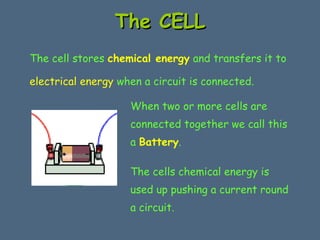
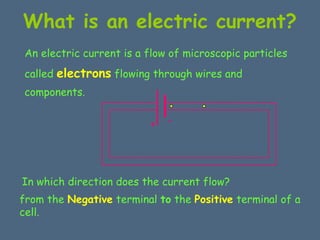
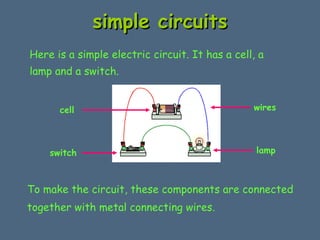
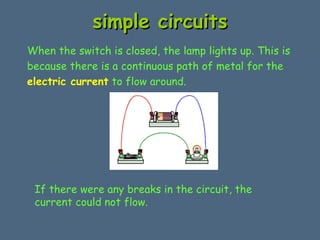
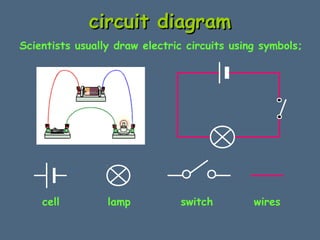
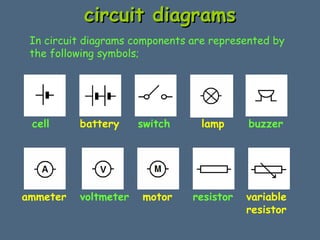
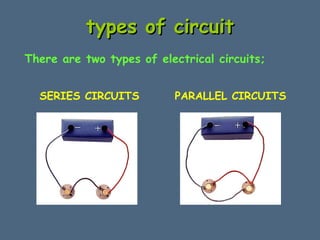
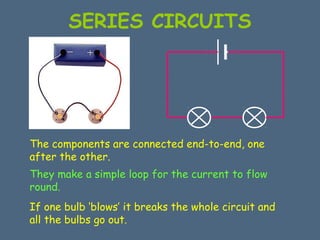
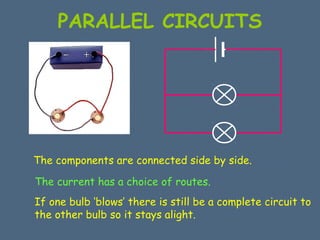
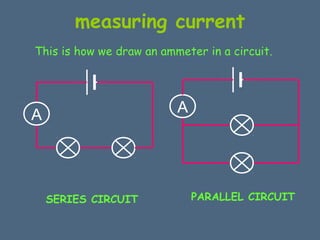
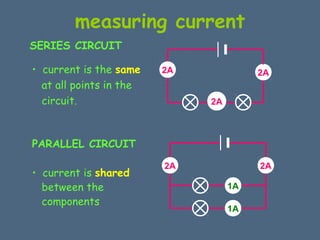
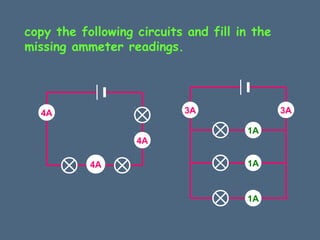
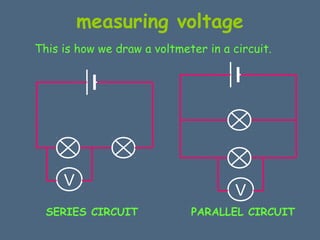
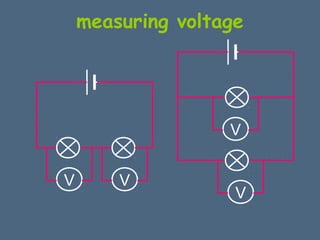
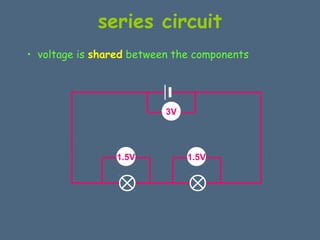
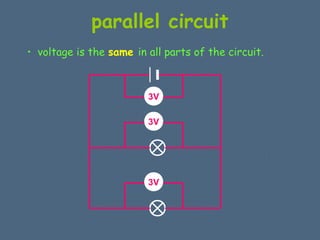
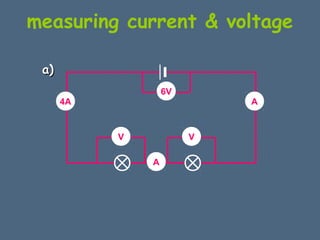
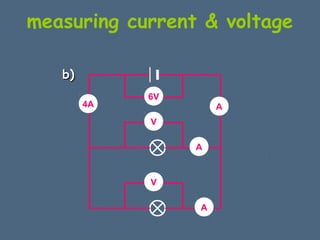
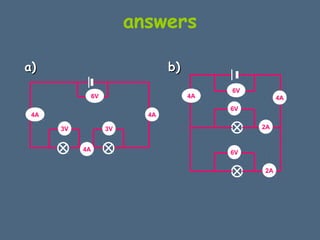
This document discusses electrical circuits and their components. It explains that a cell stores chemical energy and transfers it to electrical energy when connected in a circuit. Multiple cells together form a battery. Current is a flow of electrons that moves from the negative terminal to the positive terminal of a cell. Simple circuits are demonstrated with a cell, wires, switch and lamp. Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent components. There are two main types of circuits - series circuits where components are end to end, and parallel circuits where components branch off from each other. The document also covers measuring current with ammeters and voltage with voltmeters, and how current and voltage behave differently in series versus parallel circuits.