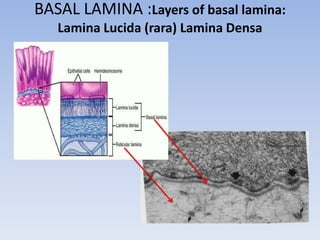
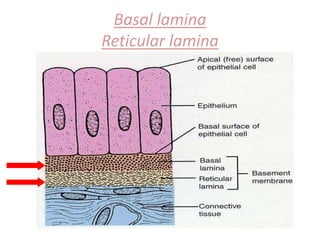
The document discusses elastin, fibronectin, and basal lamina, highlighting their structure, function, and genetic information associated with their synthesis. Elastin is an elastic protein critical for connective tissue integrity, while fibronectin is a glycoprotein that facilitates various cell functions. The basal lamina serves as a supportive and regulatory structure for cell behavior and interaction.