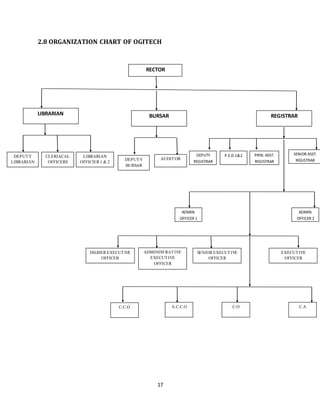
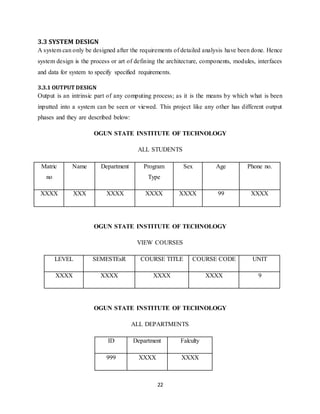
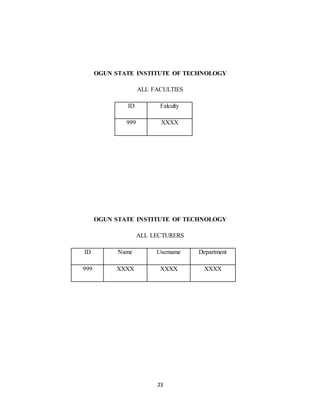
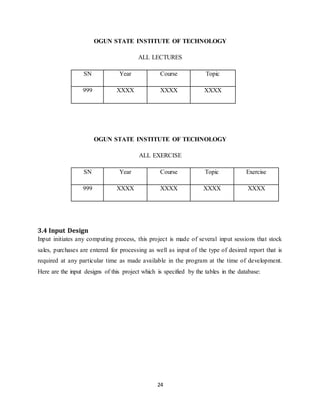
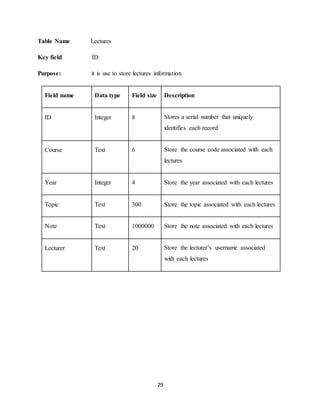
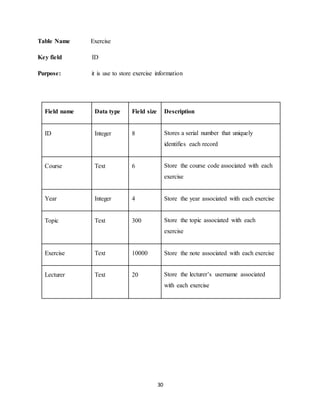
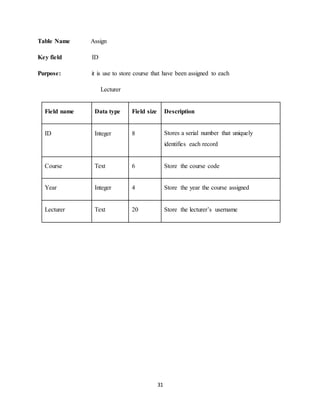
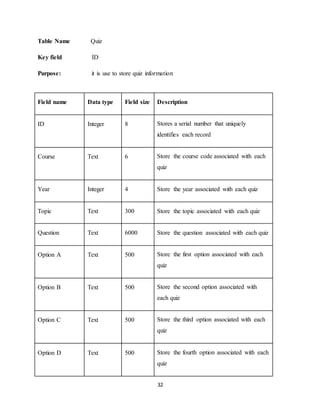
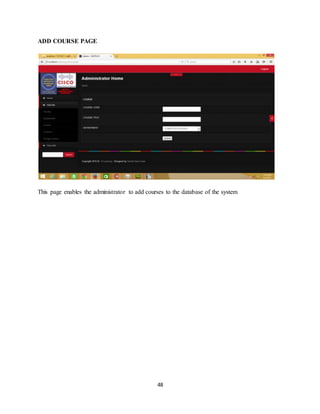
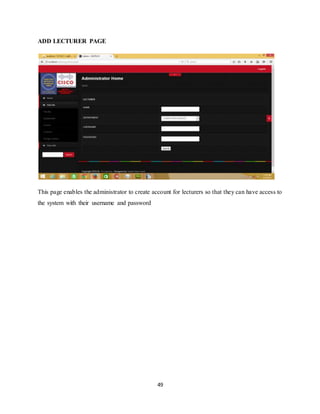
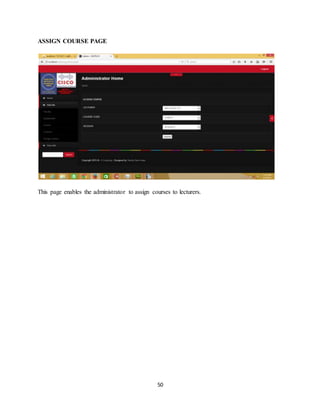
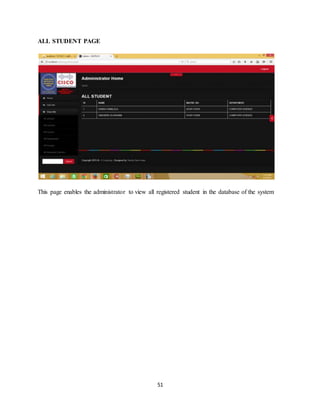
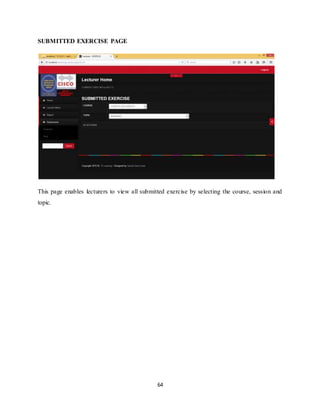
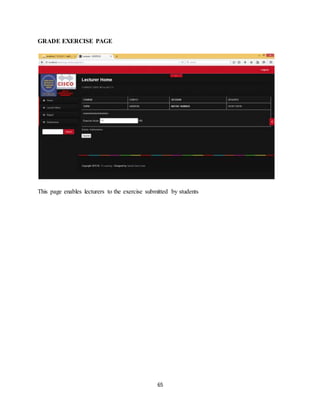
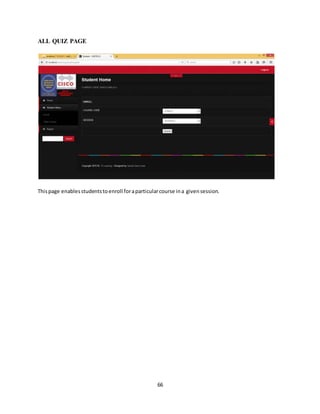
