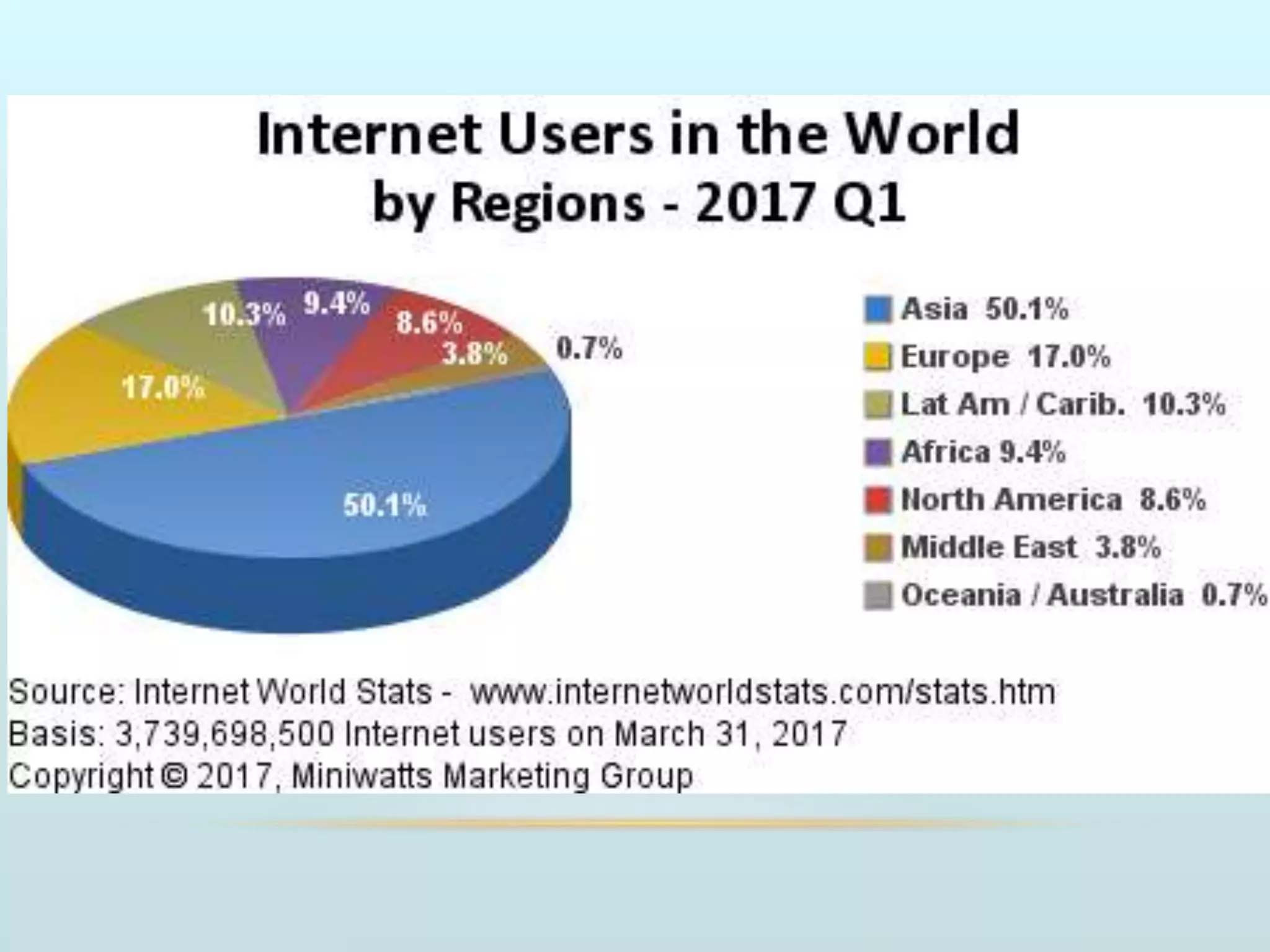
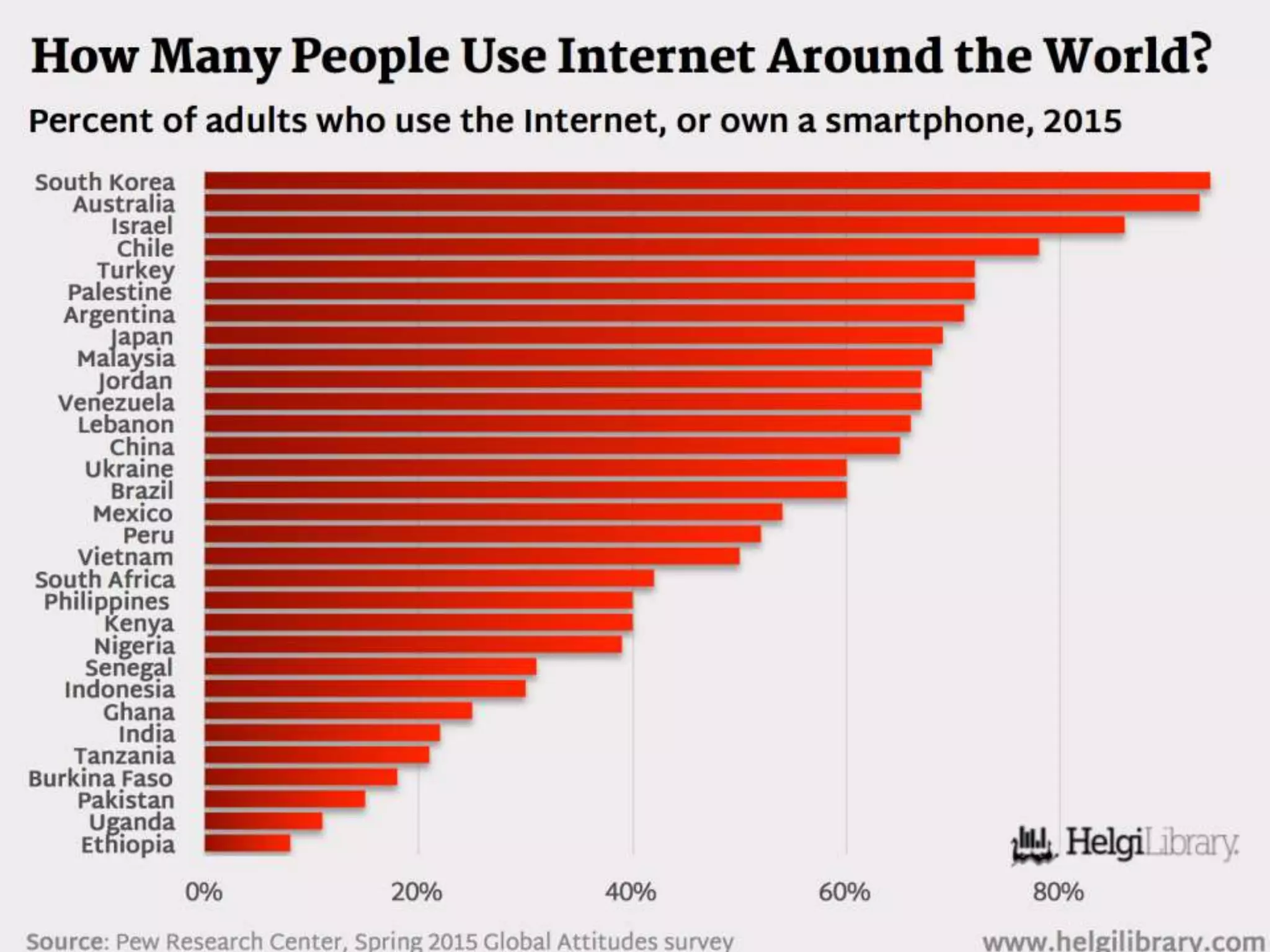
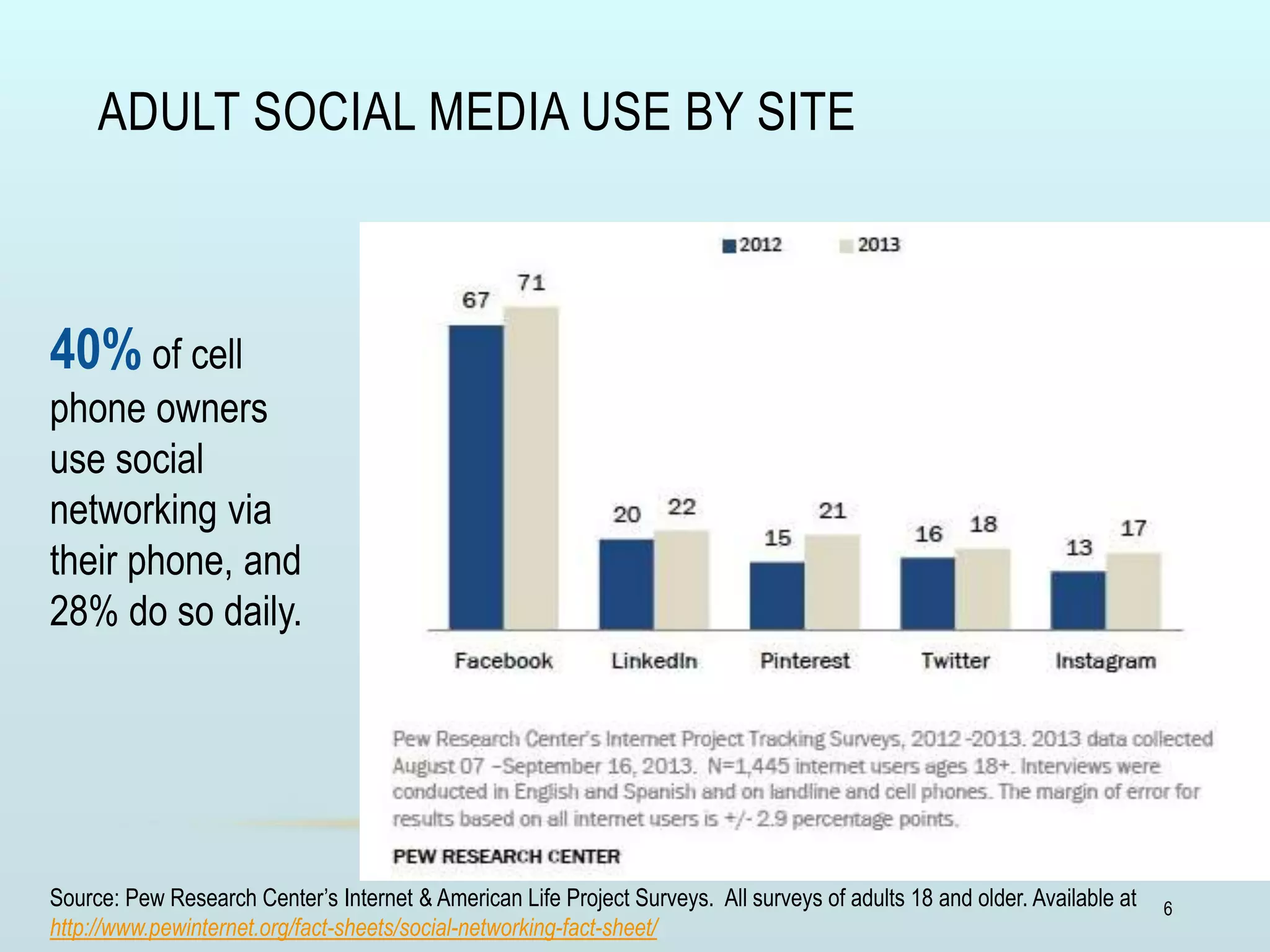
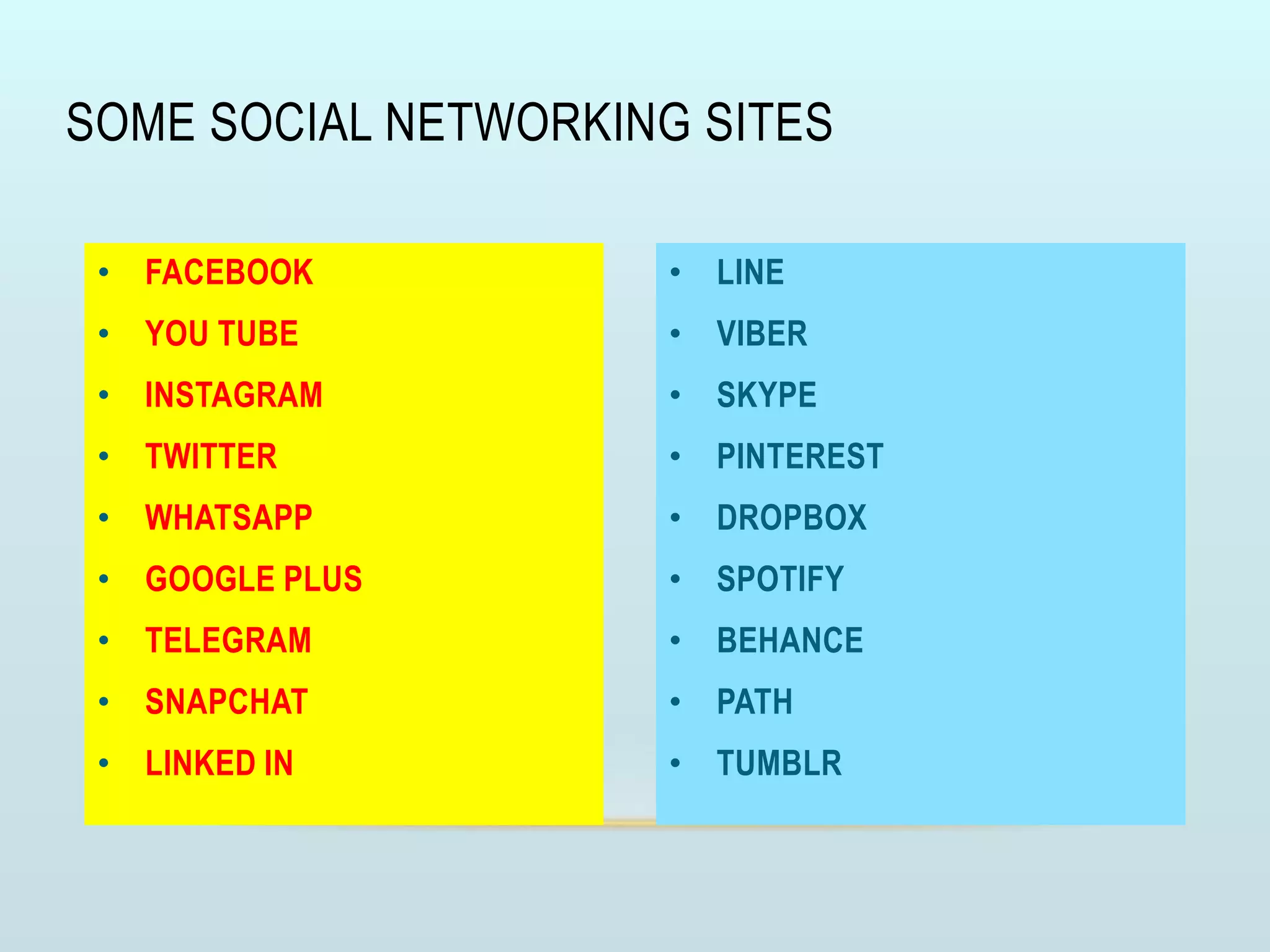
