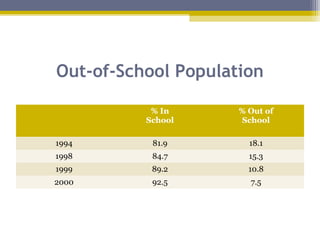
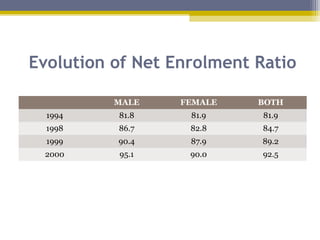
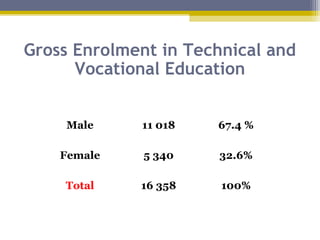
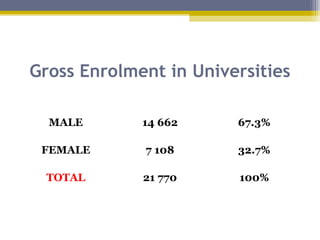
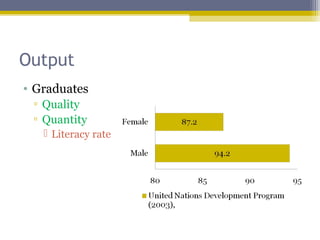
The document provides an overview of the educational system of Zimbabwe. It discusses the country's geography, population, government, and economy. It then examines the immediate and secondary environments influencing Zimbabwe's education, including government regulations, political and economic factors, social movements, technology, and culture. It provides details on inputs, processes, organization, programs, testing, and outputs of the educational system. In summary, the document analyzes the key components and influences shaping education in Zimbabwe at multiple levels.