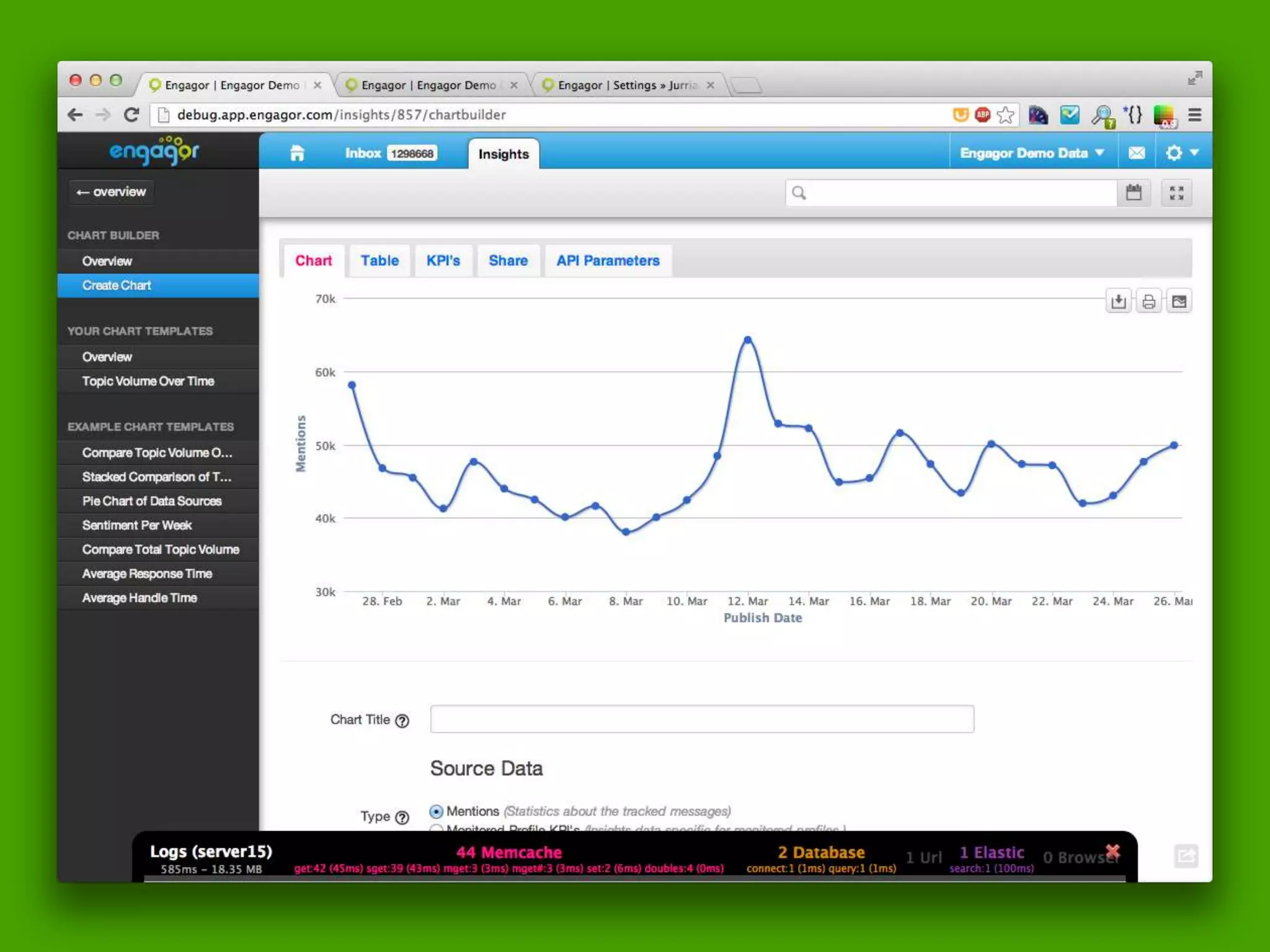
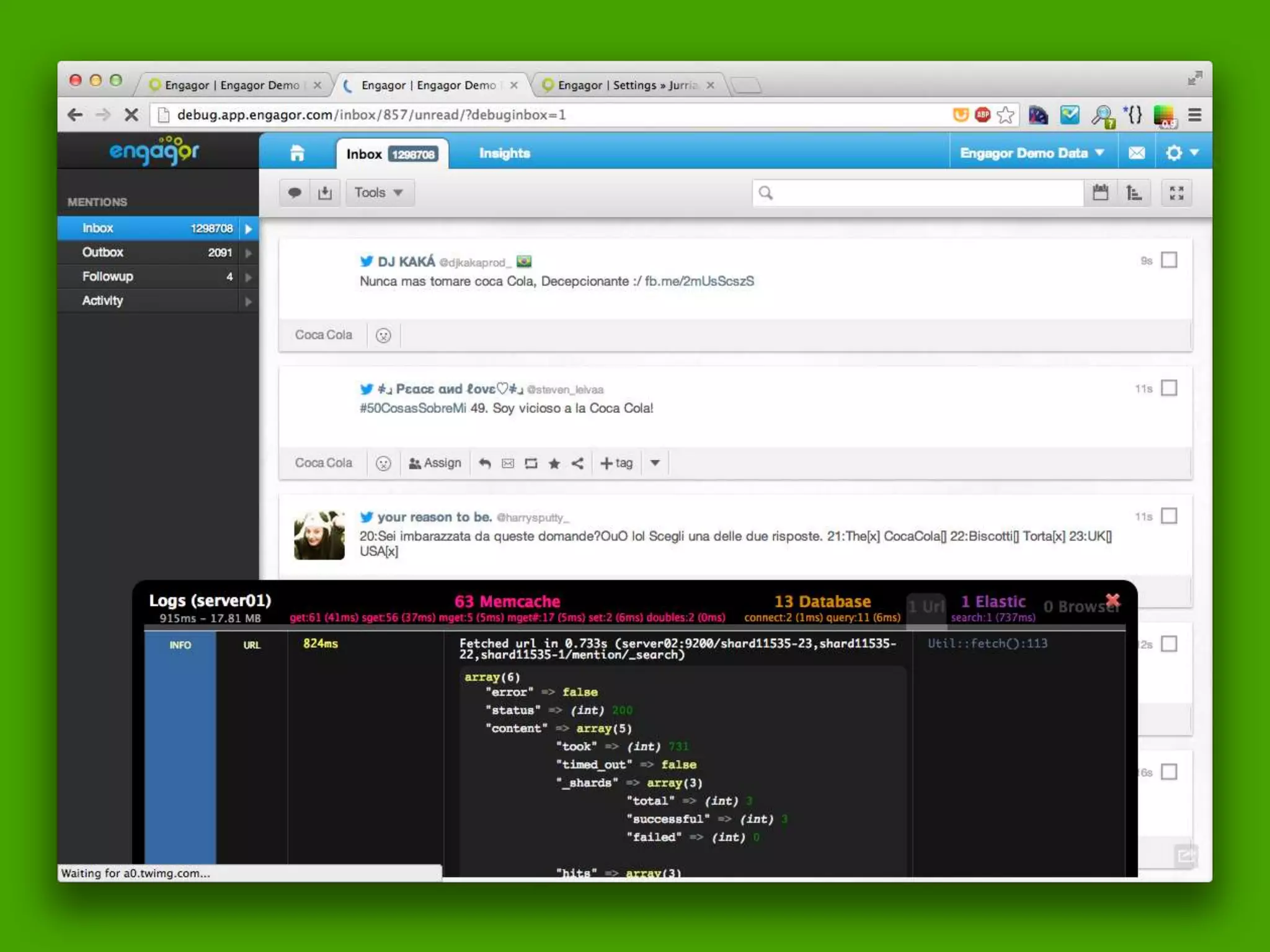
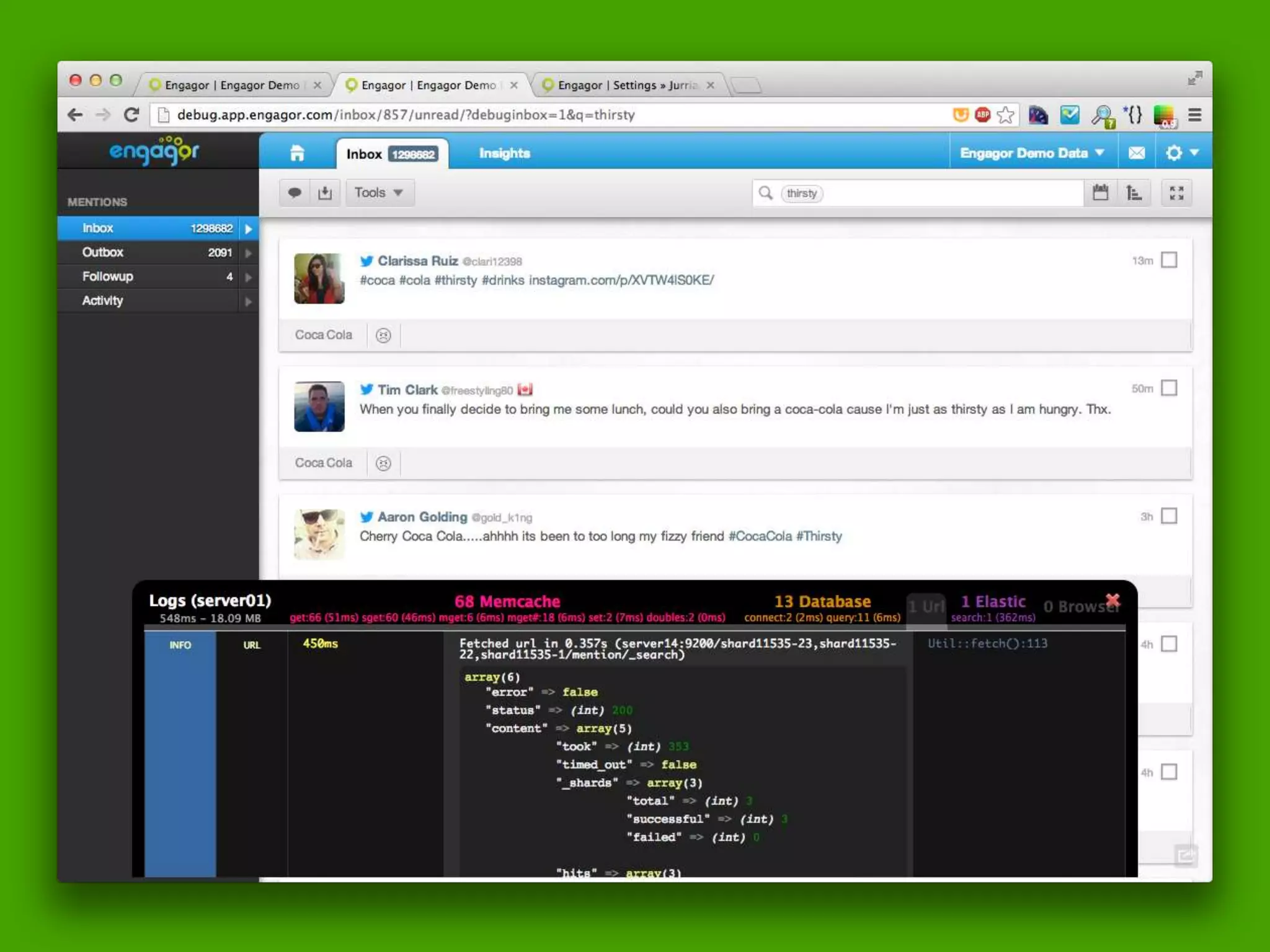
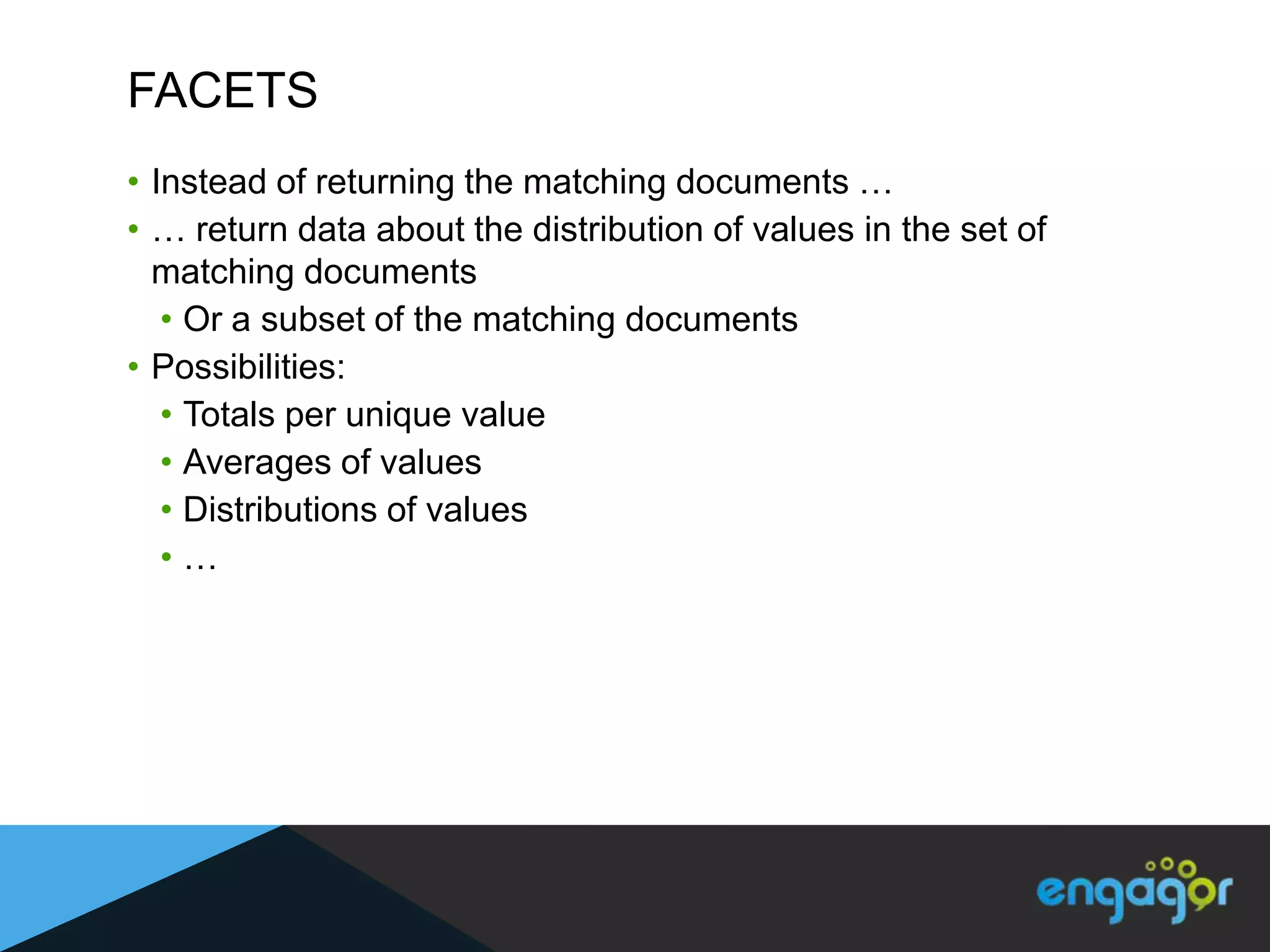
