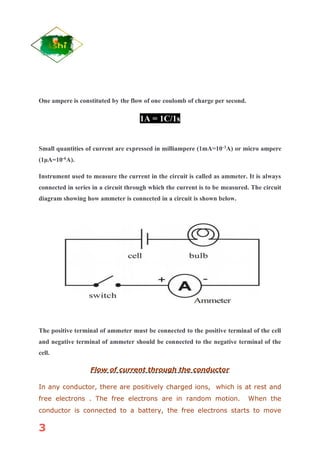
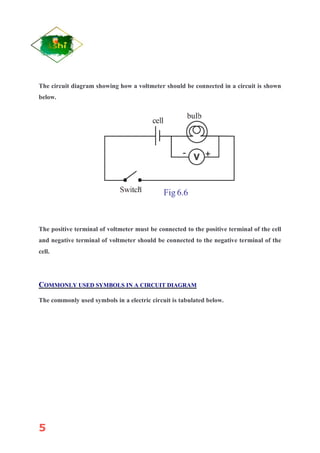
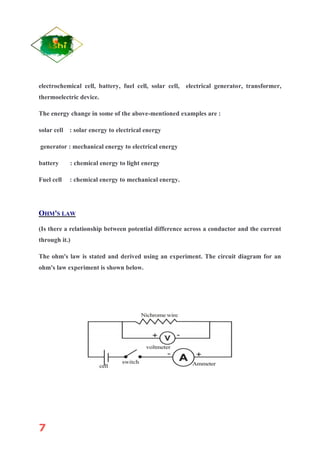
Electricity is the flow of electrons in a circuit. Current is the flow of electric charge, measured in amperes (A). The direction of electron flow is opposite to the direction of conventional current. Resistance is a measure of how much a material opposes the flow of electric current. Resistance depends on the material's resistivity, length, and cross-sectional area. According to Ohm's law, the current through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied. Cells can be connected in series, where the total voltage is the sum of individual voltages, or parallel, where the total current is the sum of individual currents.