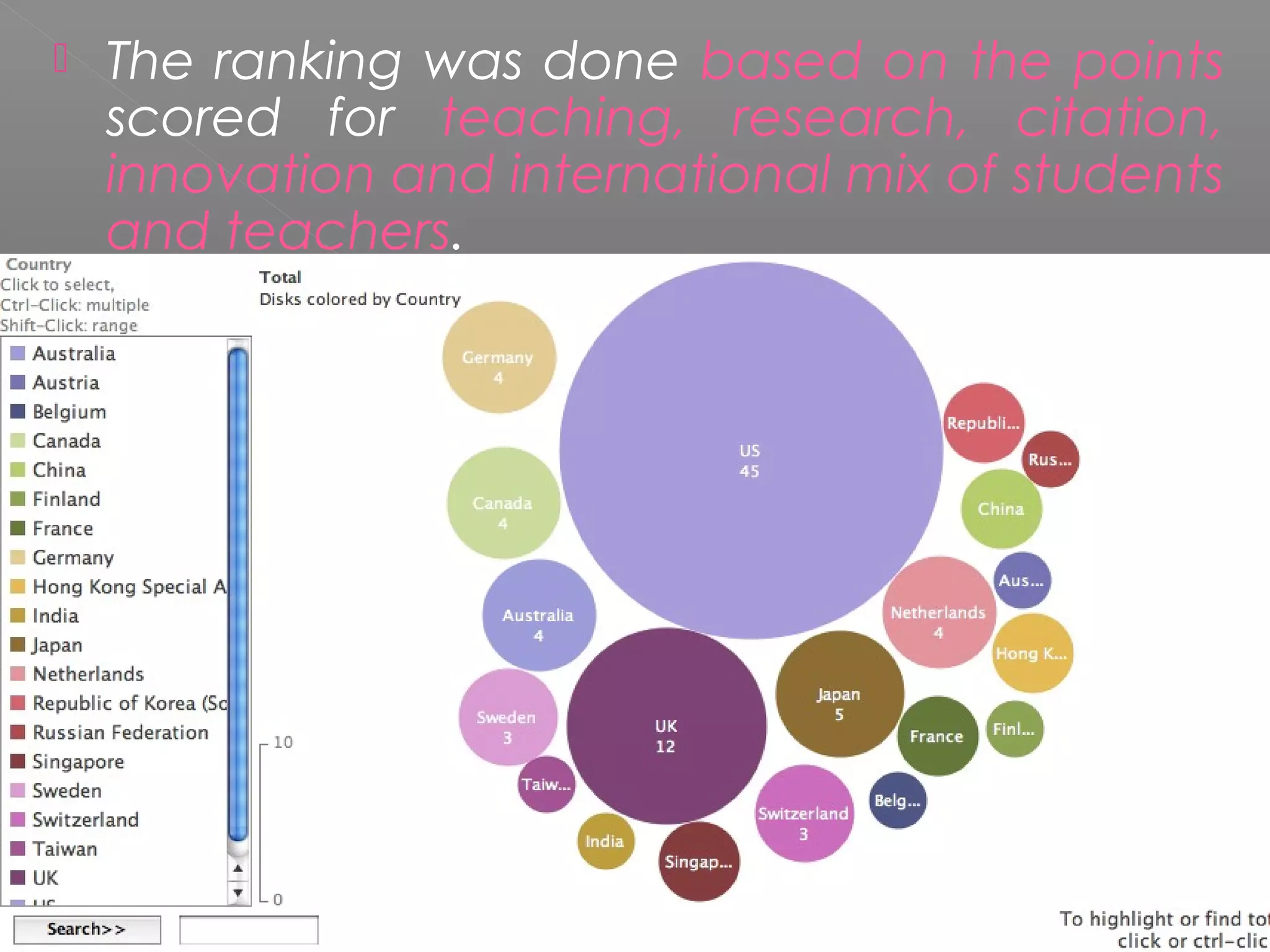
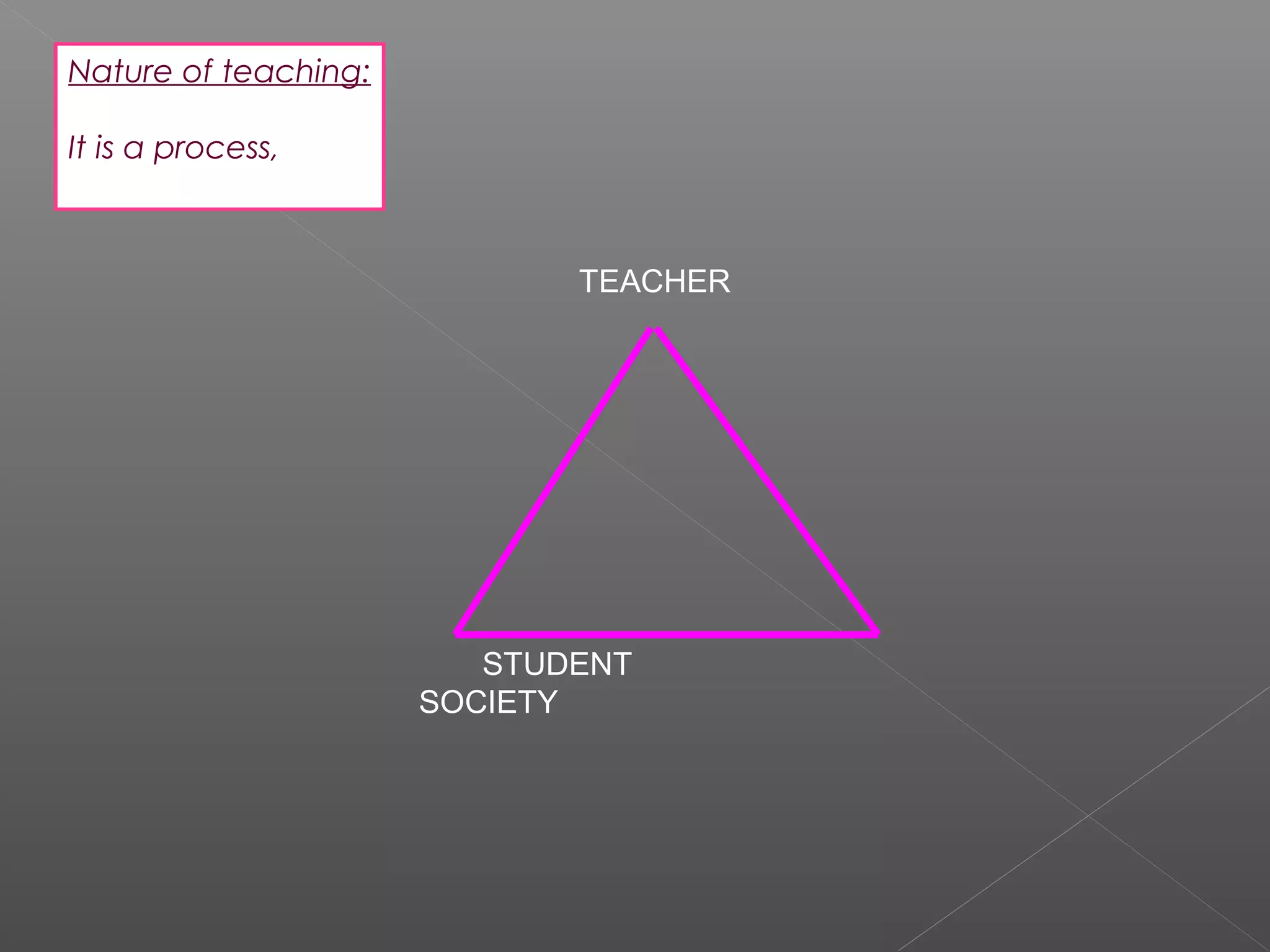
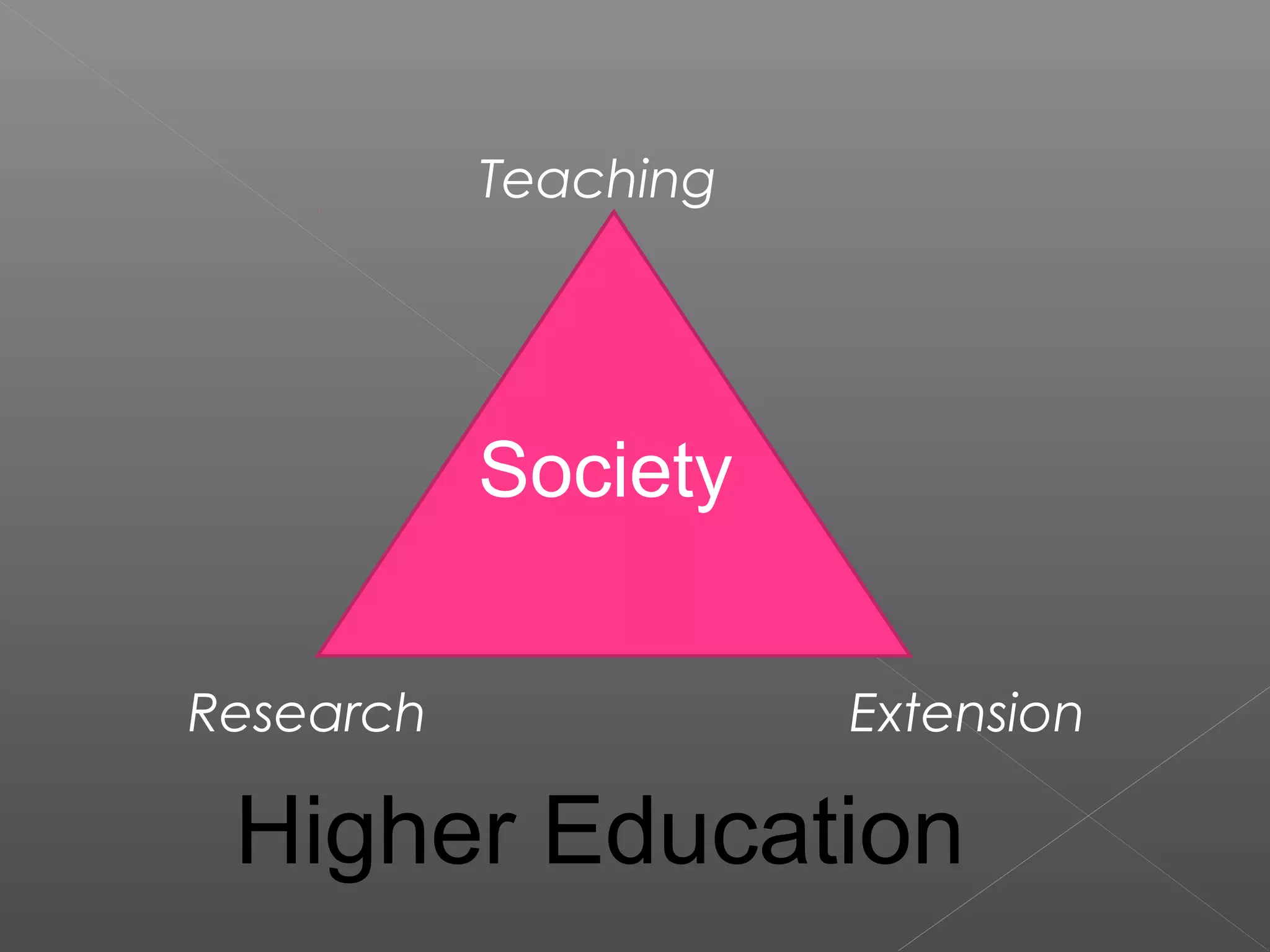
The document discusses higher education in India. It notes that while India has the third largest higher education system, it only provides access to 12% of the eligible age group. It emphasizes that the main purpose of universities should be to work for the benefit of society. Research, teaching, and extension are identified as the three key dimensions of higher education. Research and development are described as the backbone that brings transformation. However, no Indian university is ranked among the top 200 globally according to recent reports. The document advocates for improving research capacity in India through better infrastructure, funding, administrative support, and international collaboration.