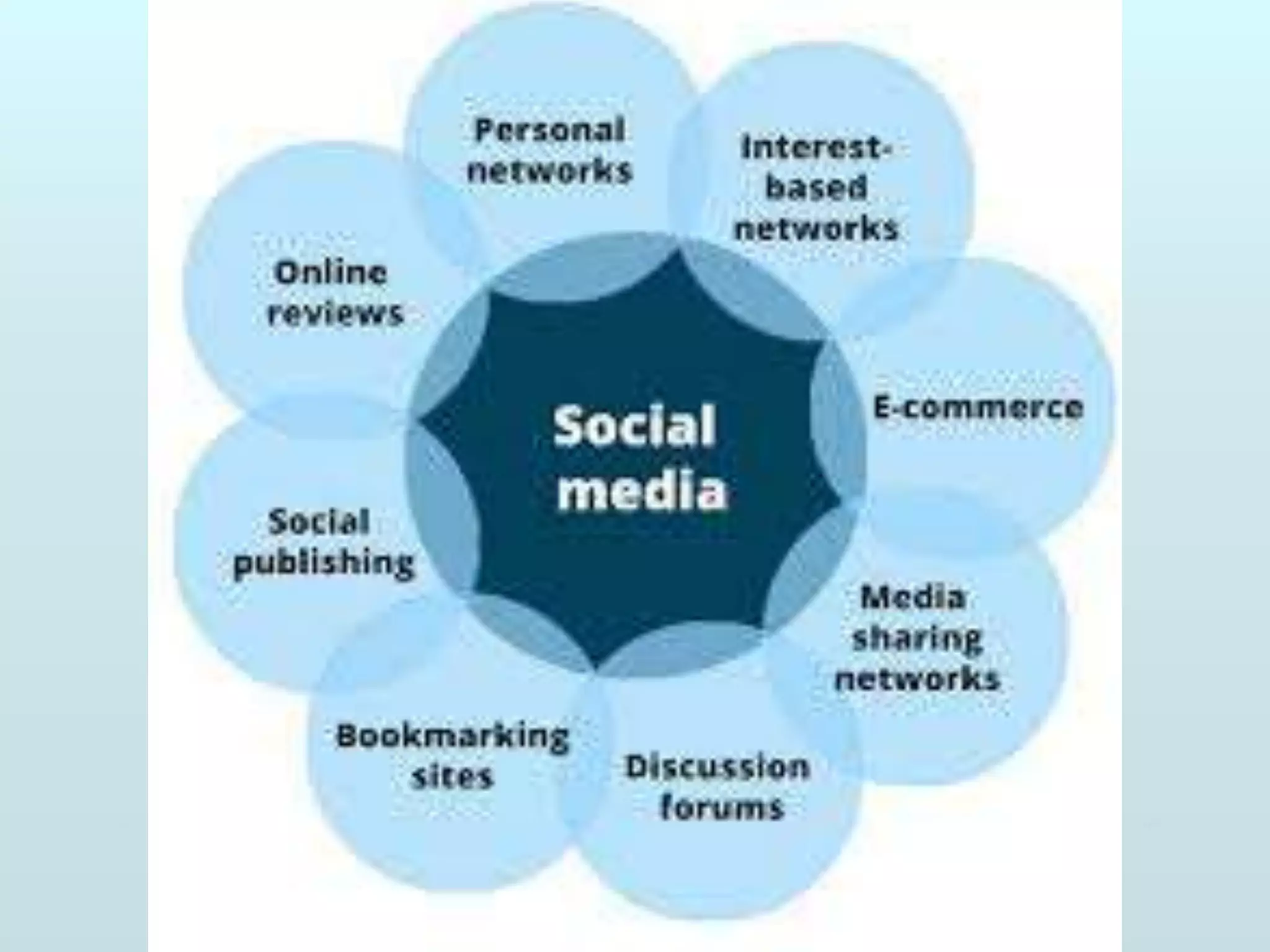
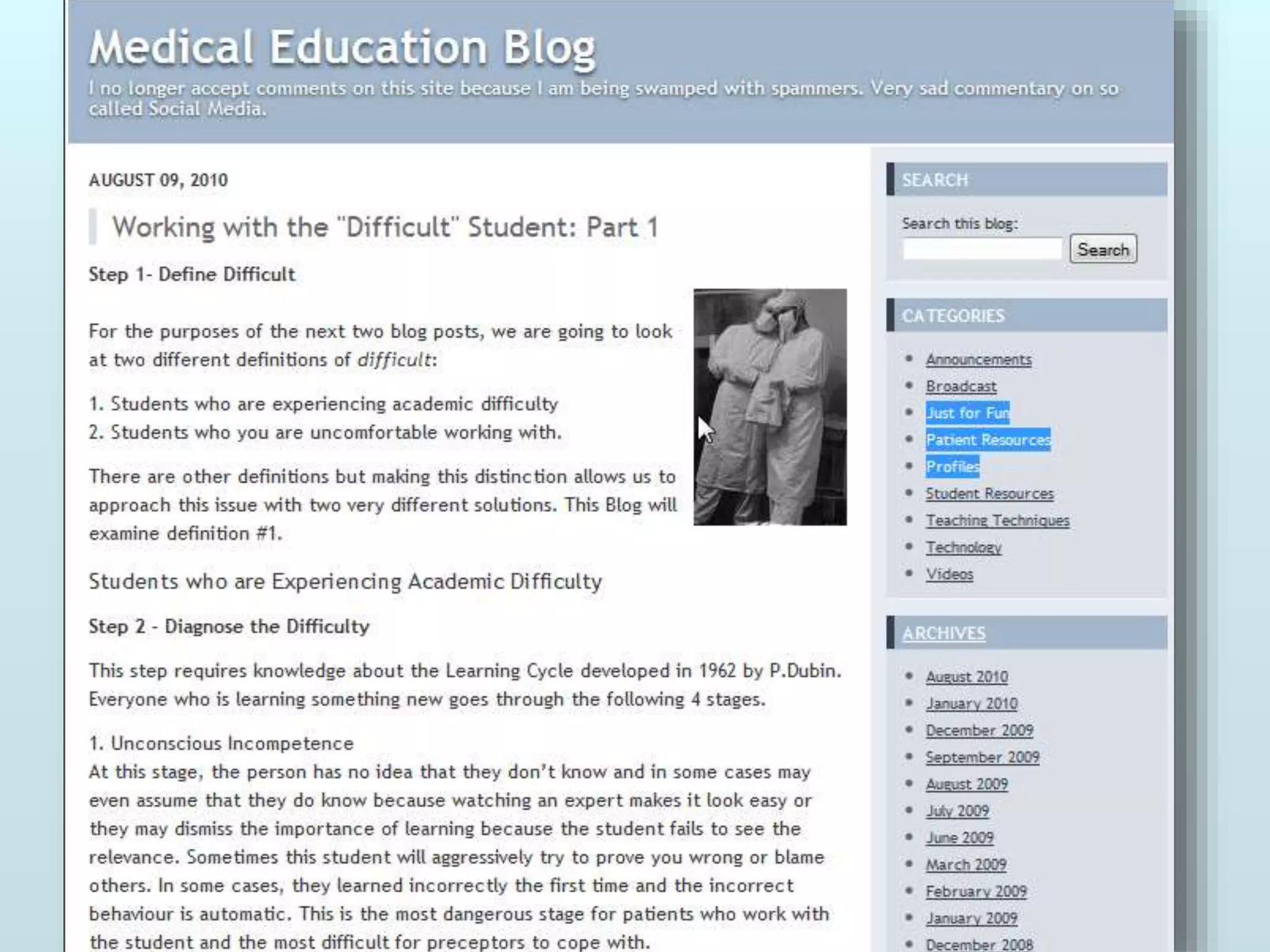
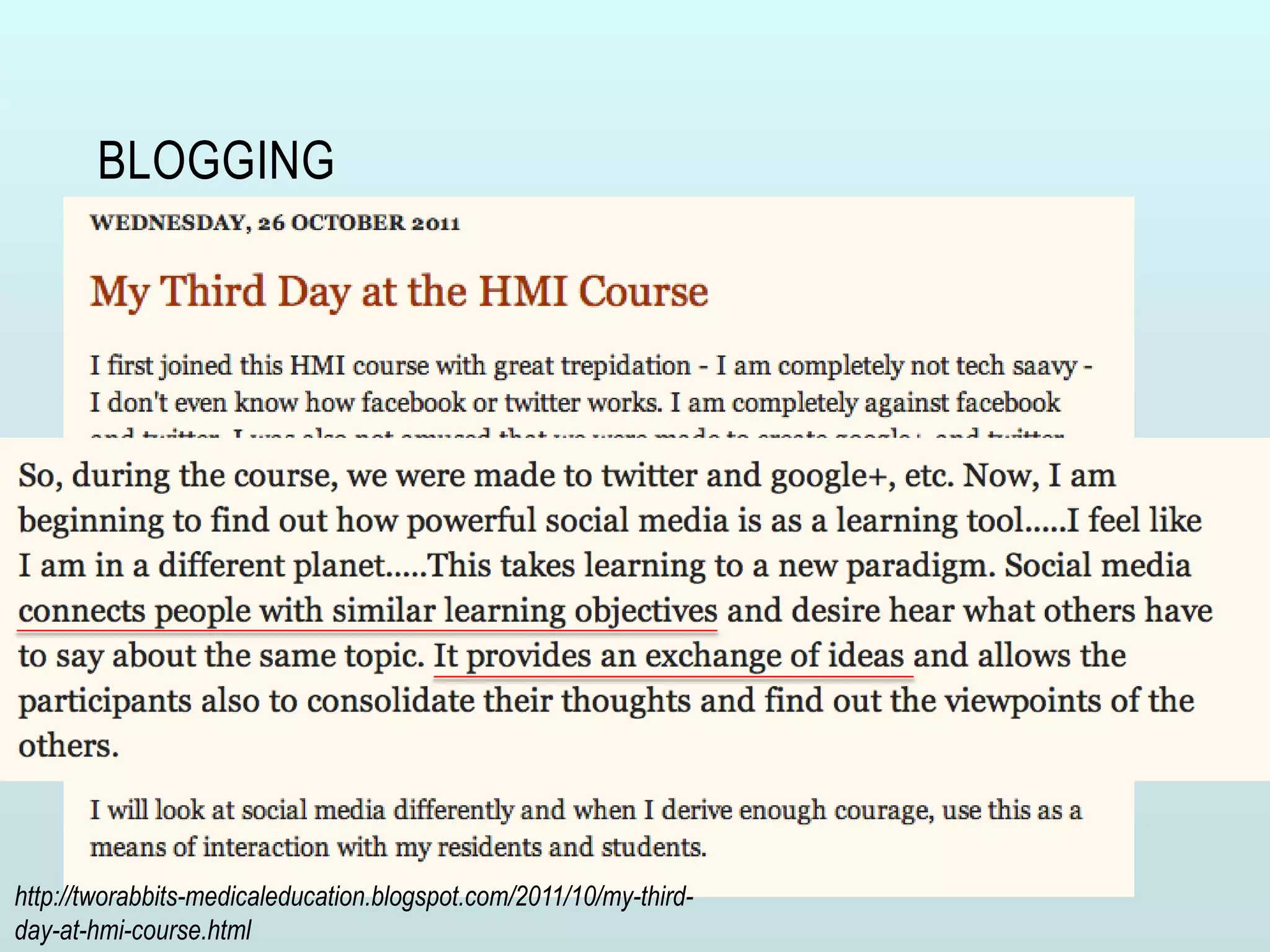
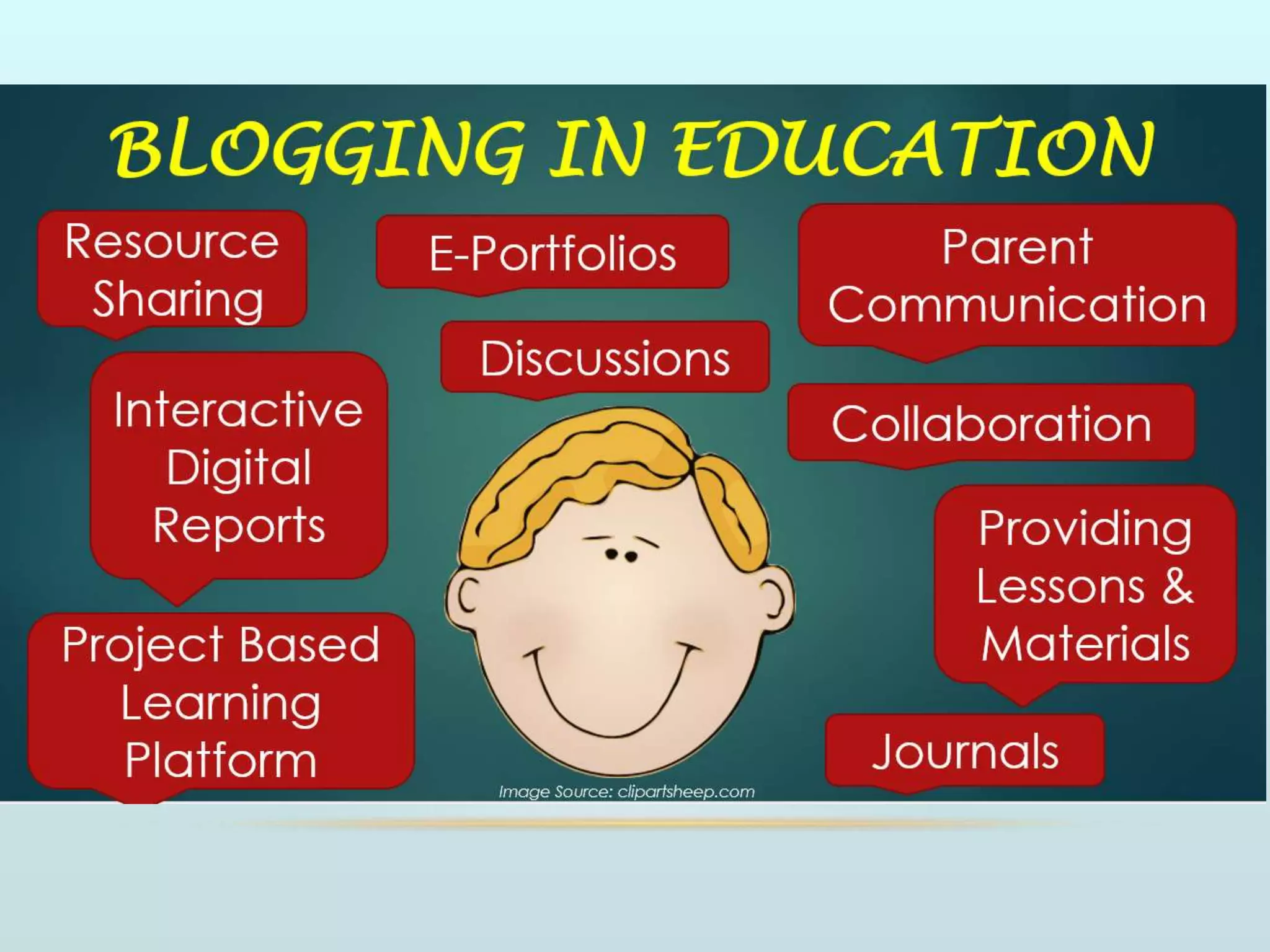
