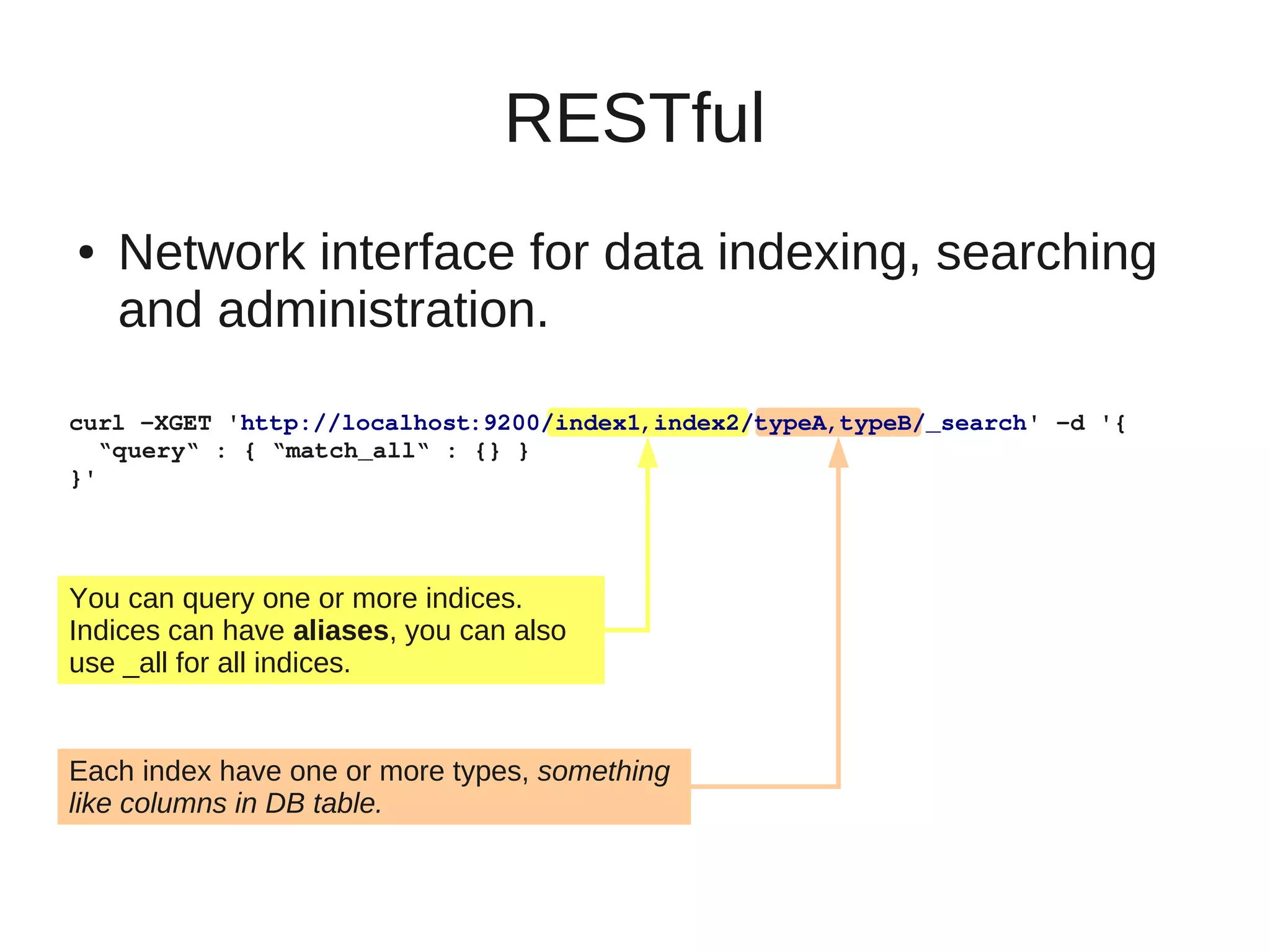
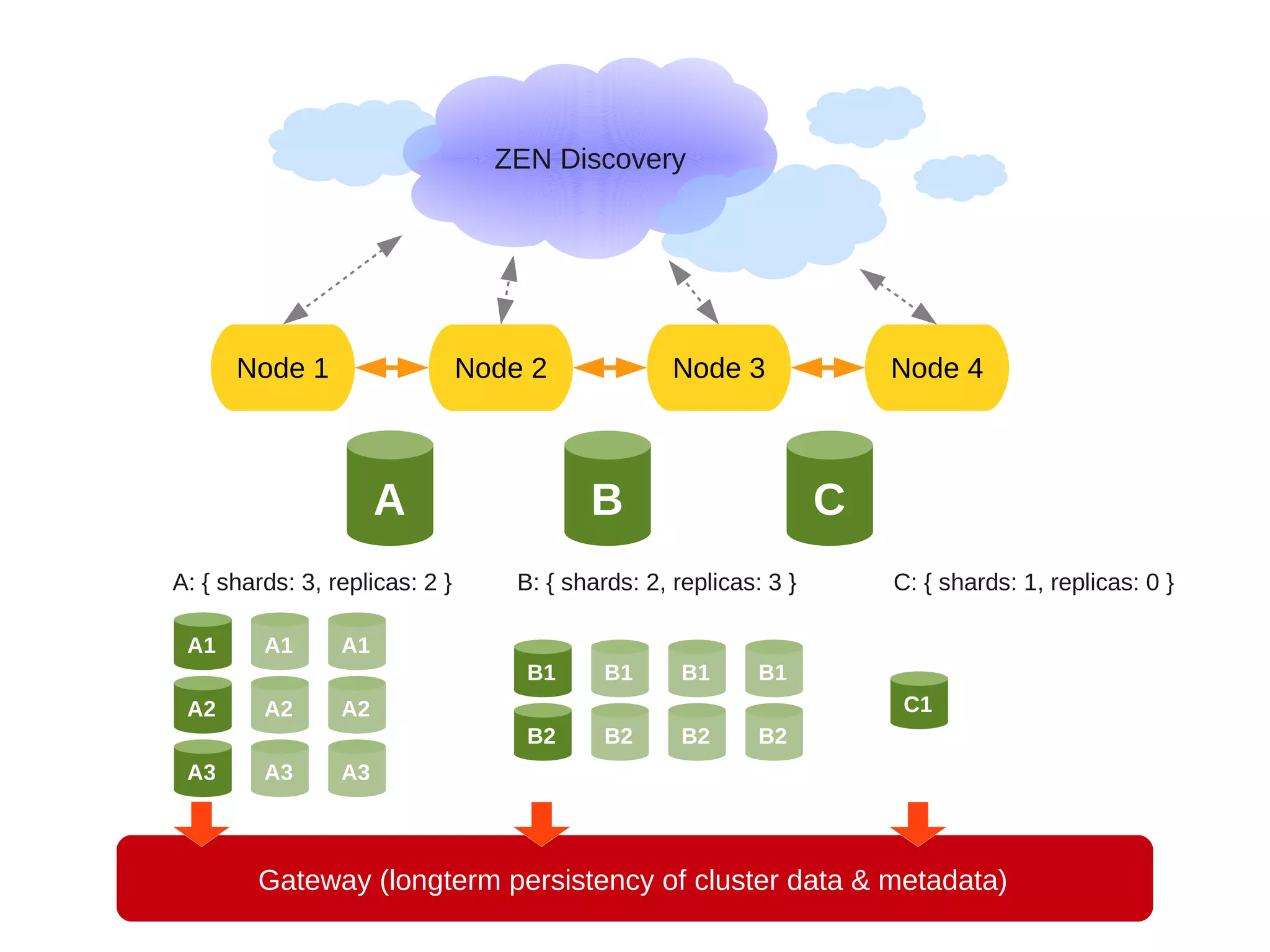
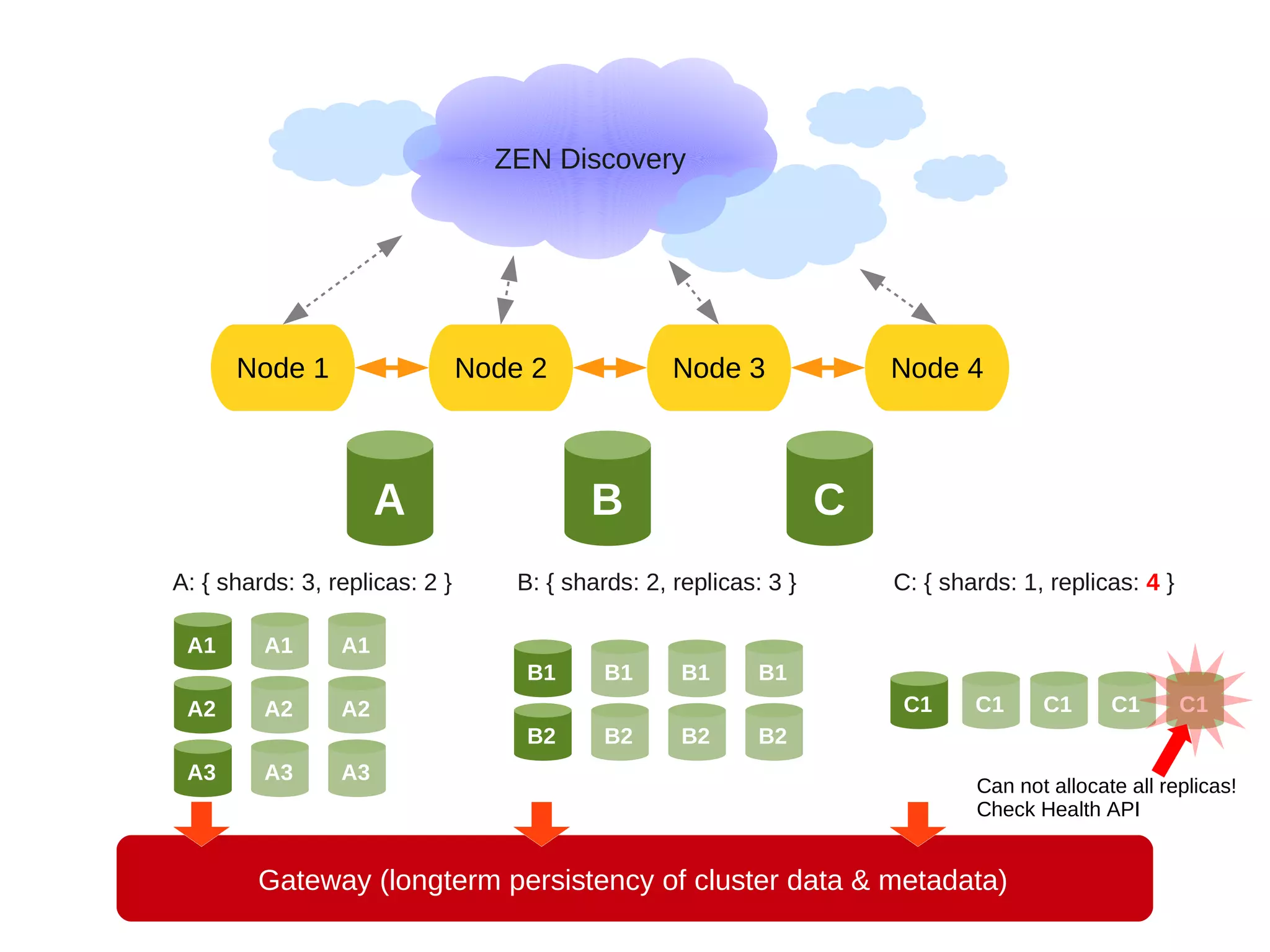
