Pawar, I understand your concern about Shylesh's participation in meetings. However, forcing or pressuring someone to speak more could backfire and damage their confidence. Instead, I suggest taking a gentler approach to help Shylesh feel comfortable contributing in his own time and way.
Some ideas: privately ask Shylesh his thoughts after meetings to get his perspective. Praise any contributions he does make to encourage further participation. When assigning tasks, consider Shylesh's strengths and give him opportunities to showcase them. Lead by example with your own clear and considerate communication style. With patience and support, Shylesh will likely gain experience and find his voice. The goal is inclusion, not domination - we all have room to


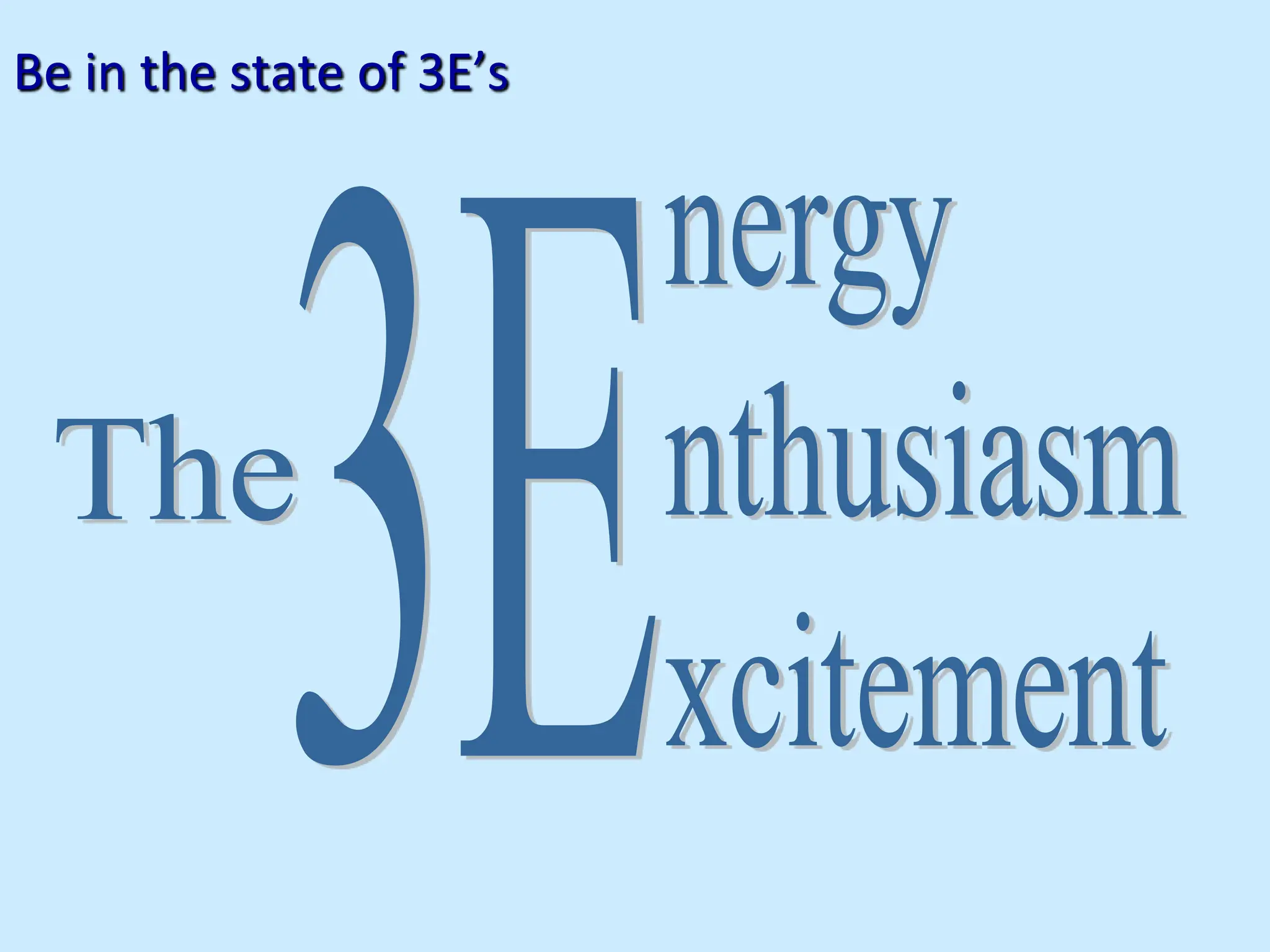


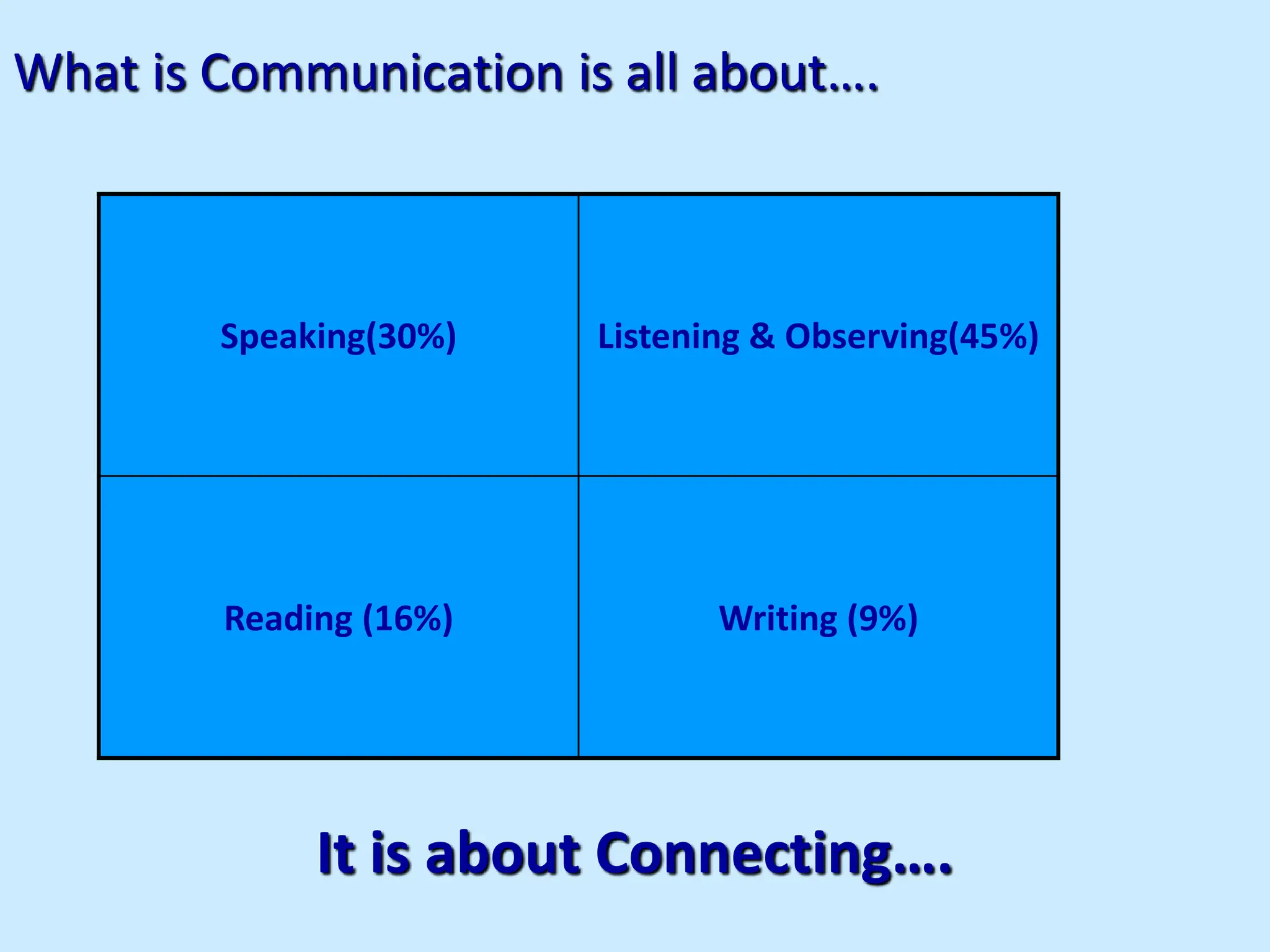

















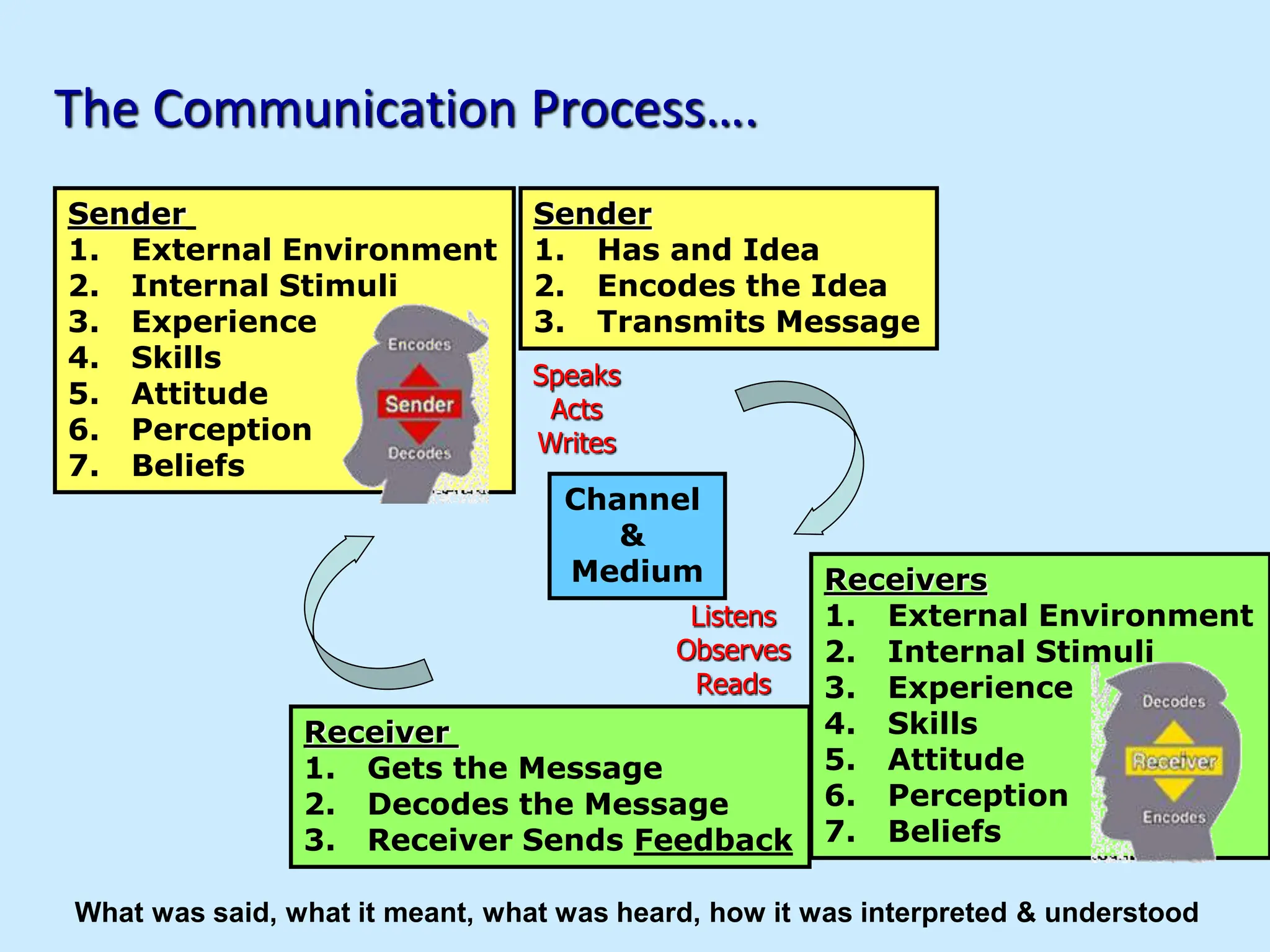










































