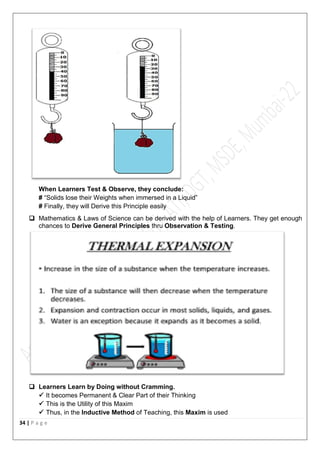
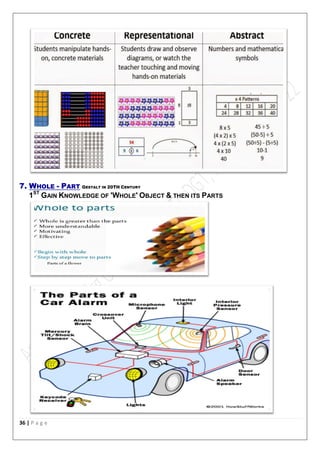
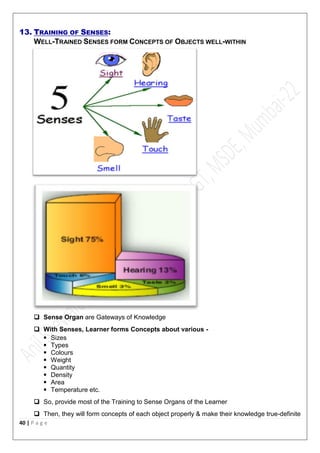
The document outlines the principles of good teaching, emphasizing characteristics such as motivation for self-learning, effective planning, and sympathy towards learners. It stresses the importance of creating a conducive learning environment, engaging students through activities, and understanding individual differences among learners. Key teaching principles include motivation, interest, learning by doing, linking content to life, and the necessity of having clear objectives in lessons.