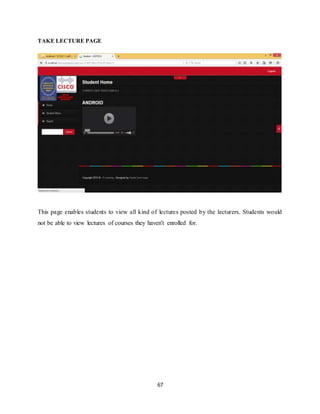
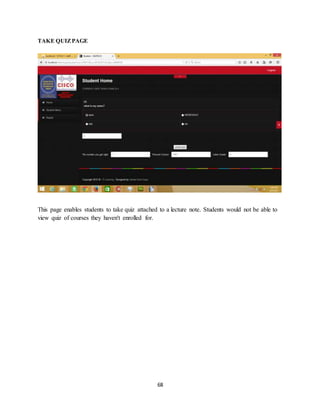
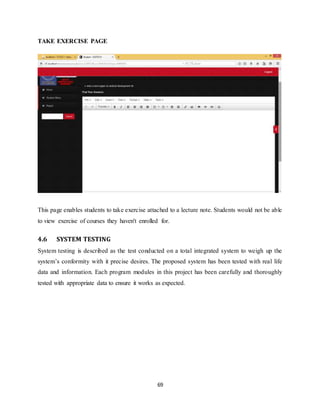
The document discusses the evolution of e-learning, its advantages, and the implementation of an automated web-based application for Ogun State Institute of Technology to enhance learning. It identifies problems with the current manual lecturing system and suggests that a structured e-learning environment can improve student engagement and performance. The proposed system will enable lecturers to upload materials and facilitate student interaction, ultimately aiming to create a comprehensive digital learning ecosystem.


