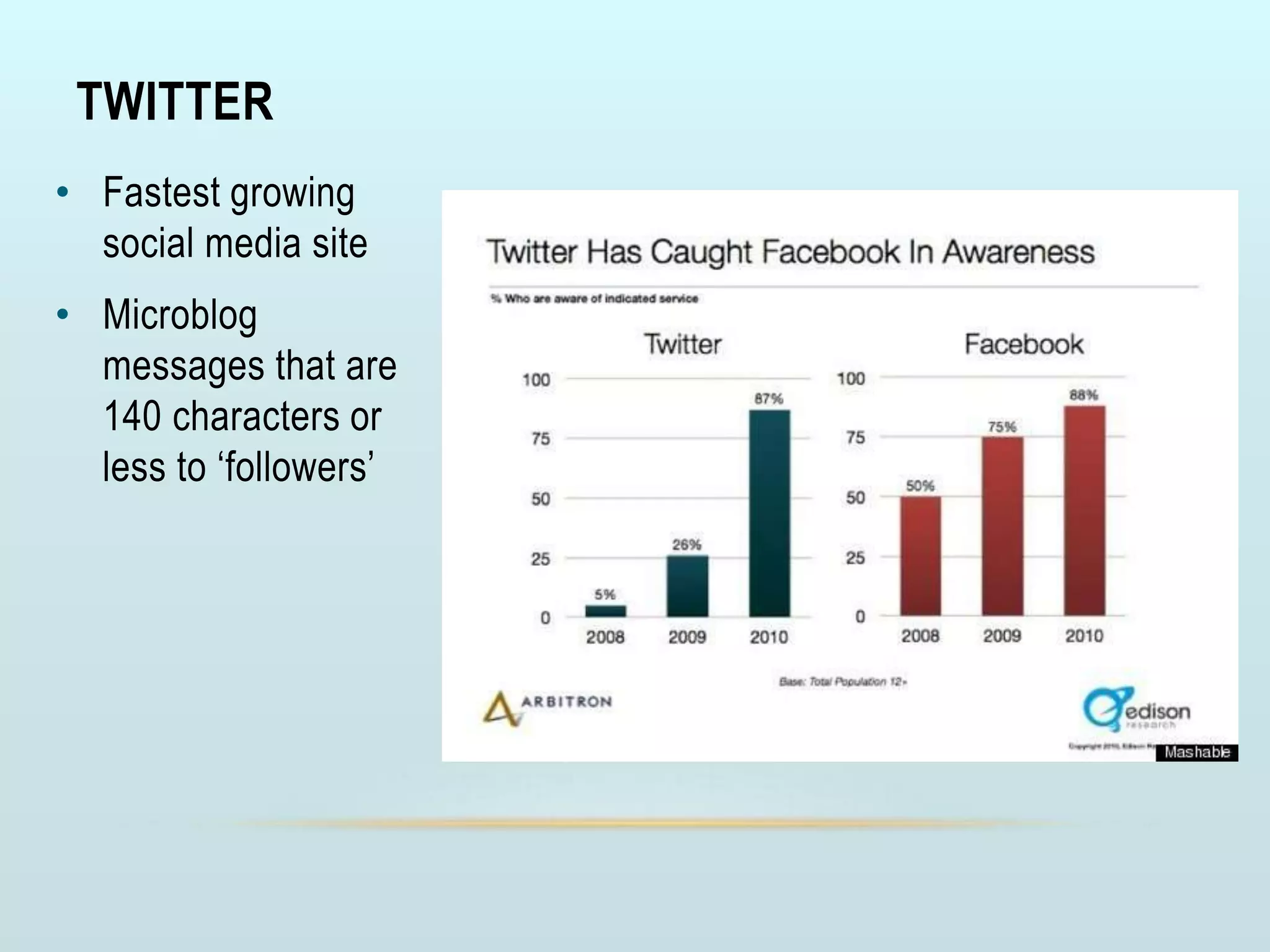
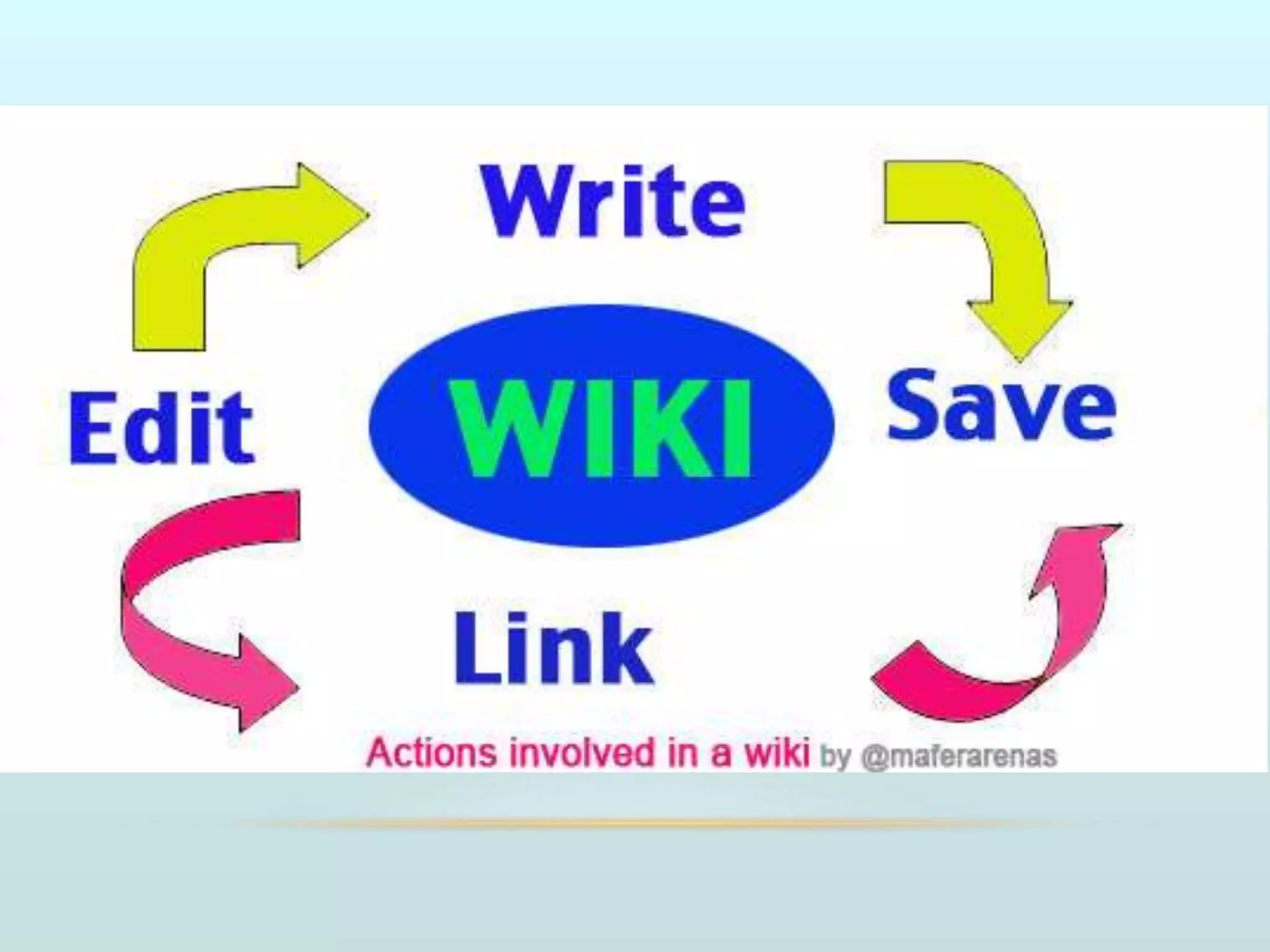
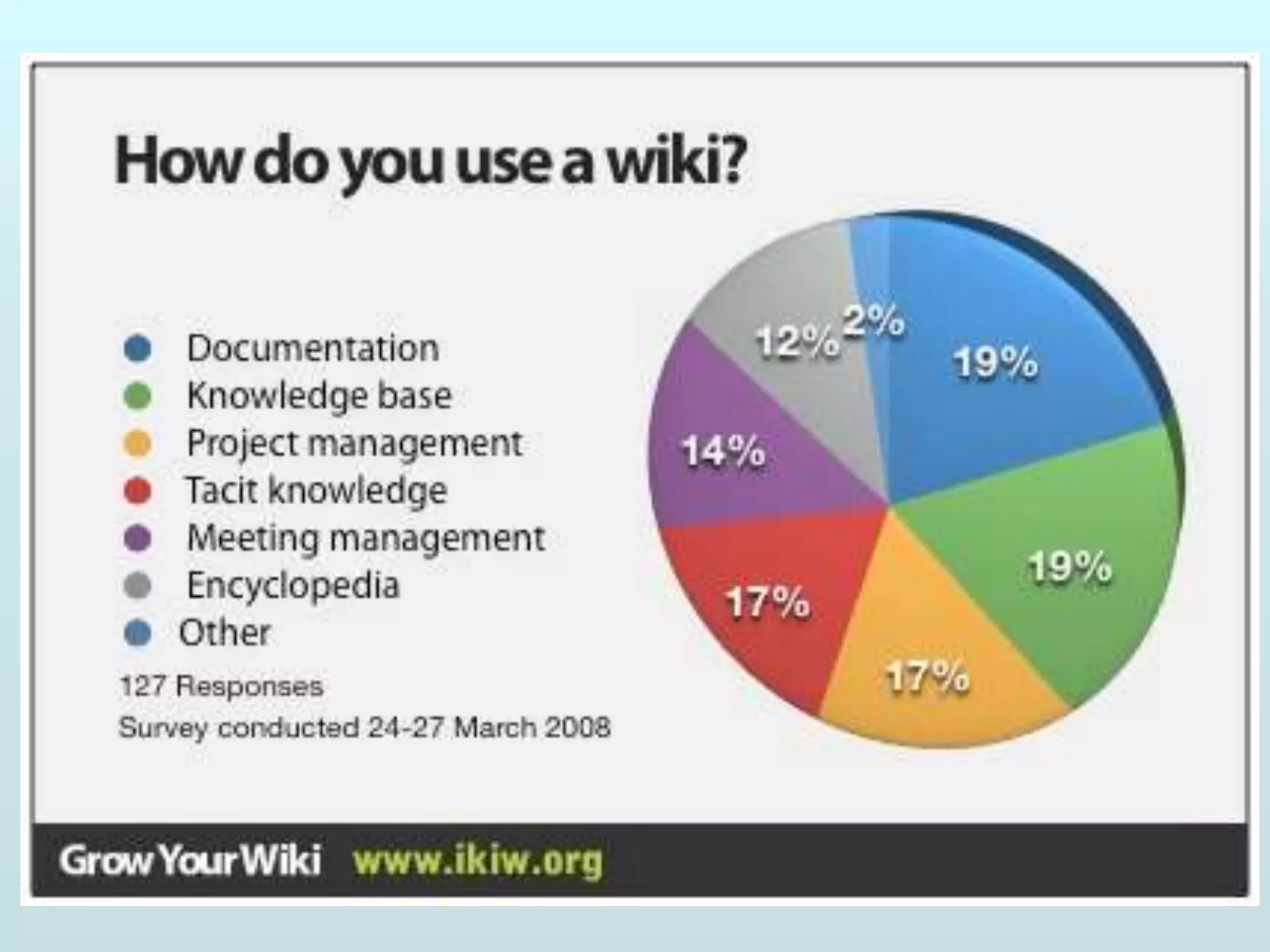
