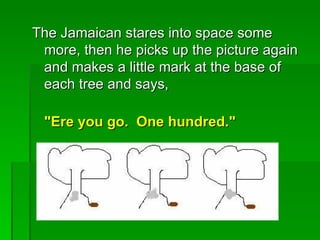
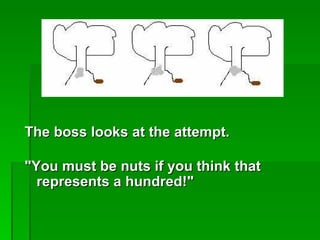
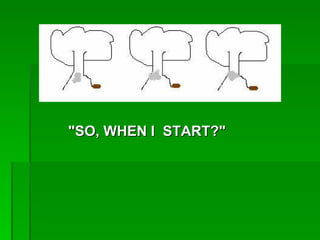
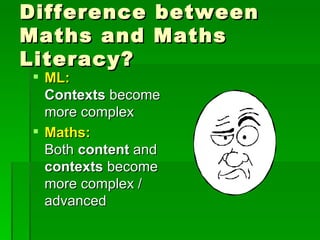
Mathematical literacy provides learners with an understanding of how mathematics is applied in everyday life and work. It focuses on using basic math concepts to solve real-world problems, rather than expanding on mathematical content like a traditional math course. Mathematical literacy prepares students for roles as self-managing individuals, contributing workers, and participating citizens by teaching skills like calculating loan repayments, reading charts and schedules, and evaluating statistical arguments. While mathematical literacy uses relevant contexts, traditional math applies concepts across both real and theoretical examples. Students planning careers in fields requiring advanced math skills should take traditional math instead of mathematical literacy.