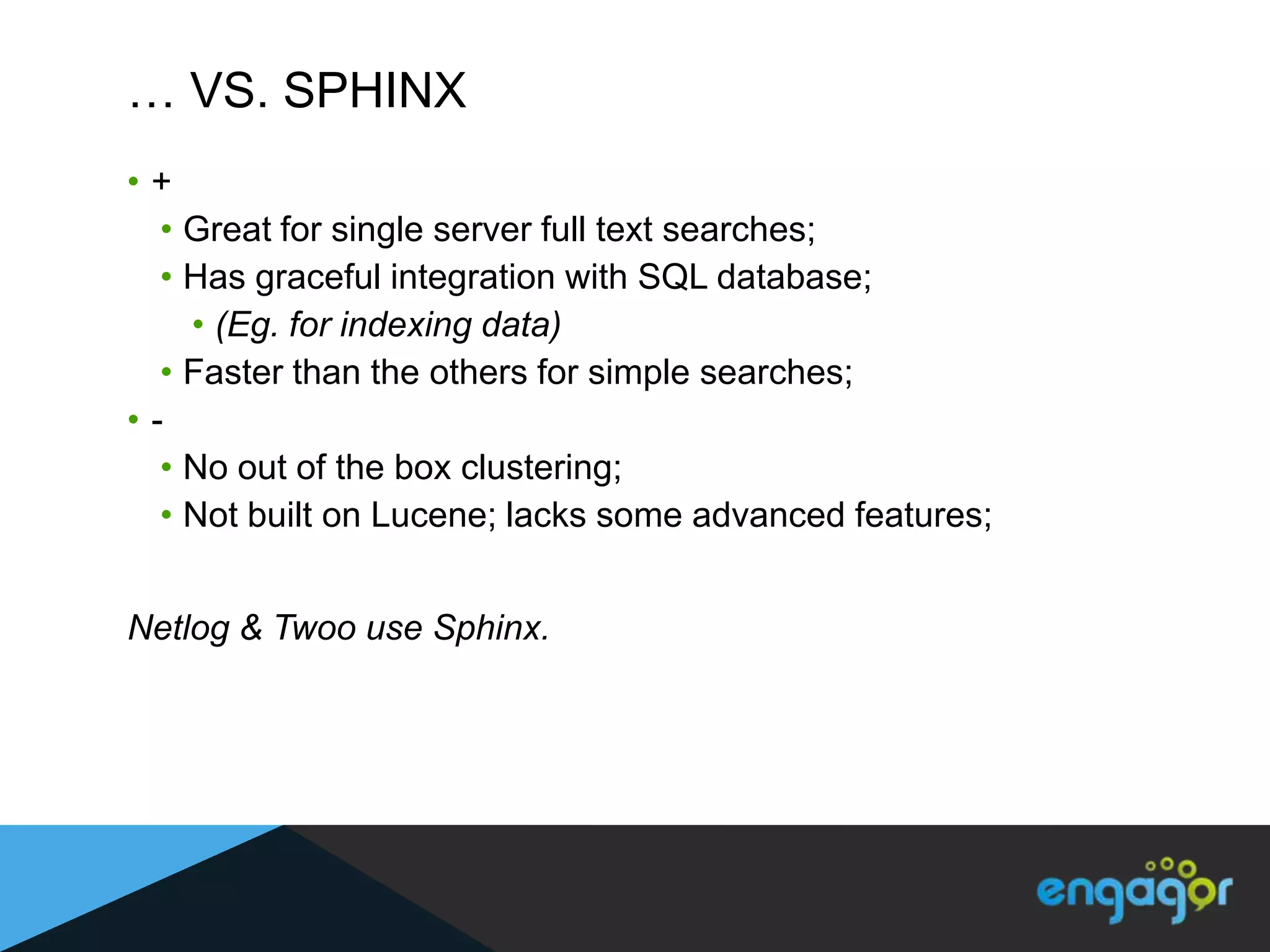
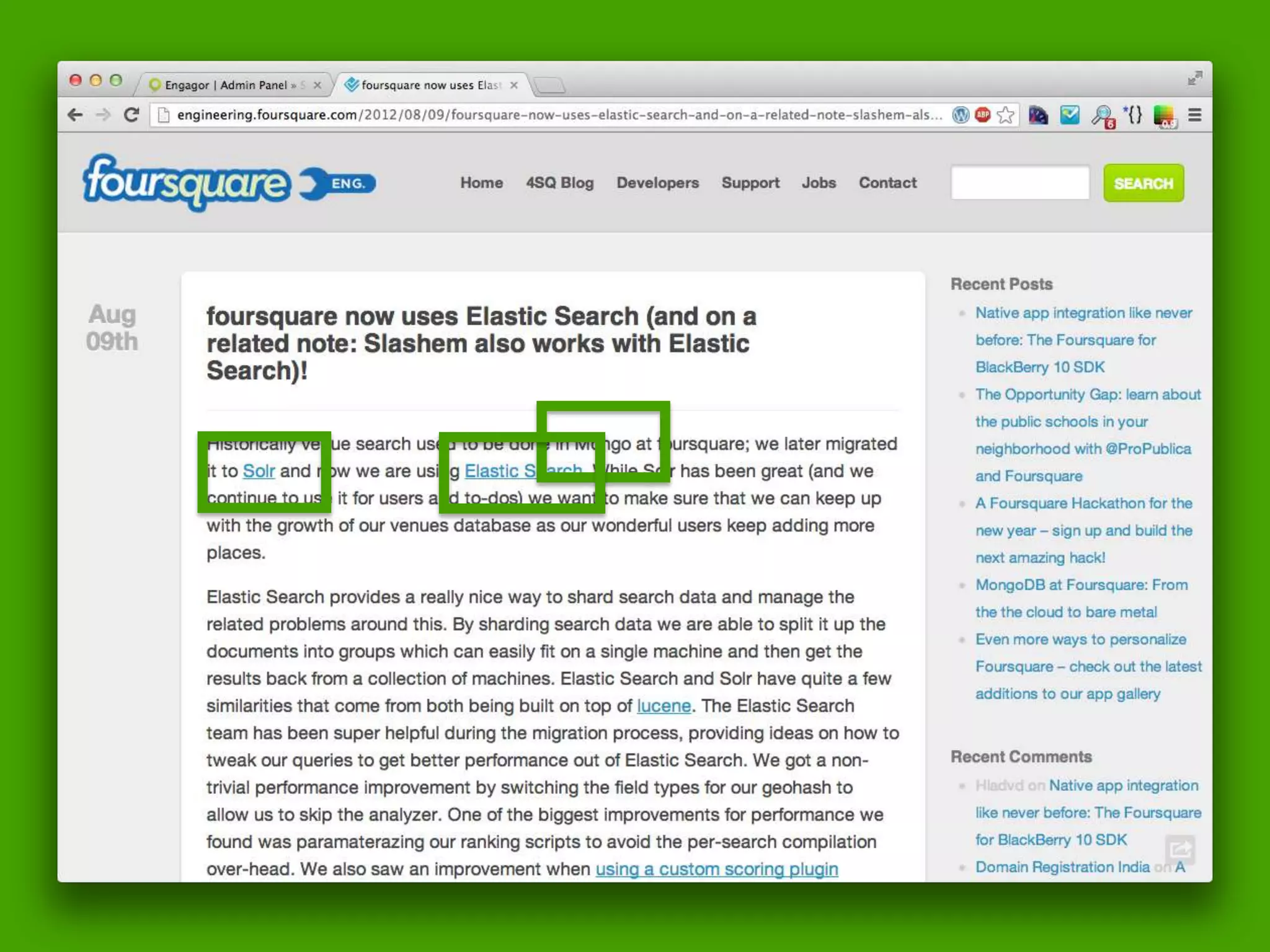
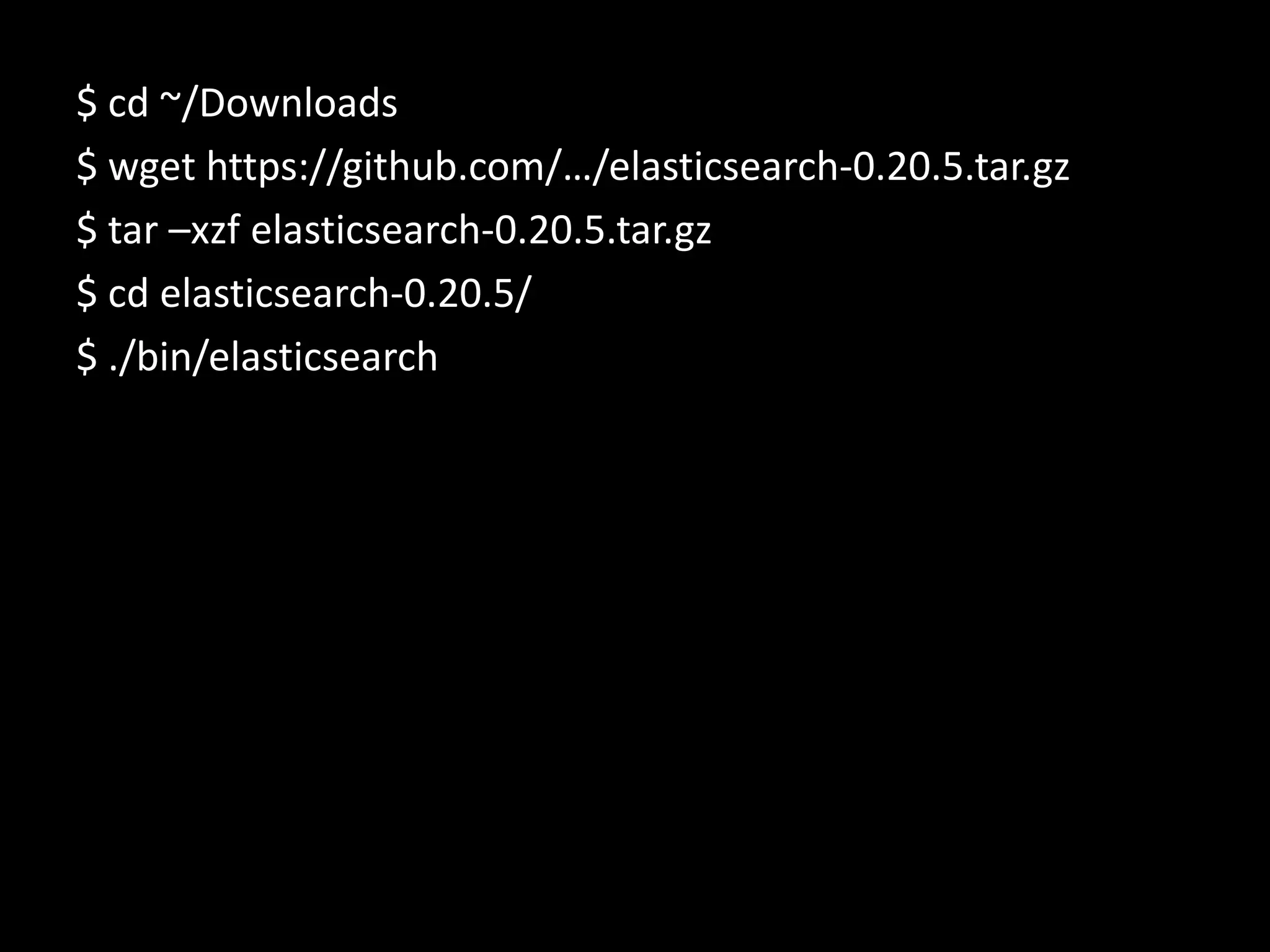
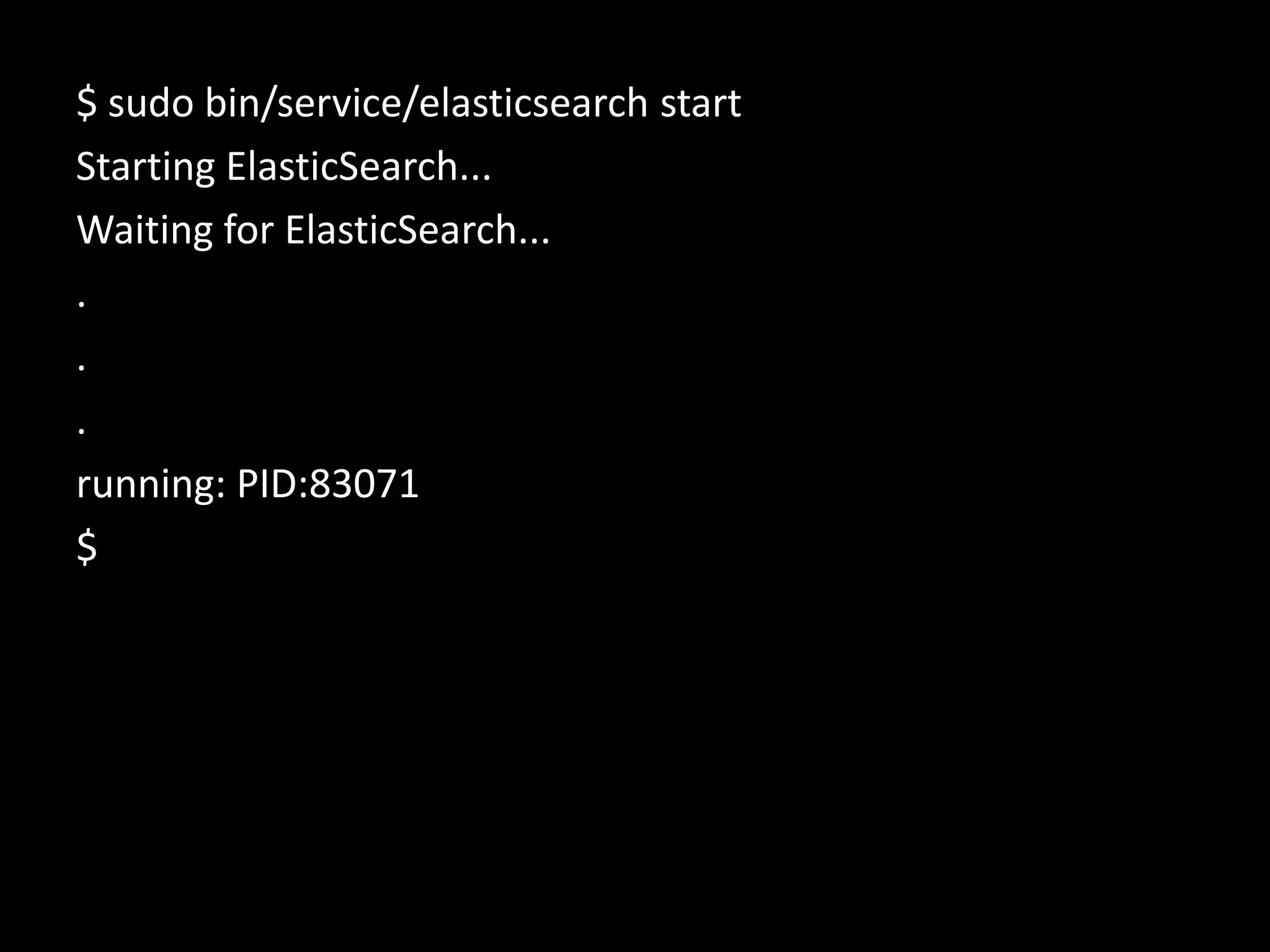
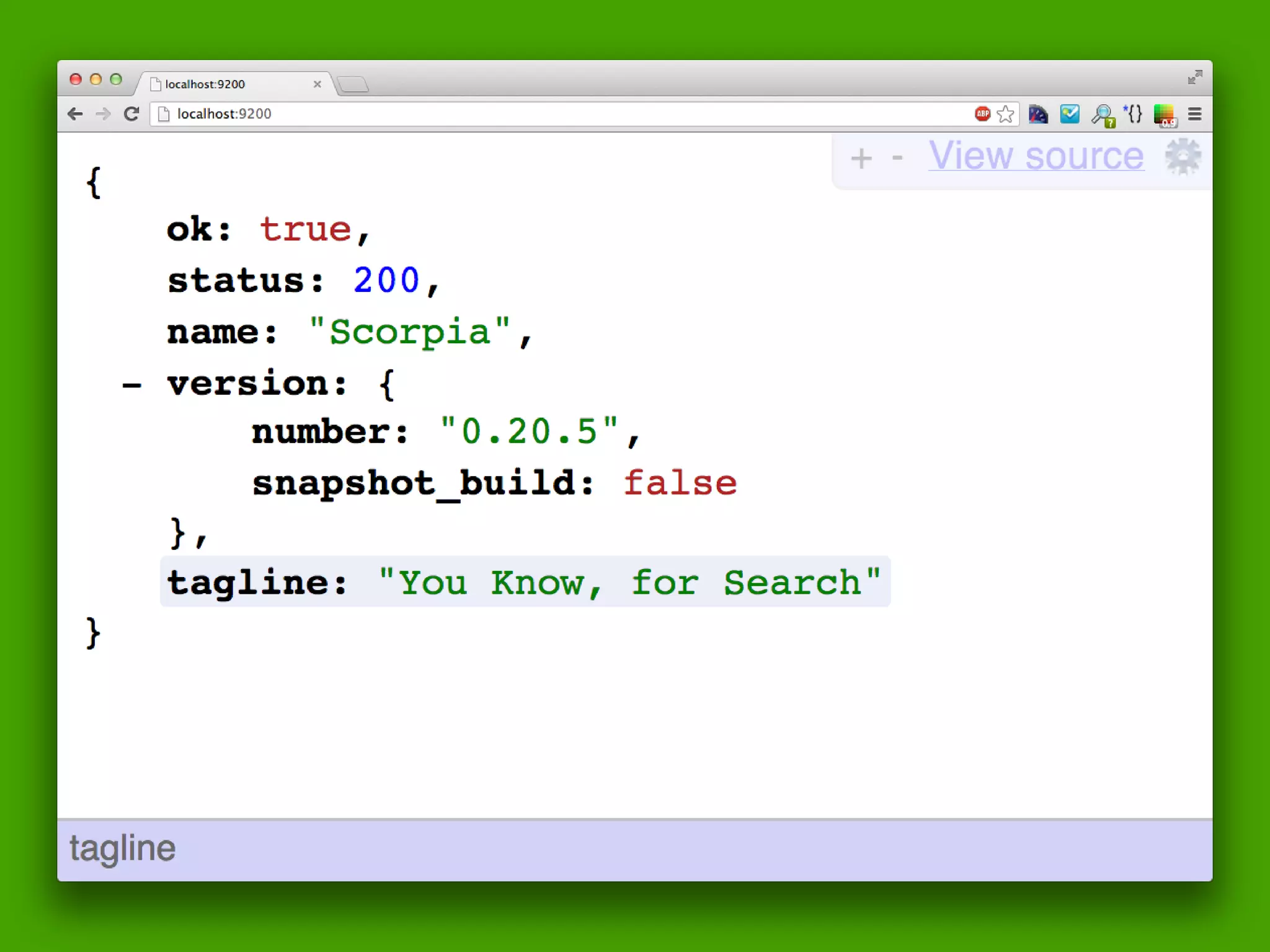
