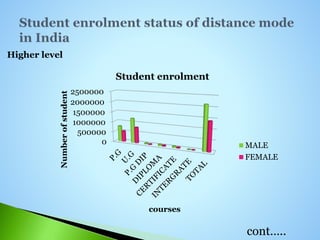
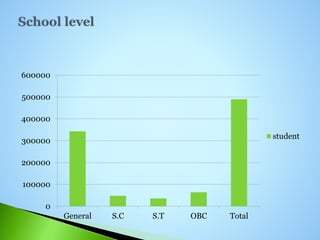
The document defines distance education as education where the learner and tutor are separated, there is influence from an educational organization, technical media is used to connect tutor and learner, two-way communication is provided, and occasional meetings are possible. It lists the major objectives of distance education as providing alternative education, reducing pressure on conventional universities, providing second chances, democratizing education, and providing continuing education. It also discusses the major causes of and statistics regarding distance education in India.