![73
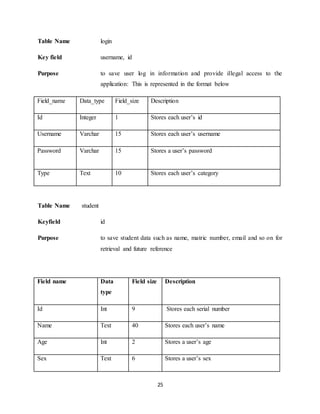
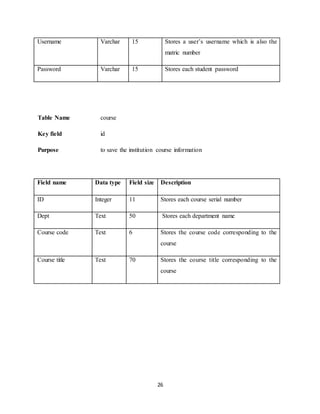
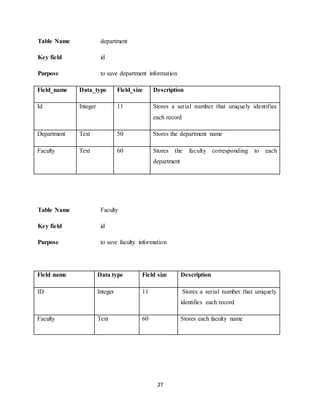
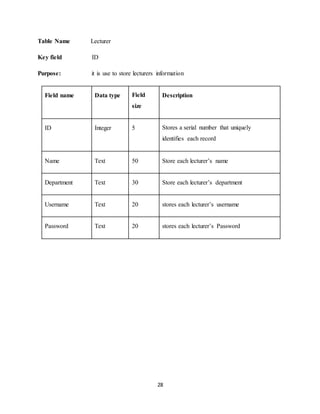
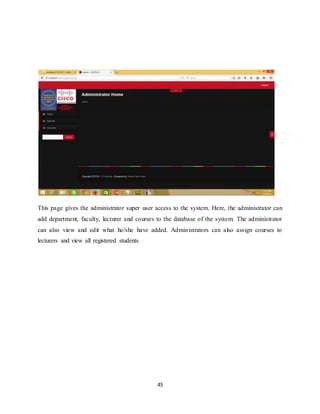
APPENDIX
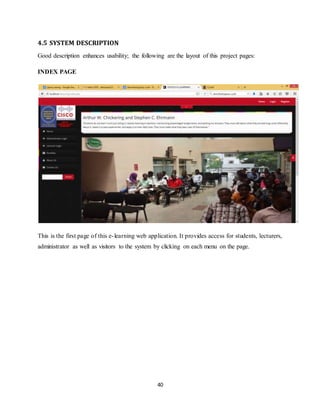
INDEX PAGE
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta charset="utf-8">
<!-- Title andother stuffs -->
<title>OGITECH E-LEARNING</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta name="description"content="">
<meta name="keywords" content="">
<meta name="author"content="">
<link href='http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:400italic,400,600,700' rel='stylesheet' type='text/css'>
<!-- Stylesheets -->
<link href="style/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Font awesome icon -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style/font-awesome.css">
<!-- Flex slider -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style/flexslider.css">
<!-- prettyPhoto-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style/prettyPhoto.css">
<!-- Main stylesheet -->
<link href="style/style.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Bootstrapresponsive-->
<link href="style/bootstrap-responsive.css"rel="stylesheet">
<!-- HTML5Support for IE -->
<!--[if lt IE 9]>
<script src="js/html5shim.js"></script>
<![endif]-->
<!-- Favicon -->
<link rel="shortcut icon"href="img/favicon/favicon.png">
</head>
<body>
<!-- Navbar starts -->
<div class="navbar navbar-fixed-top">
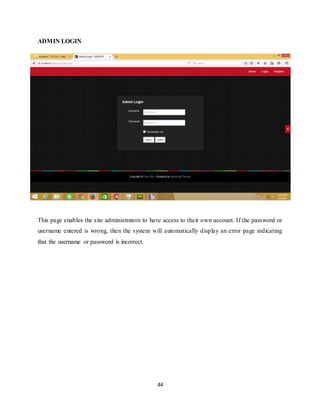
ADMIN LOGINPAGE
!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta charset="utf-8">
<!-- Title andother stuffs -->
<title>Admin Login - OGITECH</title>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta name="description"content="">
<meta name="keywords" content="">
<meta name="author"content="">
<link href='http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:400italic,400,600,700' rel='stylesheet' type='text/css'>
<!-- Stylesheets -->
<link href="style/bootstrap.css" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Font awesome icon -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style/font-awesome.css">](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mycompleteproject-151029201834-lva1-app6891/85/E-Learning-Project-Write-Up-Case-Study-Ogun-State-Institute-Of-Technology-73-320.jpg)