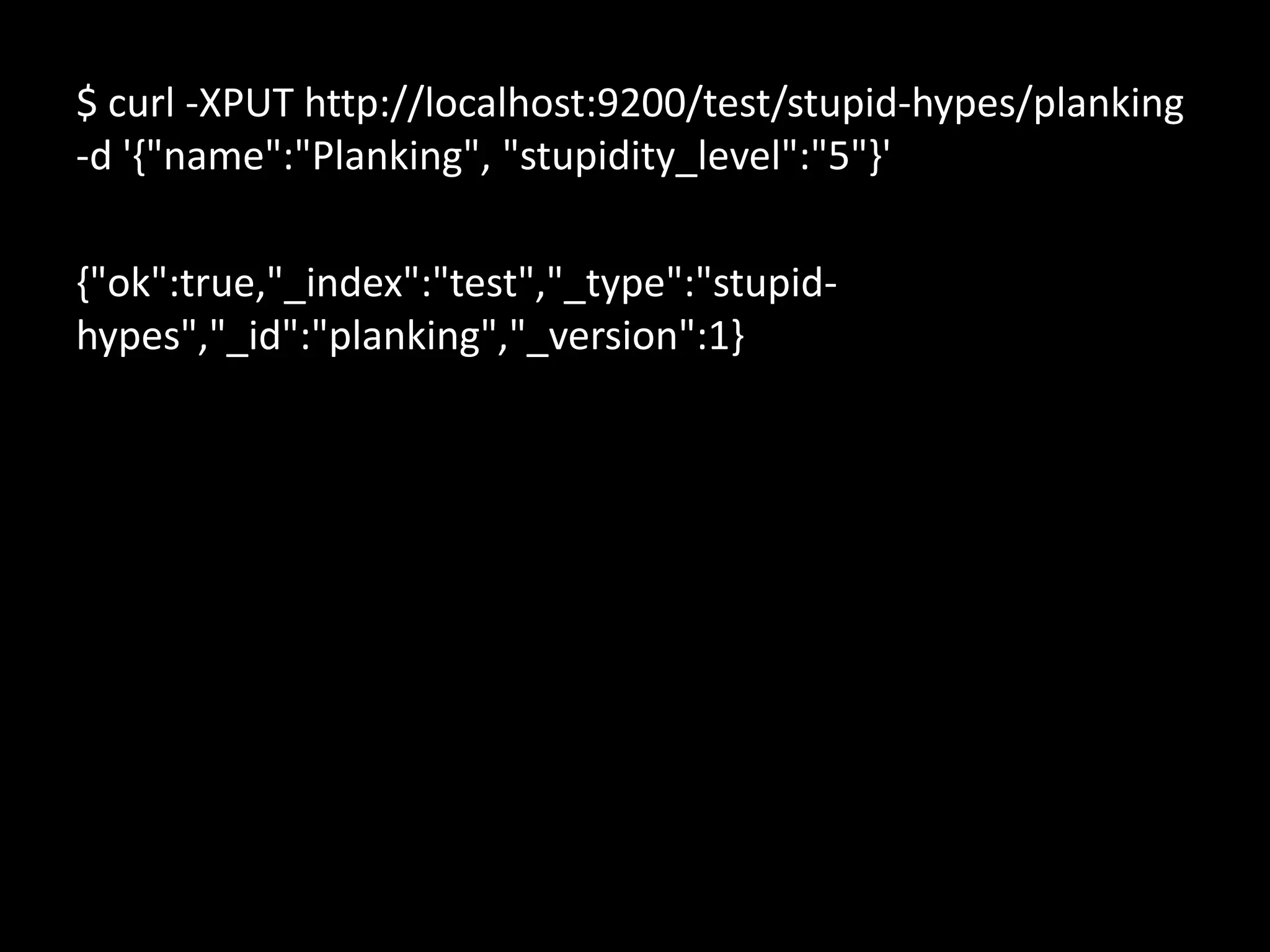
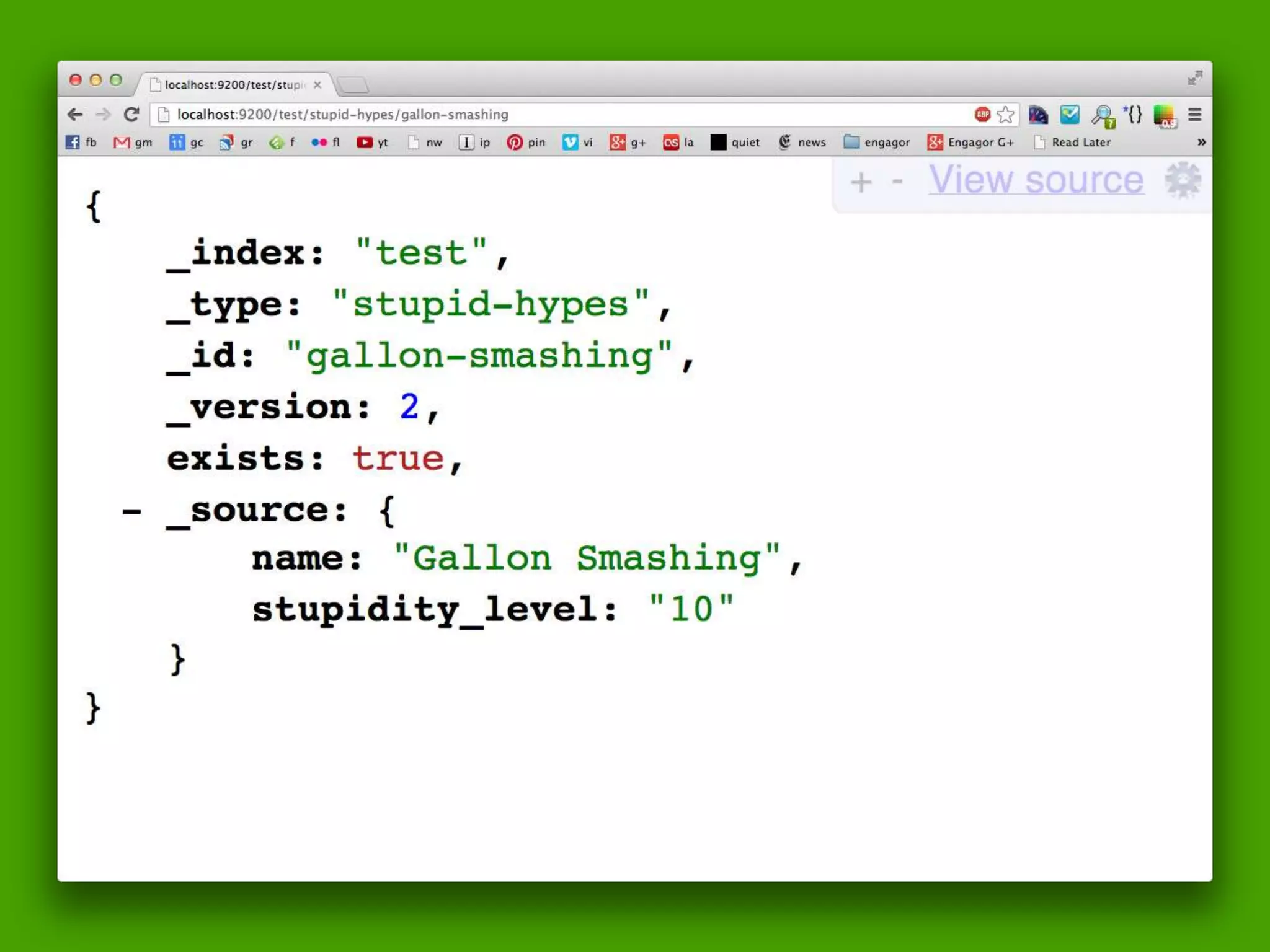
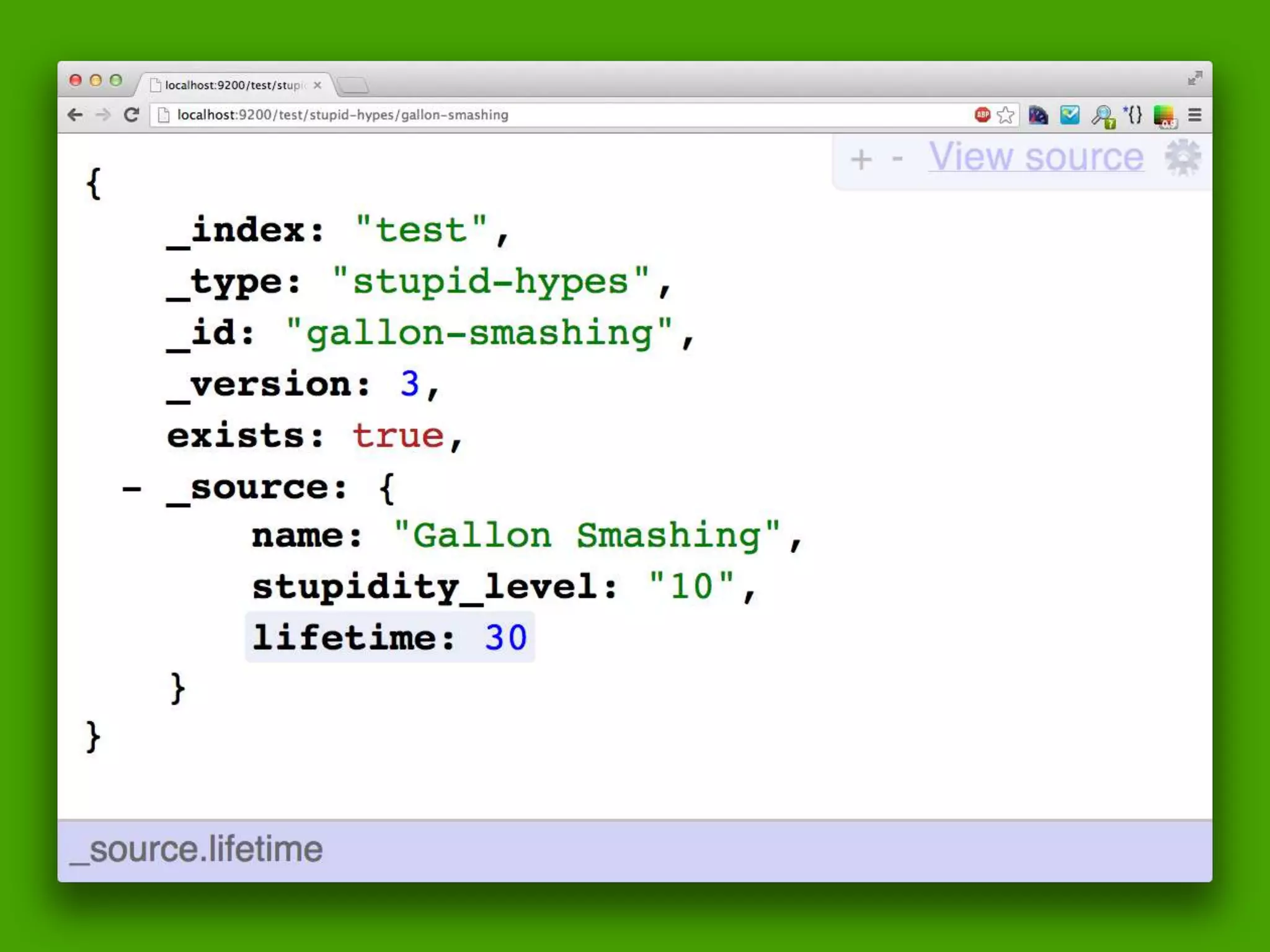
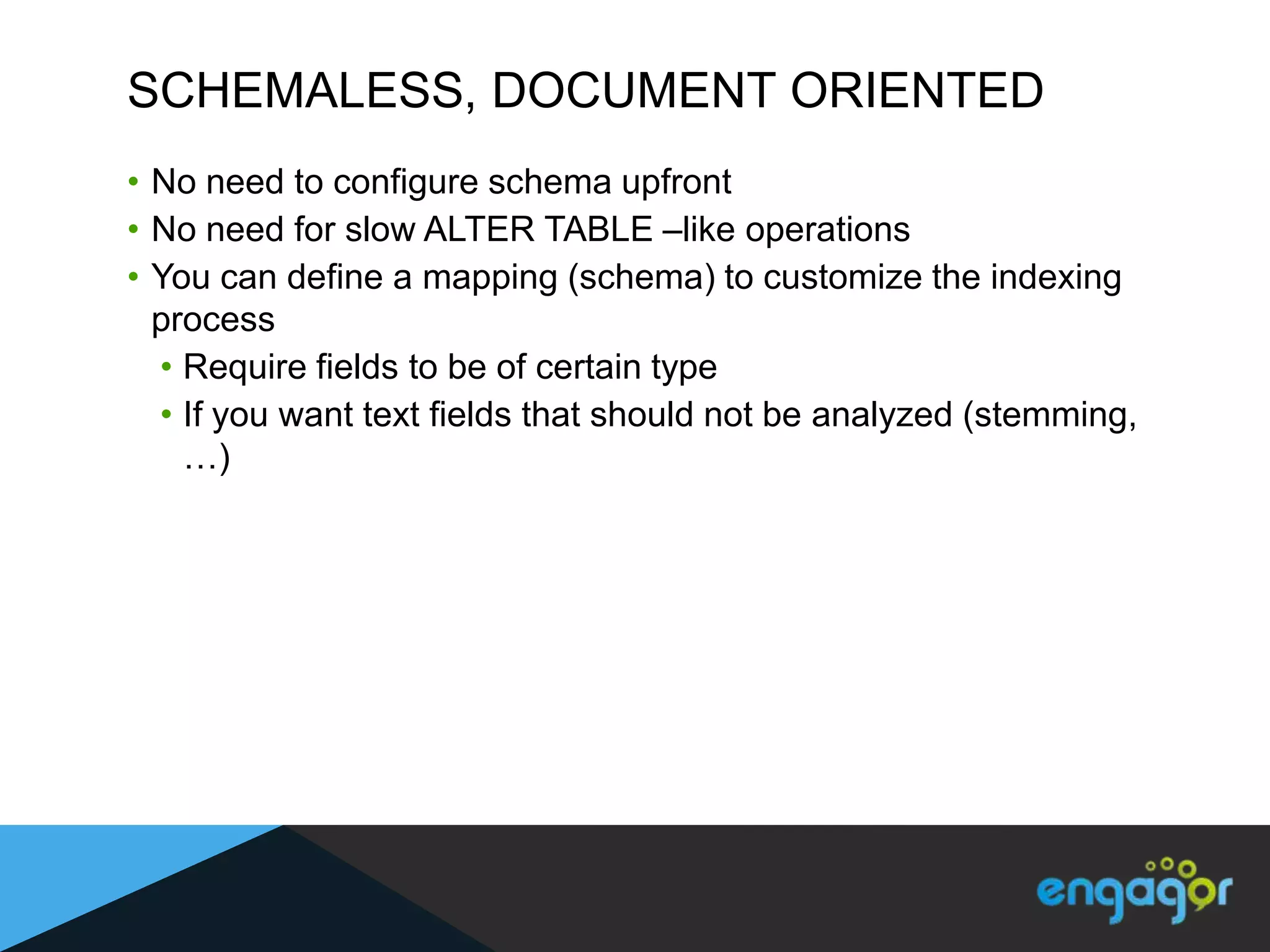