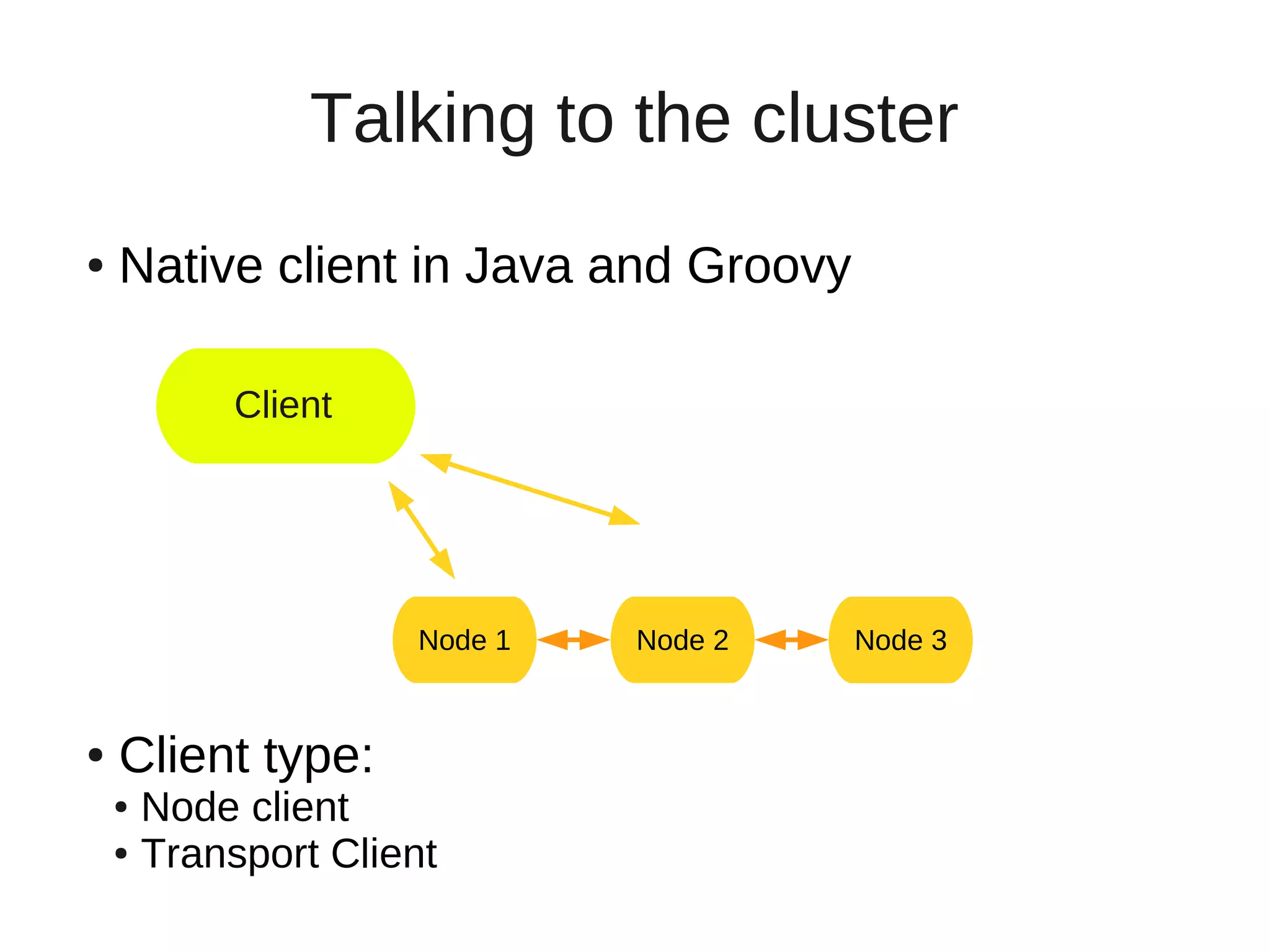
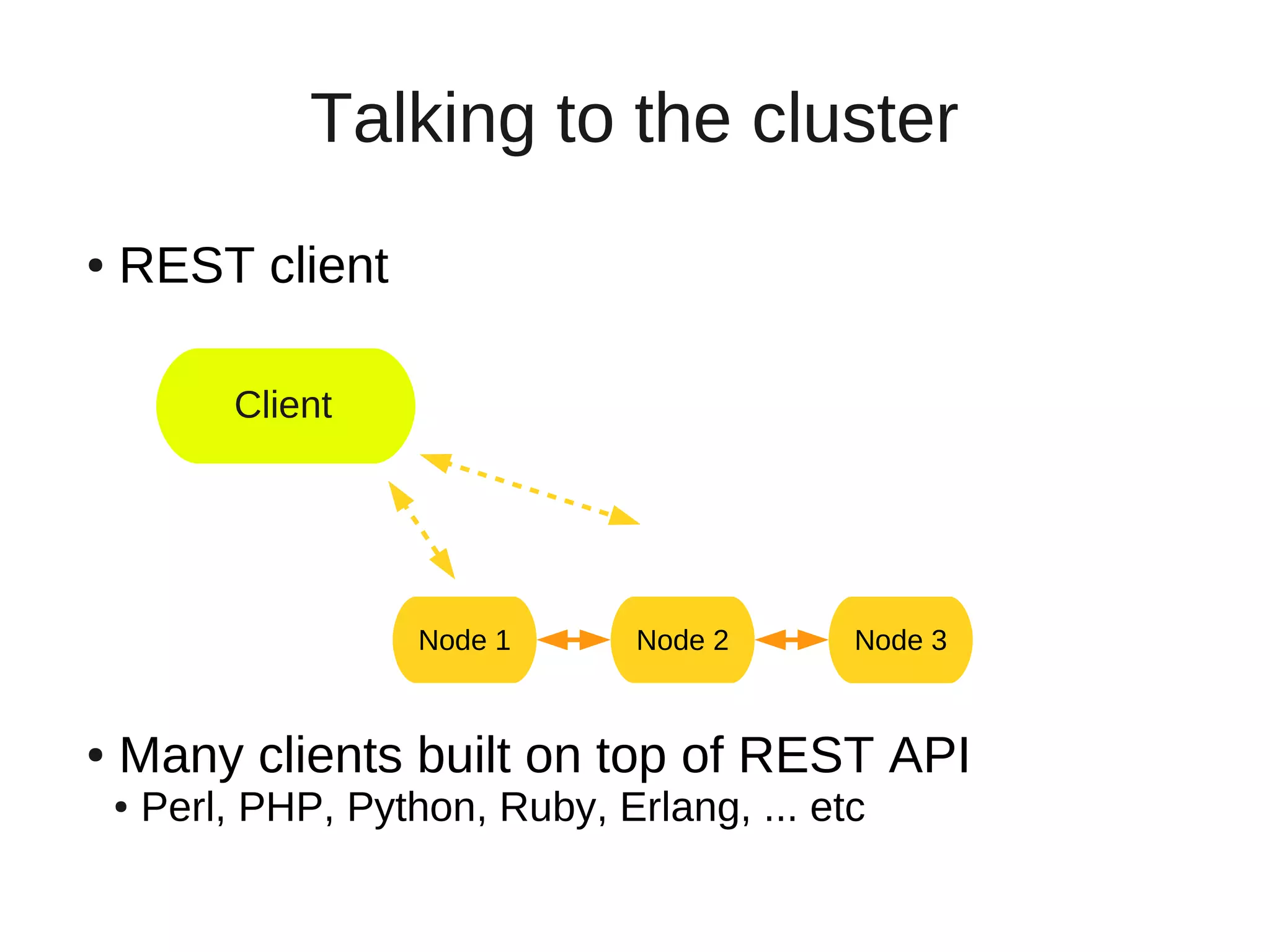
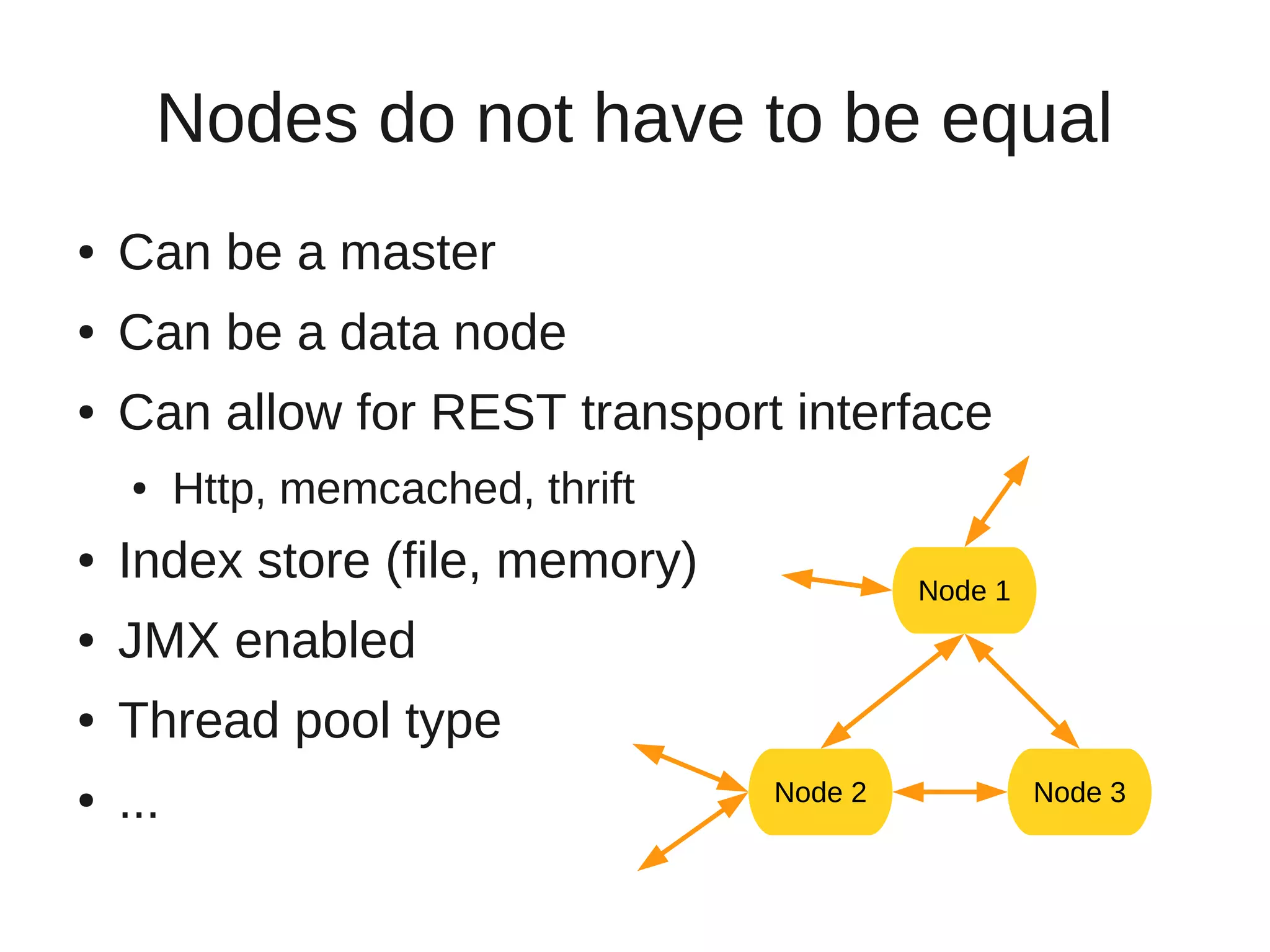
This document provides an overview of ElasticSearch, an open source, distributed, RESTful search and analytics engine. It discusses how ElasticSearch is highly available, distributed across shards and replicas, and can be deployed in the cloud. Examples are provided showing how to index and search data via the REST API and retrieve cluster health information. Advanced features like faceting, scripting, parent/child relationships, and versioning are also summarized.