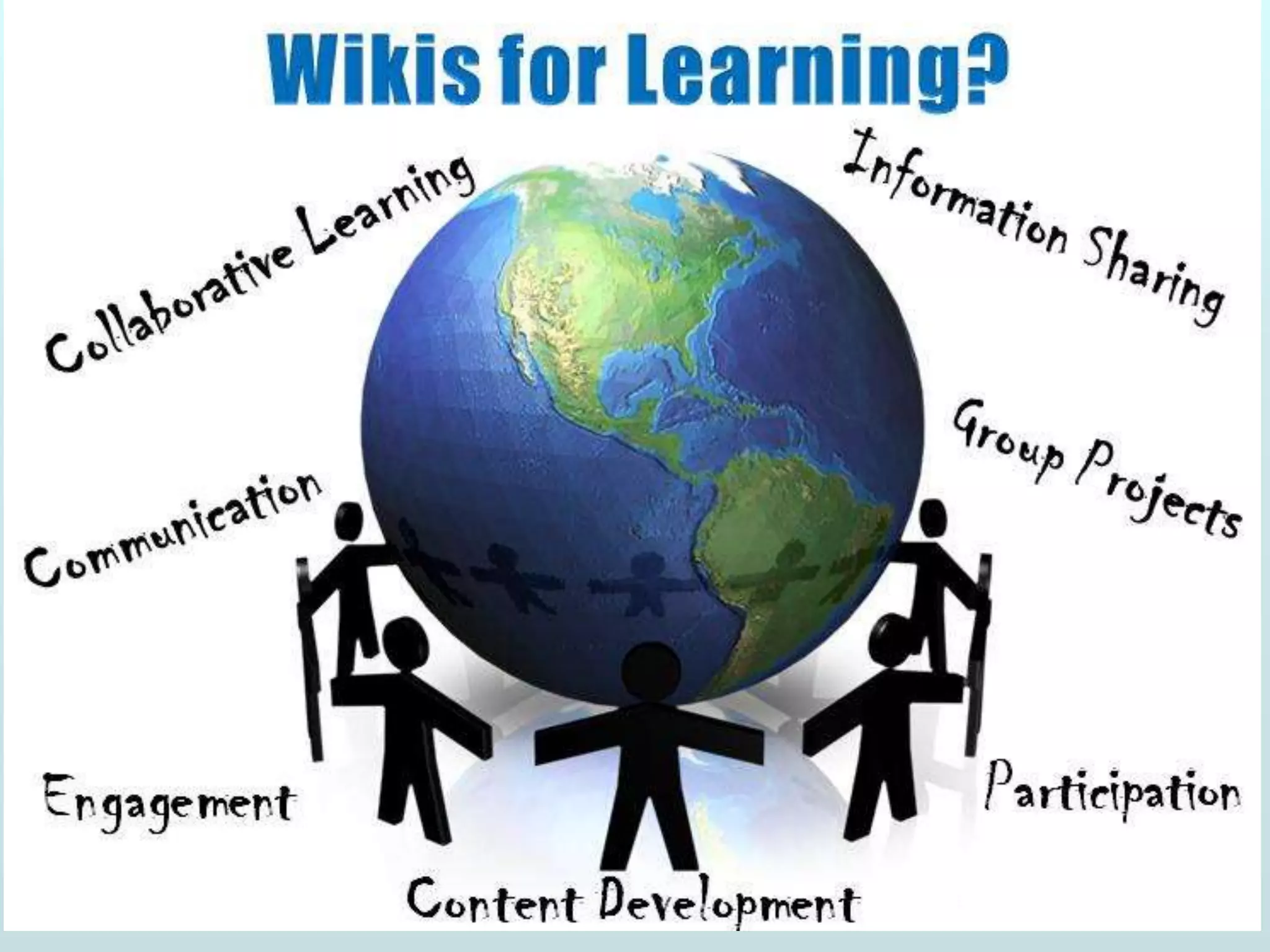
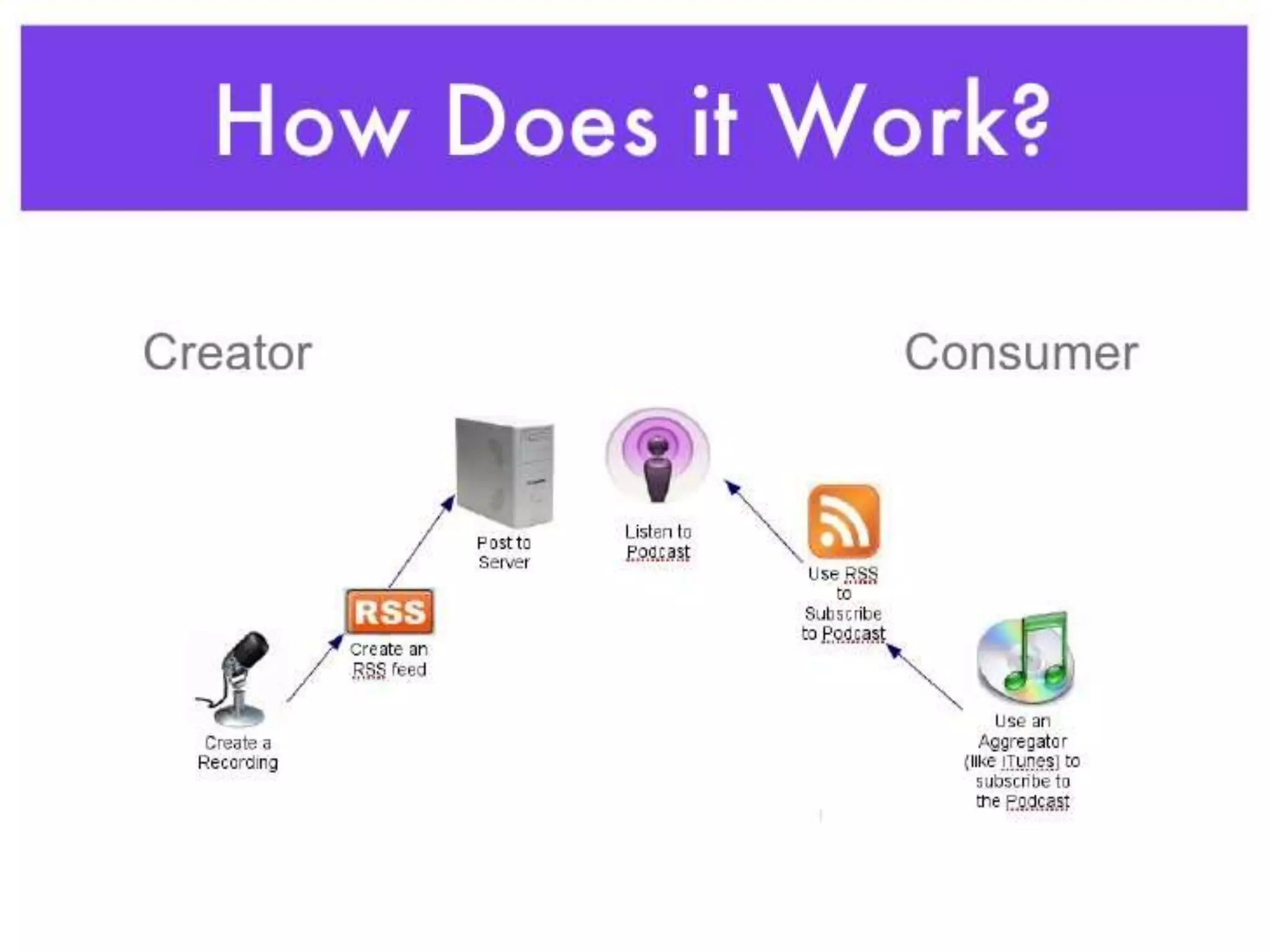
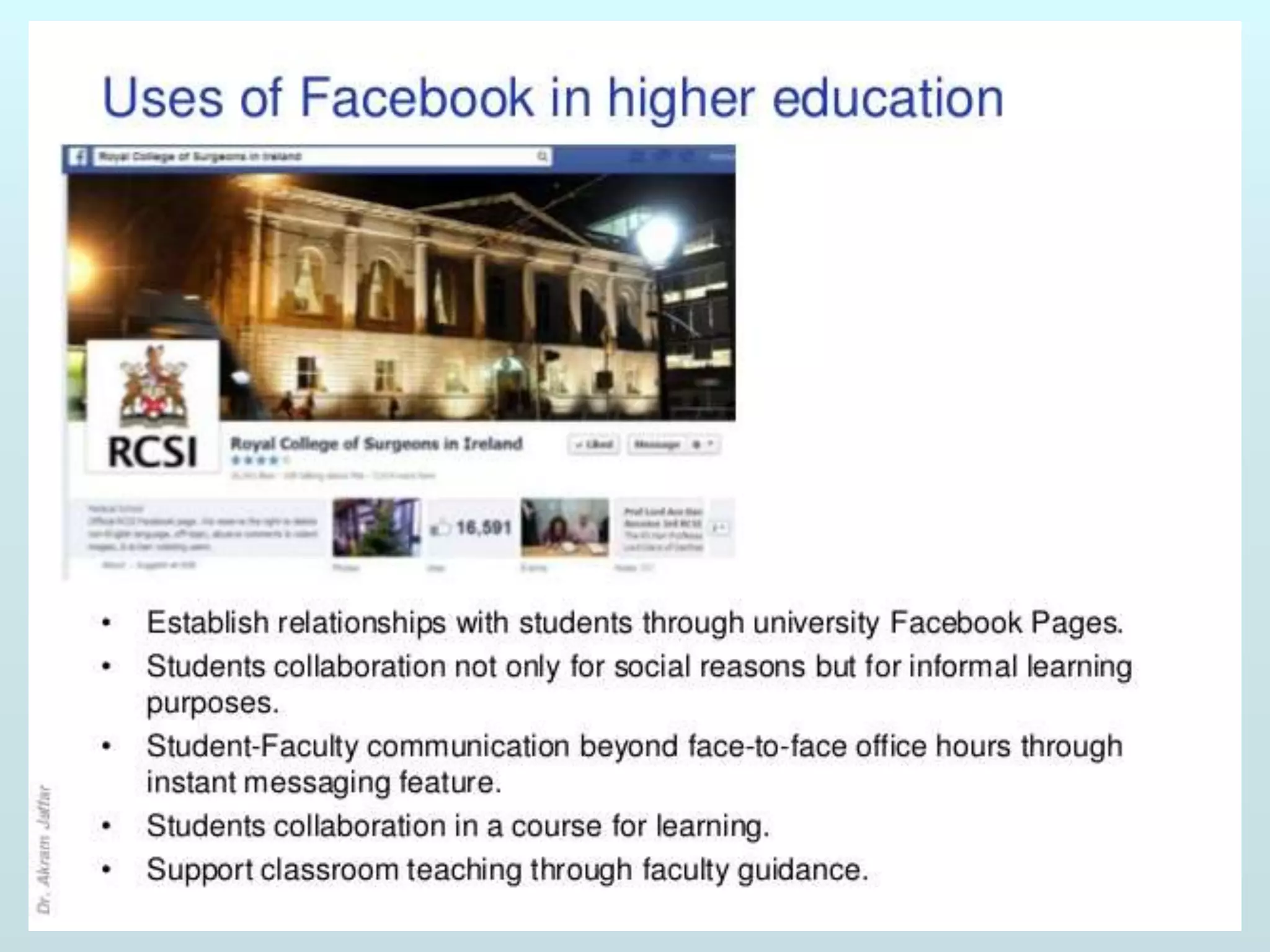
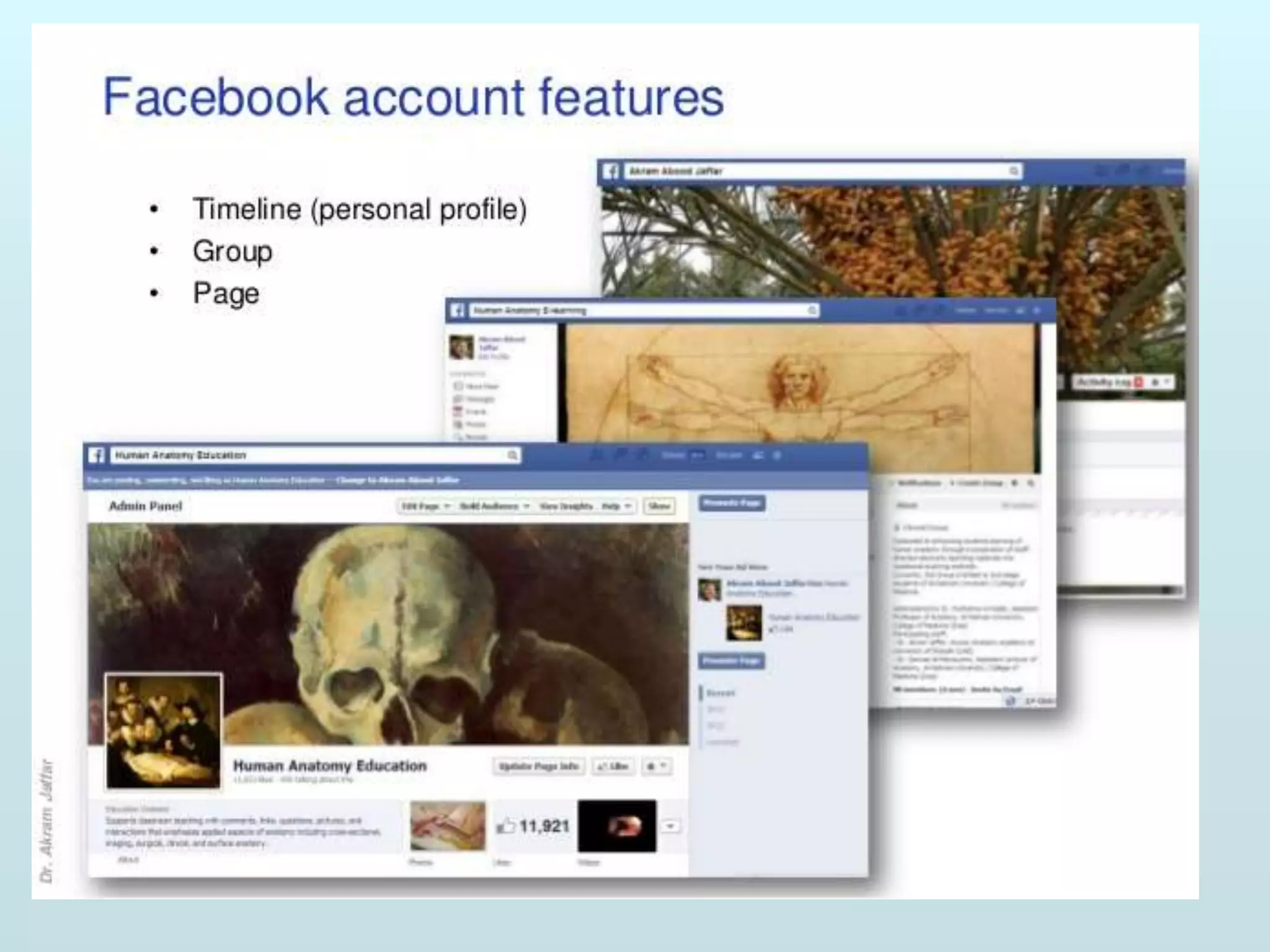