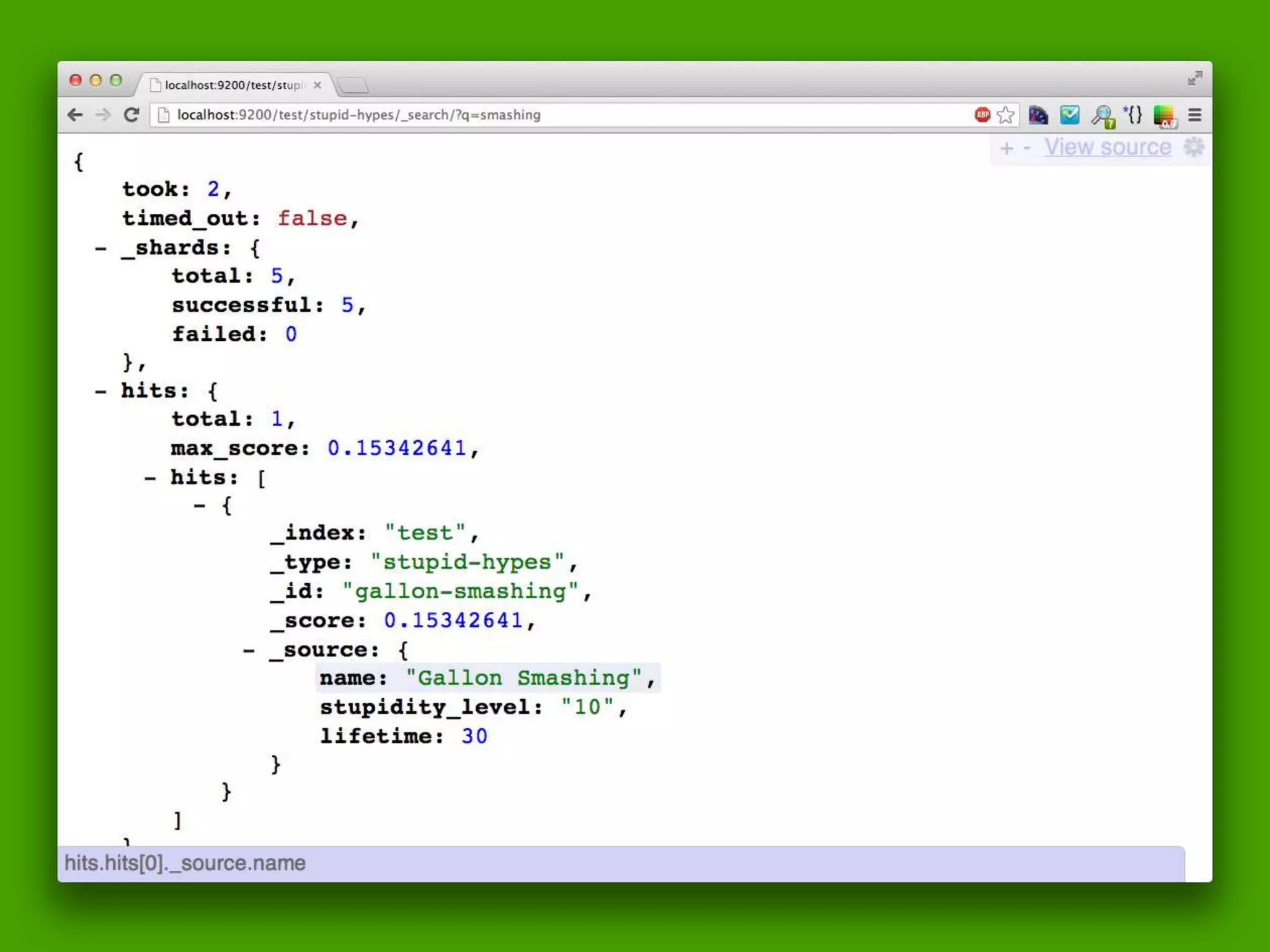
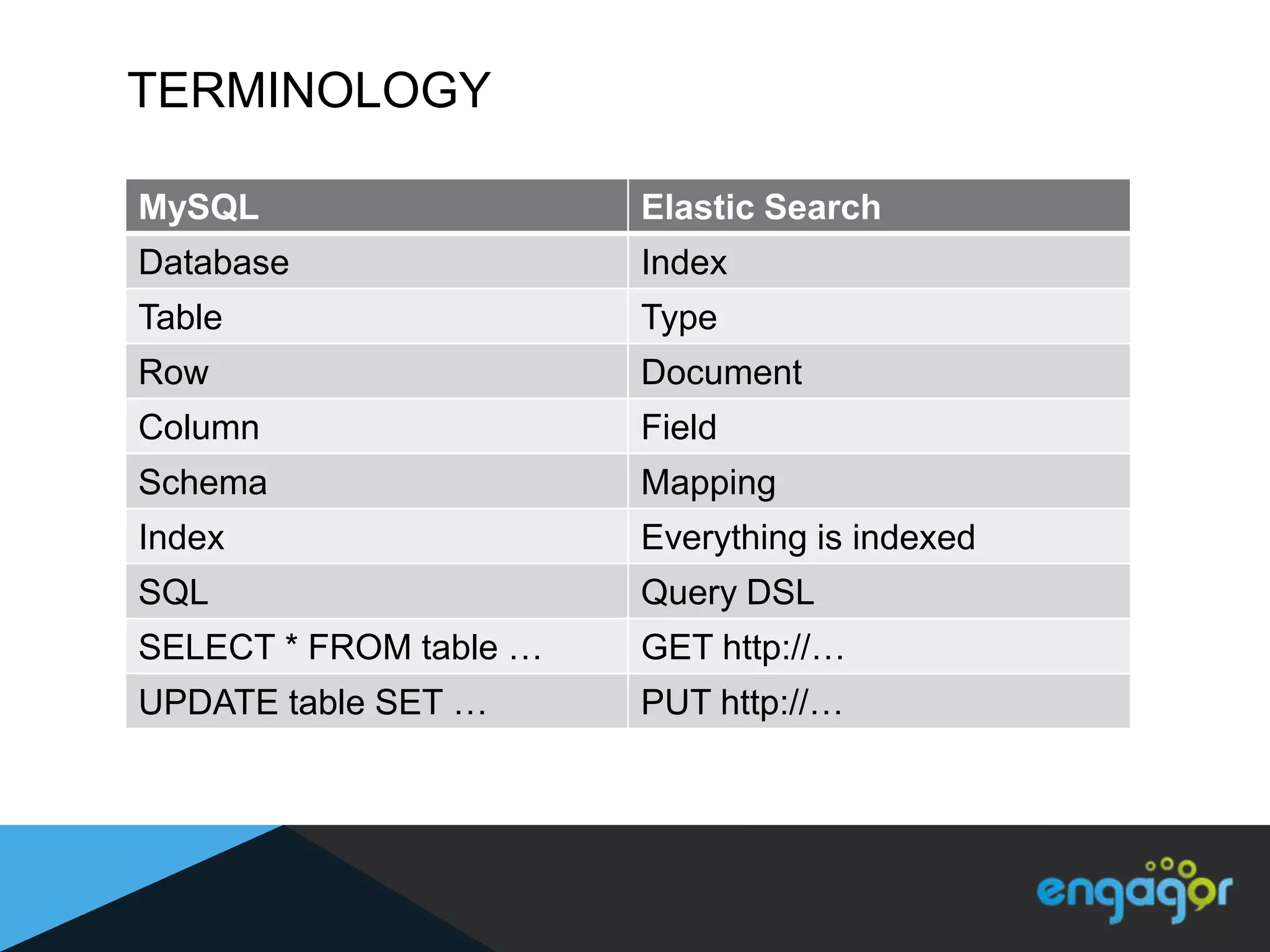
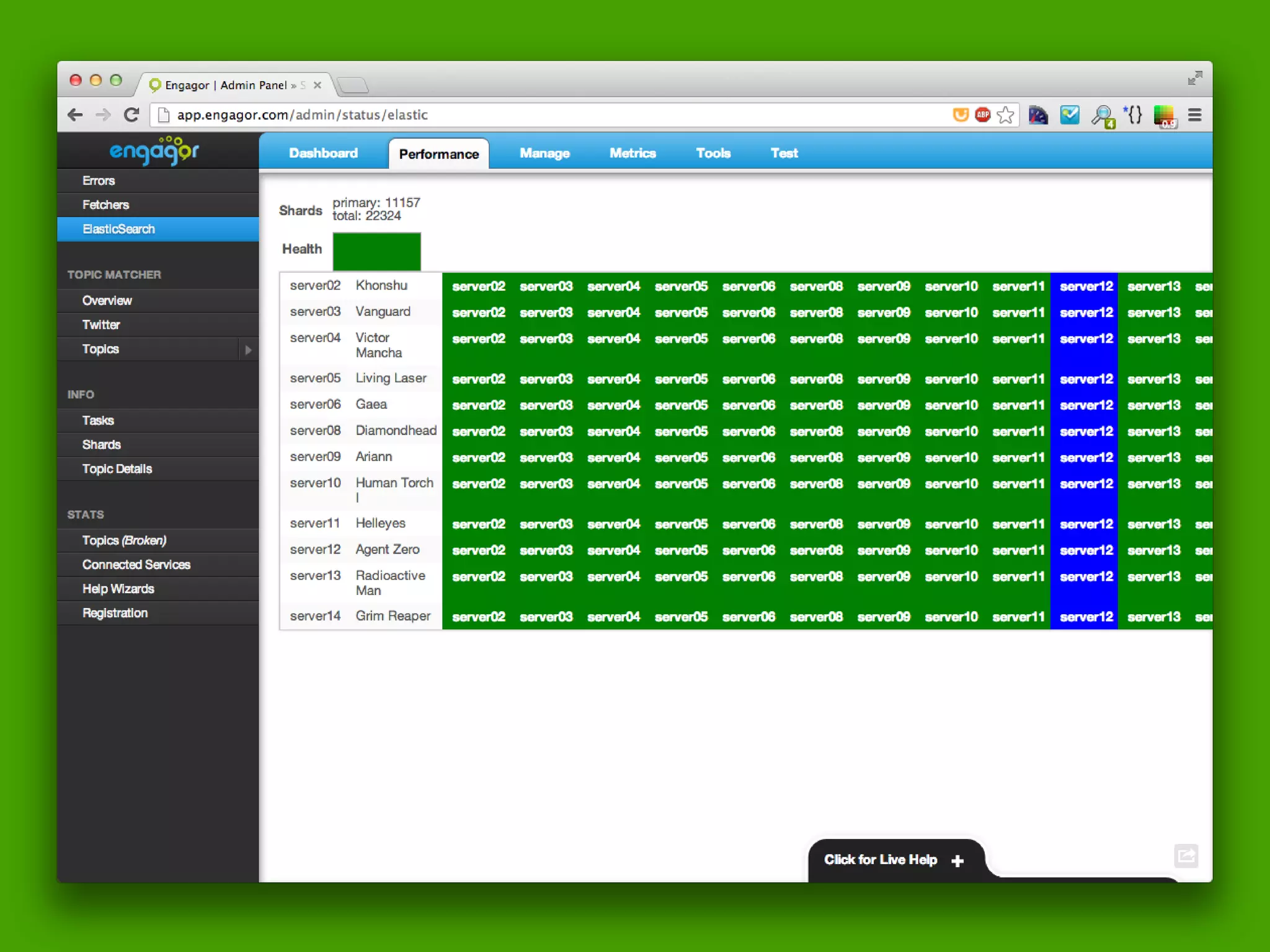
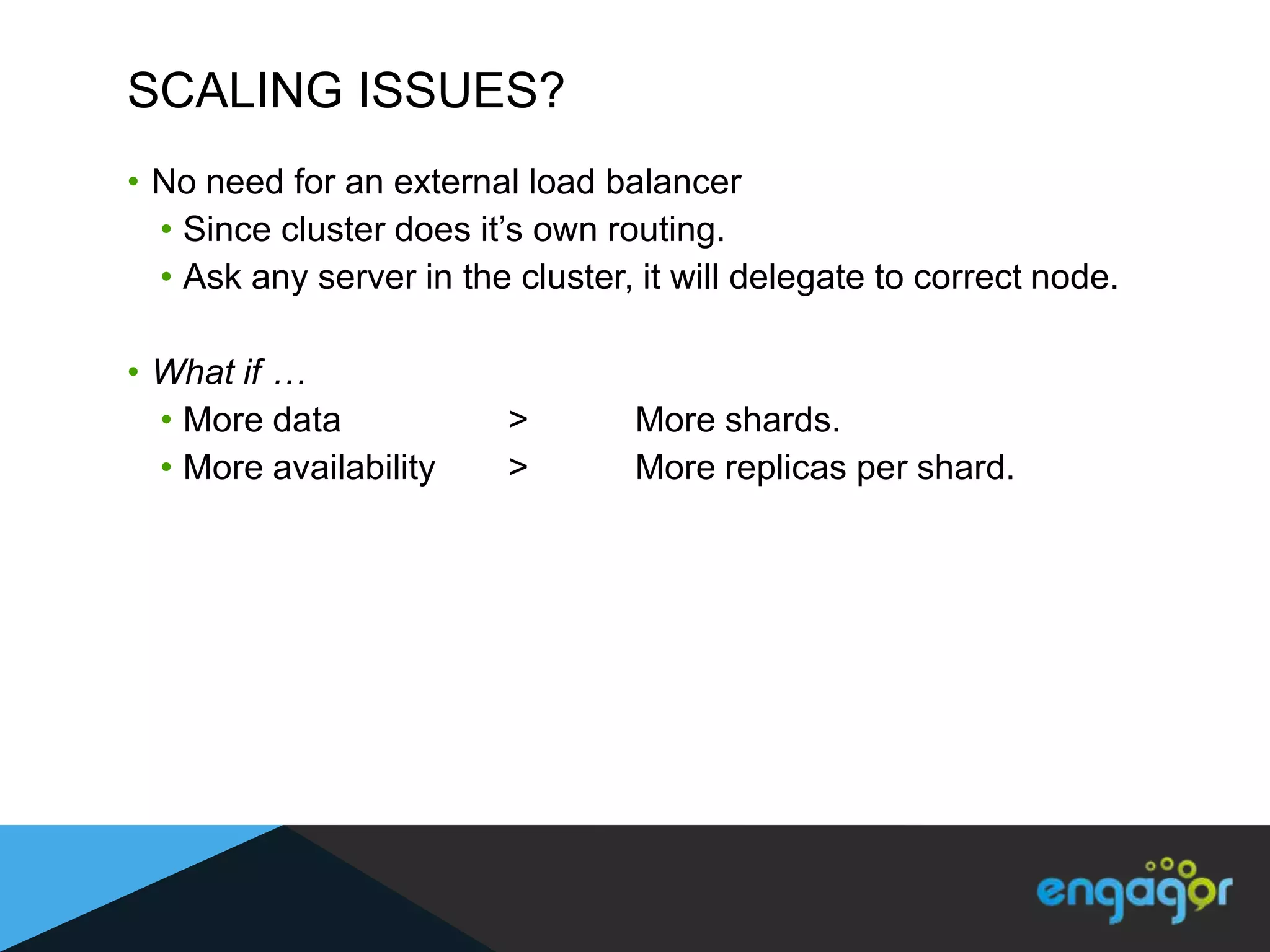
