This document discusses the application of Gauss's law to calculate electric field intensity in two situations:
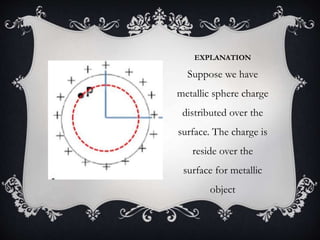
1) Inside a hollow metallic sphere with charge distributed over its surface. Using Gauss's law, the electric field inside the sphere is found to be zero, showing how electric force can be shielded.
2) Near an infinite sheet with uniform surface charge density. A Gaussian cylinder is used to calculate the flux, yielding an electric field intensity of σ/(2ε0) perpendicular to the sheet. Gauss's law allows calculating electric fields for complex charge distributions.