![“When the going gets tough, the tough get Assertive”
– Triad Role Play
• Observer’s Feedback Form :
• Choice of Words
• Tonality of Voice [too polite / harsh]
• Non-Verbal Cues [nodding, eye contact, facial exp, etc]
• Excuses/Unnecessary Justifications & Apologies
• Accusations/Allegations and Blame Game/Finger-pointing
• Focus on facts/data or assumptions/perceptions
• Quality of Responses = Proactive / Reactive](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs3essentials-of-business-communicationskills-240130110519-f6938d7d/75/Essentials-of-Business-Communication-Skills-72-2048.jpg)




![PRESENTATION SKILLS – VISUAL ASPECTS [Body
Language]
• Posture
• Gesture
• Eye Contact
• Facial Expressions
• Usage of Space](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs3essentials-of-business-communicationskills-240130110519-f6938d7d/75/Essentials-of-Business-Communication-Skills-77-2048.jpg)
![PRESENTATION SKILLS – VOCAL ASPECTS [Delivery &
Conviction]
• Volume – Audibility & Variation
• Pitch – Inflexion Patterns
• Tone – Mood & Emotion in Voice
• Pacing & Pausing – Breath Control
• Pronunciation & Diction [Clarity]
• Conviction & Enthusiasm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs3essentials-of-business-communicationskills-240130110519-f6938d7d/75/Essentials-of-Business-Communication-Skills-78-2048.jpg)
![PRESENTATION SKILLS – VERBAL ASPECTS [Matter &
Structure]
• Content (Depth / Treatment of Subject)
• Supporting Matter (Examples / Illustrations / References /
Statistics)
• Flow & Structure (Seamless transition / Organized thought
process / 4T structure)
• Language Proficiency (Fluency / Sentence Construction)
• Delivery Style (Conversational / Interactive / Q&A /
Humour)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cs3essentials-of-business-communicationskills-240130110519-f6938d7d/75/Essentials-of-Business-Communication-Skills-79-2048.jpg)
