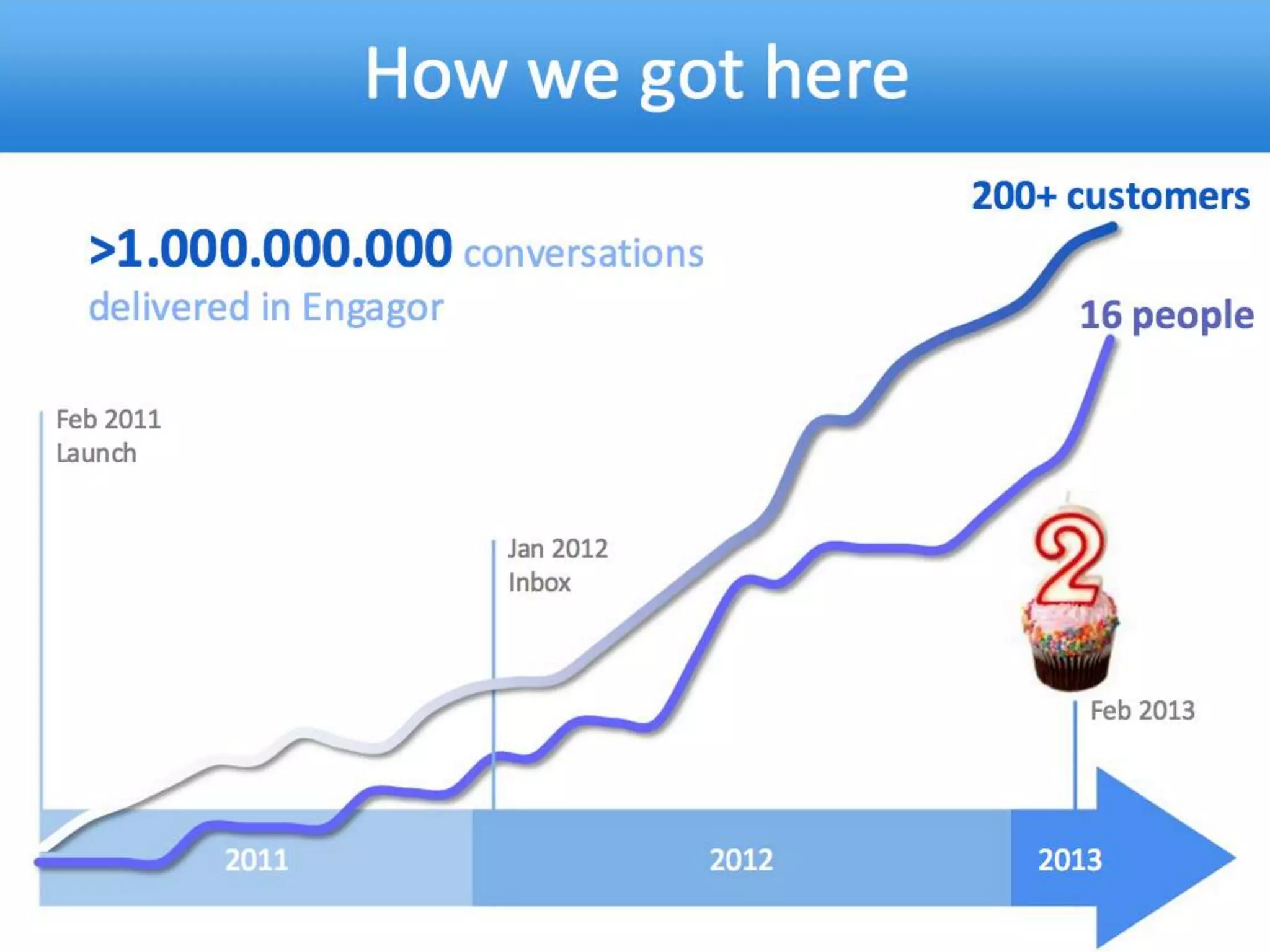
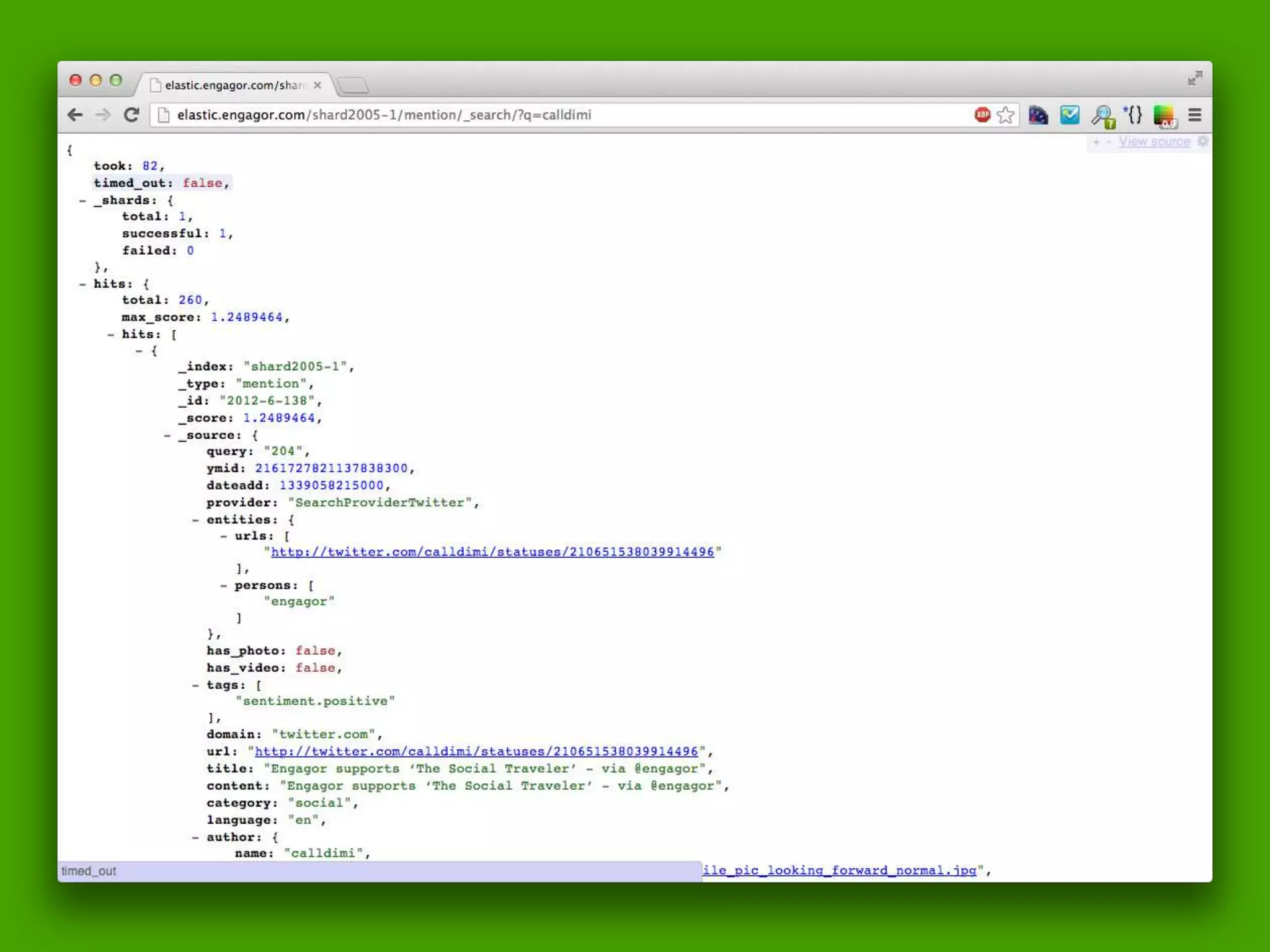
The document discusses technical details of implementing full-text search using PHP/MySQL and highlights advanced features of Elasticsearch, a distributed search engine built on Apache Lucene. It covers aspects such as data indexing, tokenization, stemming, filtering, and relevance scoring. Additionally, it compares Elasticsearch with other search engines like Solr and Sphinx, and outlines the benefits of using Elasticsearch for efficient and scalable search solutions.


