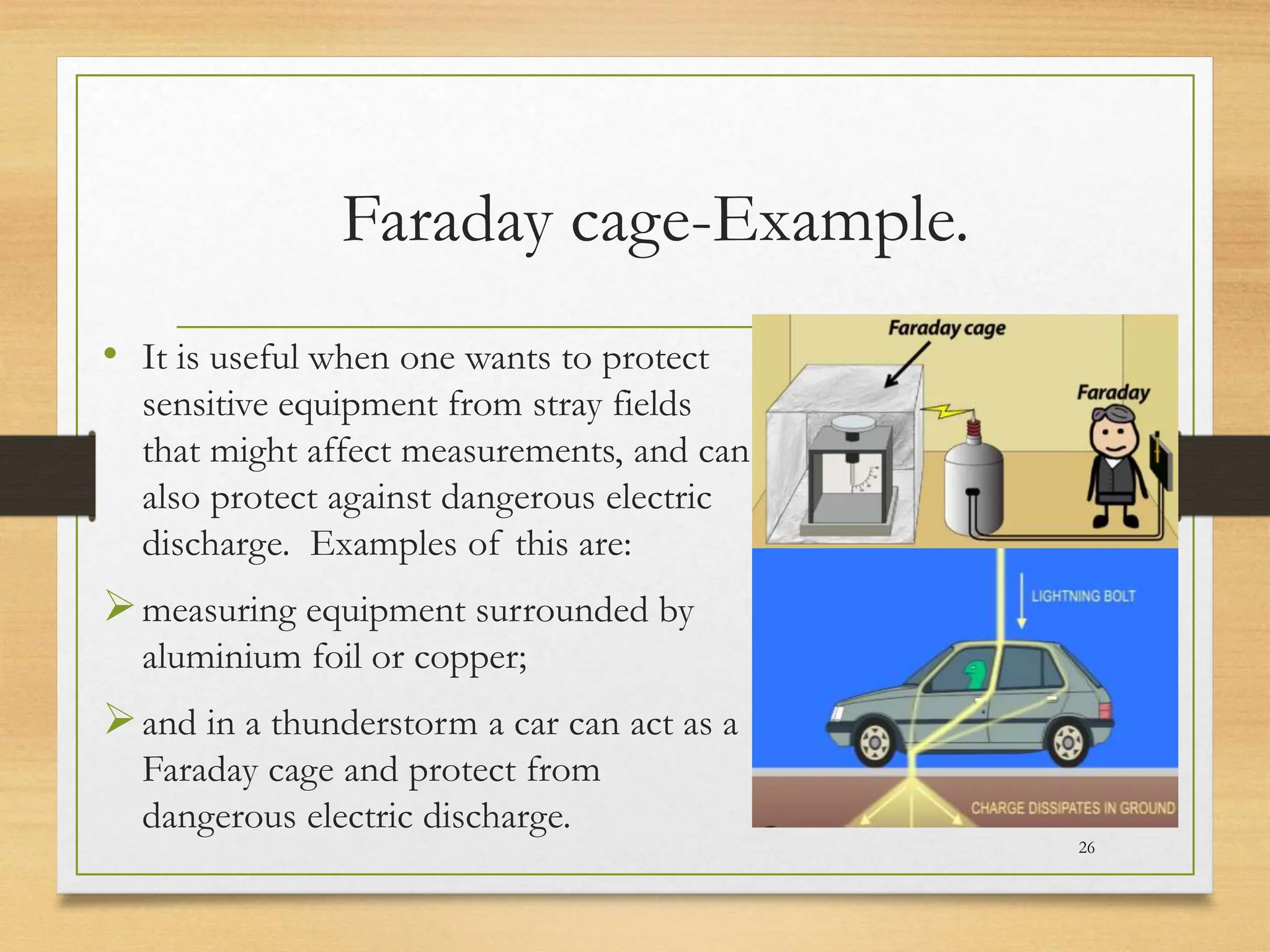
3) When a conductor is in electrostatic equilibrium, the electric field inside is zero. Any charges reside on the surface of the conductor. The electric field just outside the conductor is perpendicular to the surface with a magnitude proportional to the surface charge density.