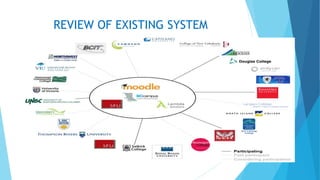
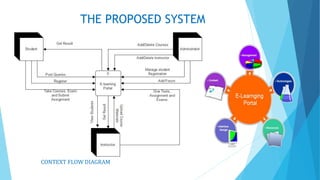
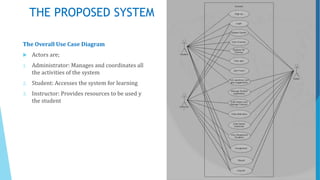
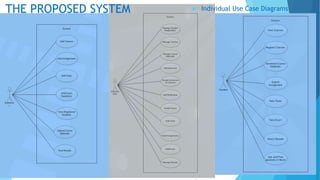
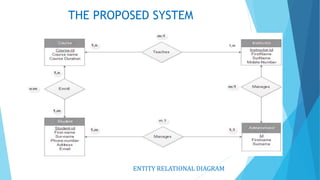
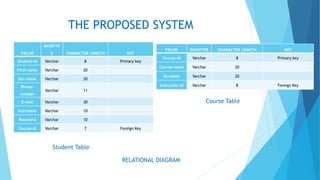
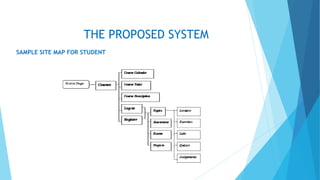
The document discusses the design and implementation of an e-learning system aimed at enhancing traditional classroom learning methods in computer science. It identifies issues such as students' difficulties in grasping concepts and the need for a more engaging learning approach. The proposed system includes multimedia features, concurrent access, and efficient management of student records to facilitate better learning experiences.