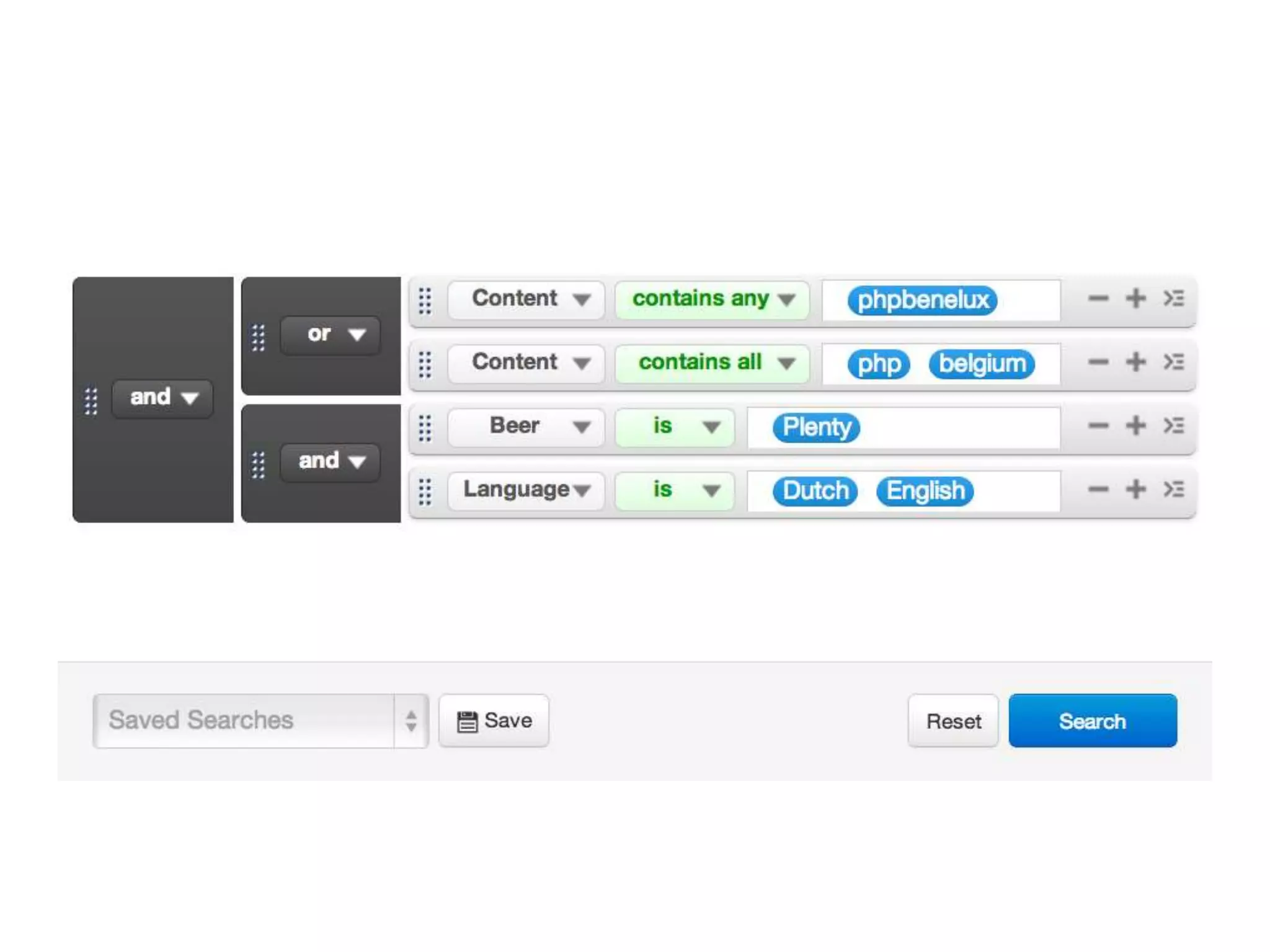































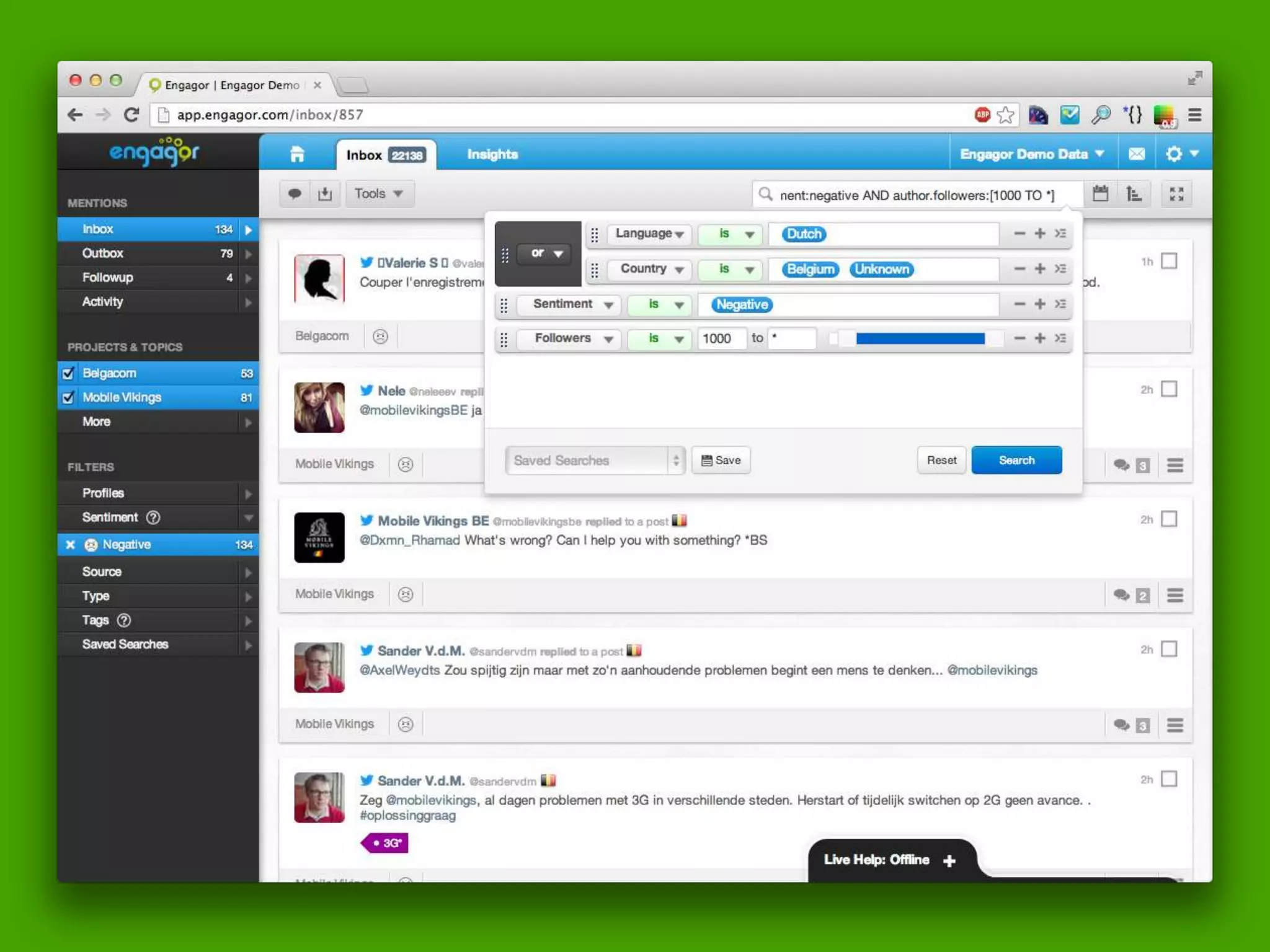
![Query DSL Example:
(language:nl OR location.country:be OR location.country:aa)
(tag:sentiment.negative) author.followers:[1000 TO *] (-
sub_category:like) ((-status:857.assigned) (-status:857.done))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elasticsearchpresentation-130327180256-phpapp01/75/An-Introduction-to-Elastic-Search-57-2048.jpg)