![74
<!-- Flex slider -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style/flexslider.css">
<!-- prettyPhoto-->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style/prettyPhoto.css">
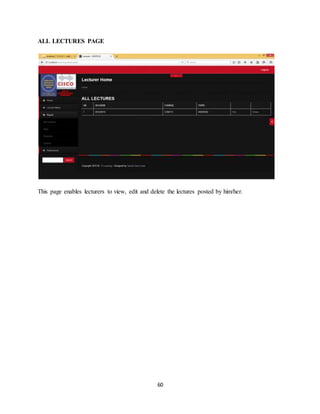
<!-- Main stylesheet -->
<link href="style/style.css" rel="stylesheet">
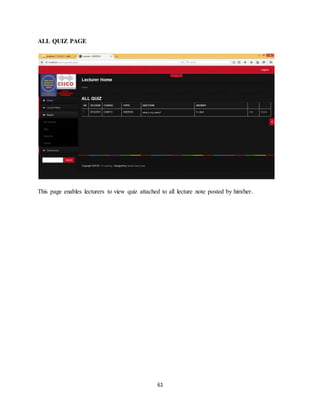
<!-- Bootstrapresponsive-->
<link href="style/bootstrap-responsive.css"rel="stylesheet">
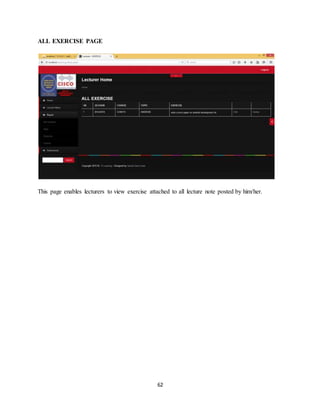
<!-- HTML5Support for IE -->
<!--[if lt IE 9]>
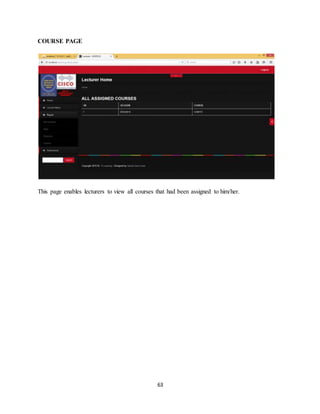
<script src="js/html5shim.js"></script>
<![endif]-->
<!-- Favicon -->
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="img/favicon/favicon.png">
</head>
<body>
<!-- Navbar starts -->
<div class="navbar navbar-fixed-top">
<div class="navbar-inner">
<div class="container-fluid">
<a class="btn btn-navbar" data-toggle="collapse"data-target=".nav-collapse">
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</a>
<div class="nav-collapse collapse">
<ul class="nav pull-right">
<li><a href="index.php">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="login.php">Login</a></li>
<li><a href="register.php">Register</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- Navbar ends -->
<!-- Sliding box starts -->
<div class="slide-box">
<div class="bor"></div>
<div class="padd">
<div class="slide-box-button">
<i class="icon-chevron-left"></i>
</div>
<h5>BernardBull</h5>
“In ordertocreate anengaginglearningexperience, the roleof instructoris optional,but therole oflearner is essential.”
<hr />
<div class="social">
<a href="#"><i class="icon-facebookfacebook"></i></a>
<a href="#"><i class="icon-twitter twitter"></i></a>
<a href="#"><i class="icon-linkedin linkedin"></i></a>
<a href="#"><i class="icon-google-plus google-plus"></i></a>
<a href="#"><i class="icon-pinterest pinterest"></i></a>
</div>
</div>
</div>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mycompleteproject-151029201834-lva1-app6891/85/E-Learning-Project-Write-Up-Case-Study-Ogun-State-Institute-Of-Technology-74-320.jpg)