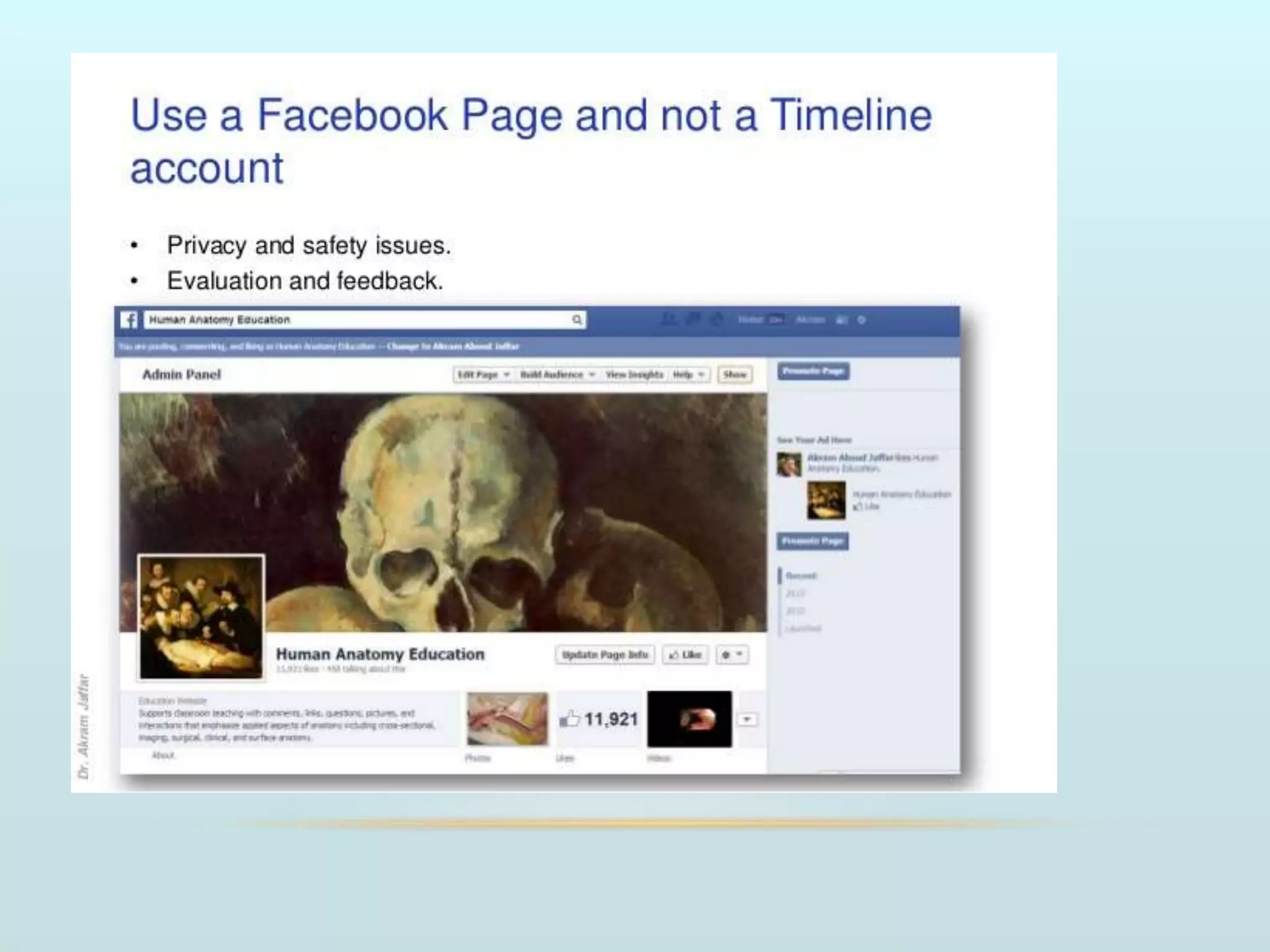
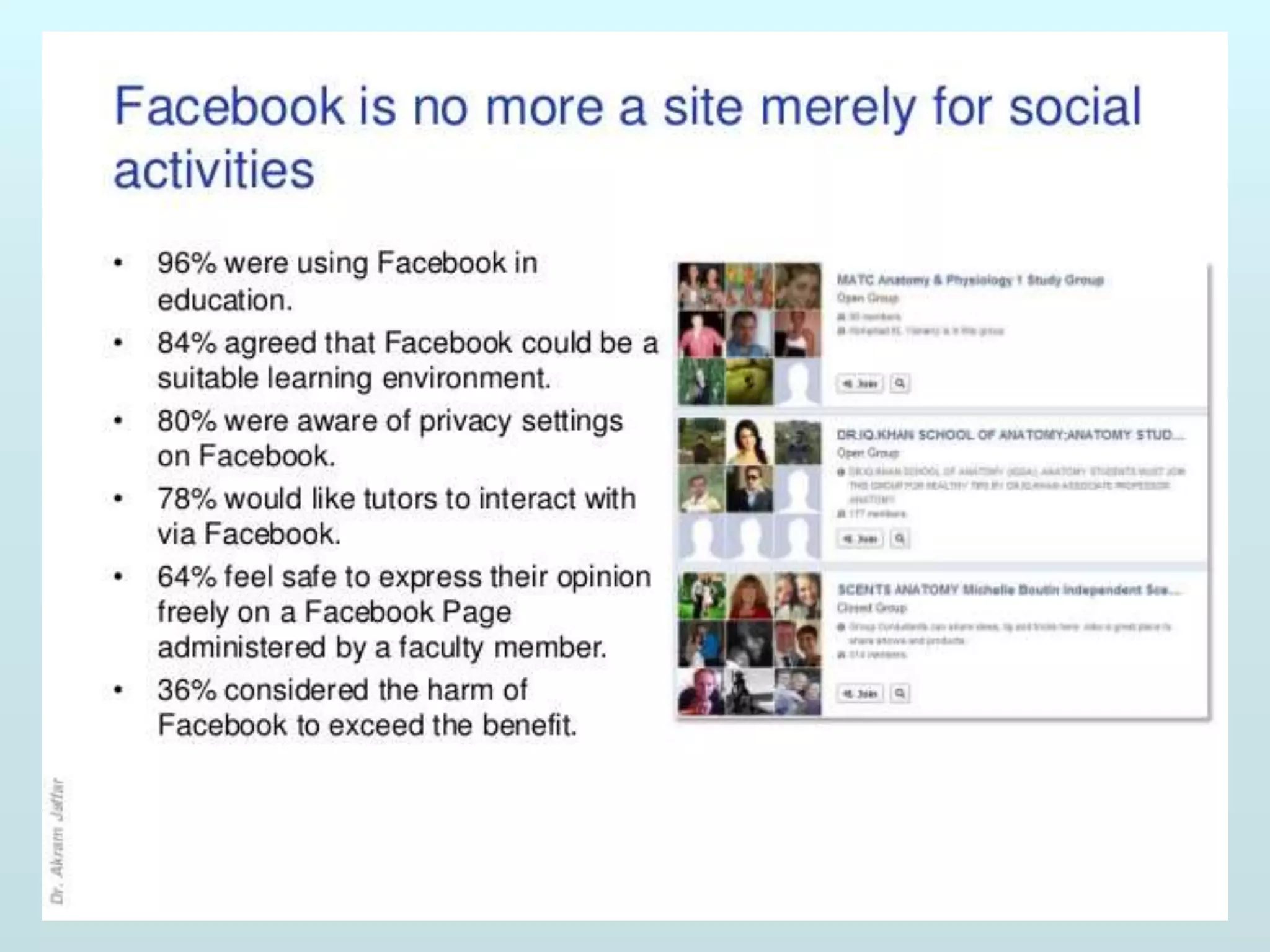
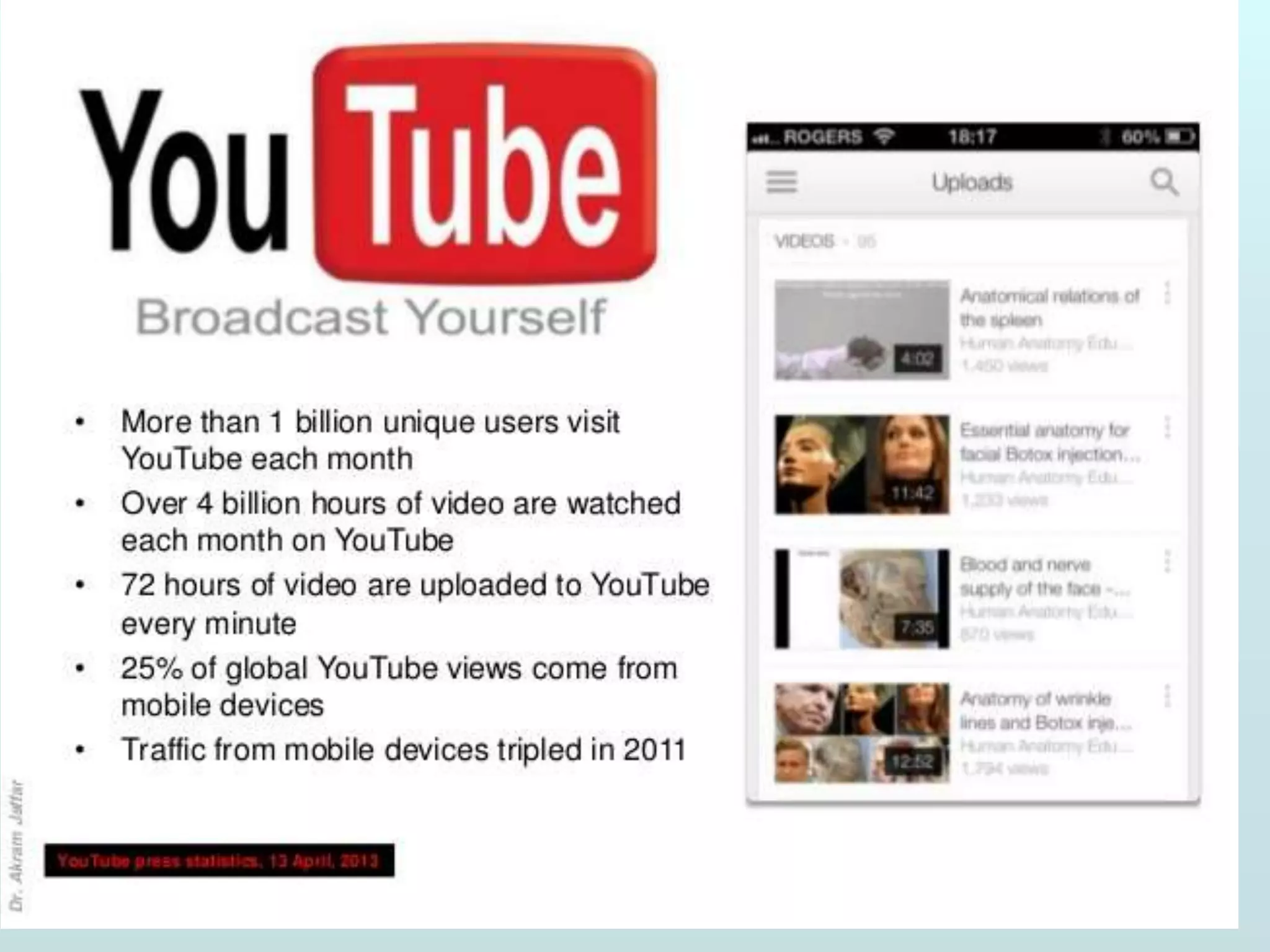
The document discusses the role of social media and educational networking in medical education, highlighting its importance for professional growth and engagement with students and patients. It outlines various platforms and tools available for educators, provides tips for effective use of social media, and emphasizes the need for responsible practices in networking. It also considers avenues for growth in medical education and encourages the use of technology to enhance teaching and learning.