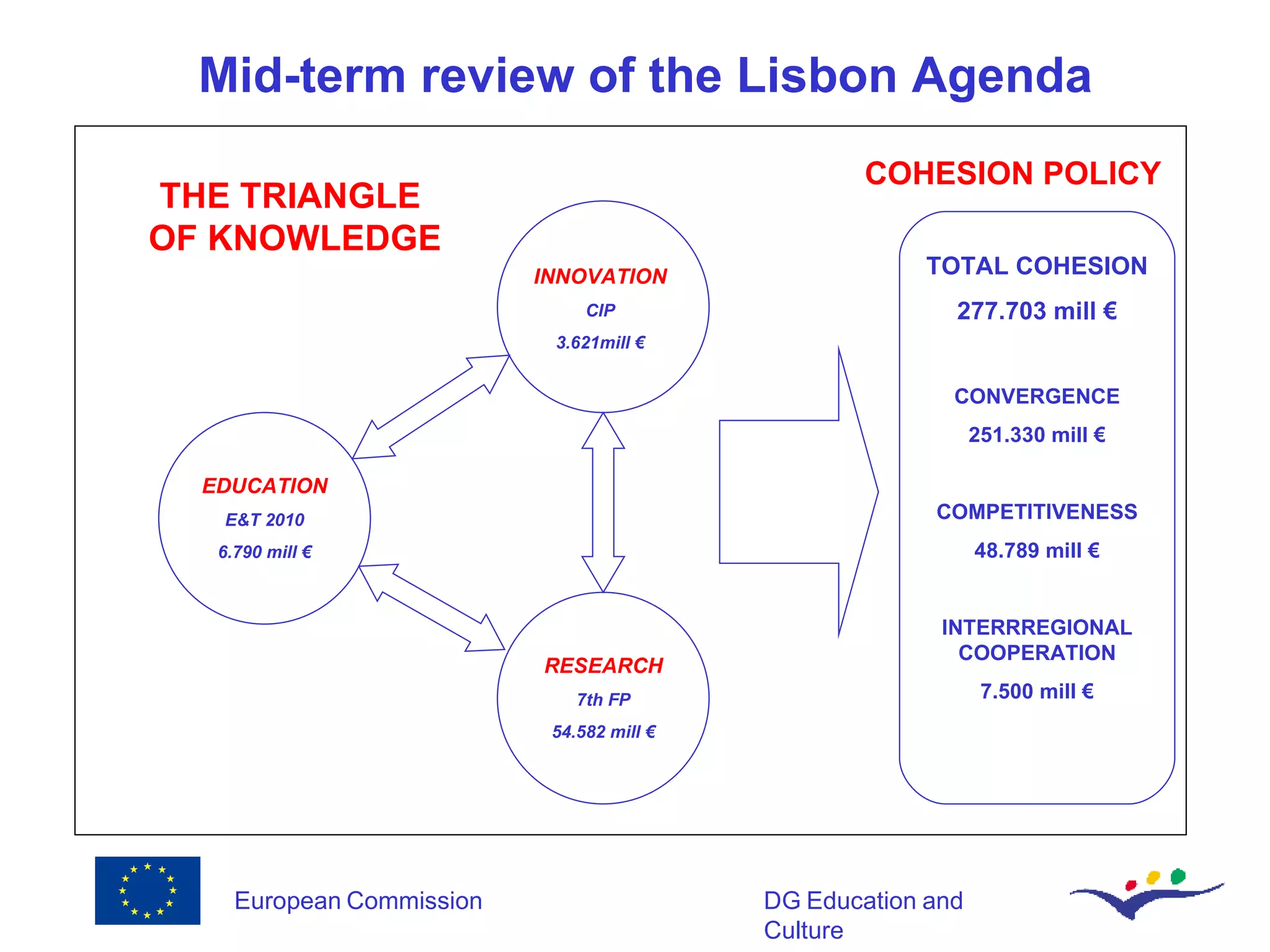
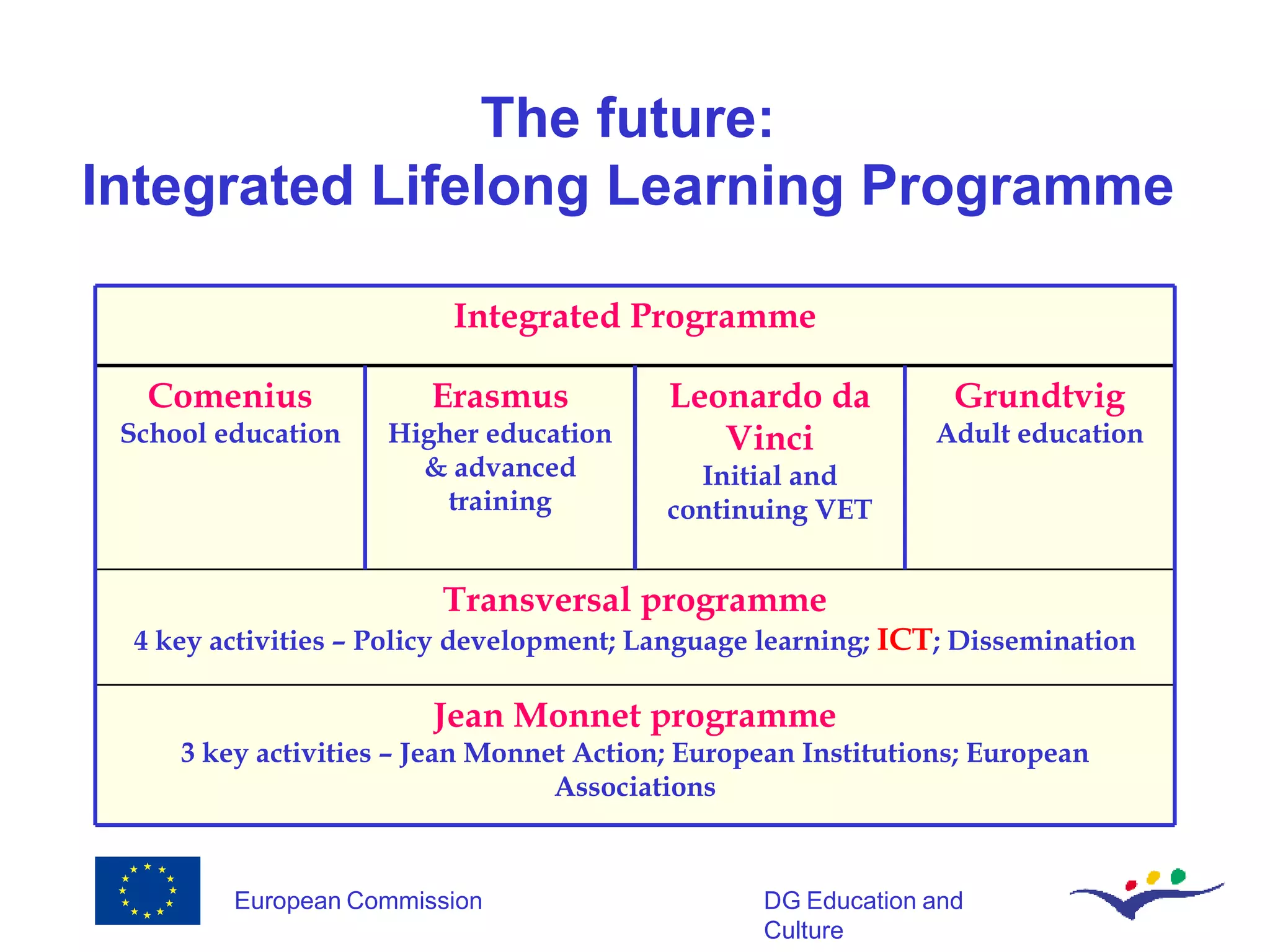
The document discusses innovation in education and training in the European Union from 2006-2010. It outlines several EU programs and funding initiatives totaling over €600 billion that aim to foster innovation through education, research, and regional development. Specifically, it focuses on how information and communication technologies can serve as an enabler of innovation in education systems by promoting collaborative and creative learning, connecting learning communities, and supporting institutional innovation. Lifelong learning is also highlighted as an innovative concept that requires transforming education systems.