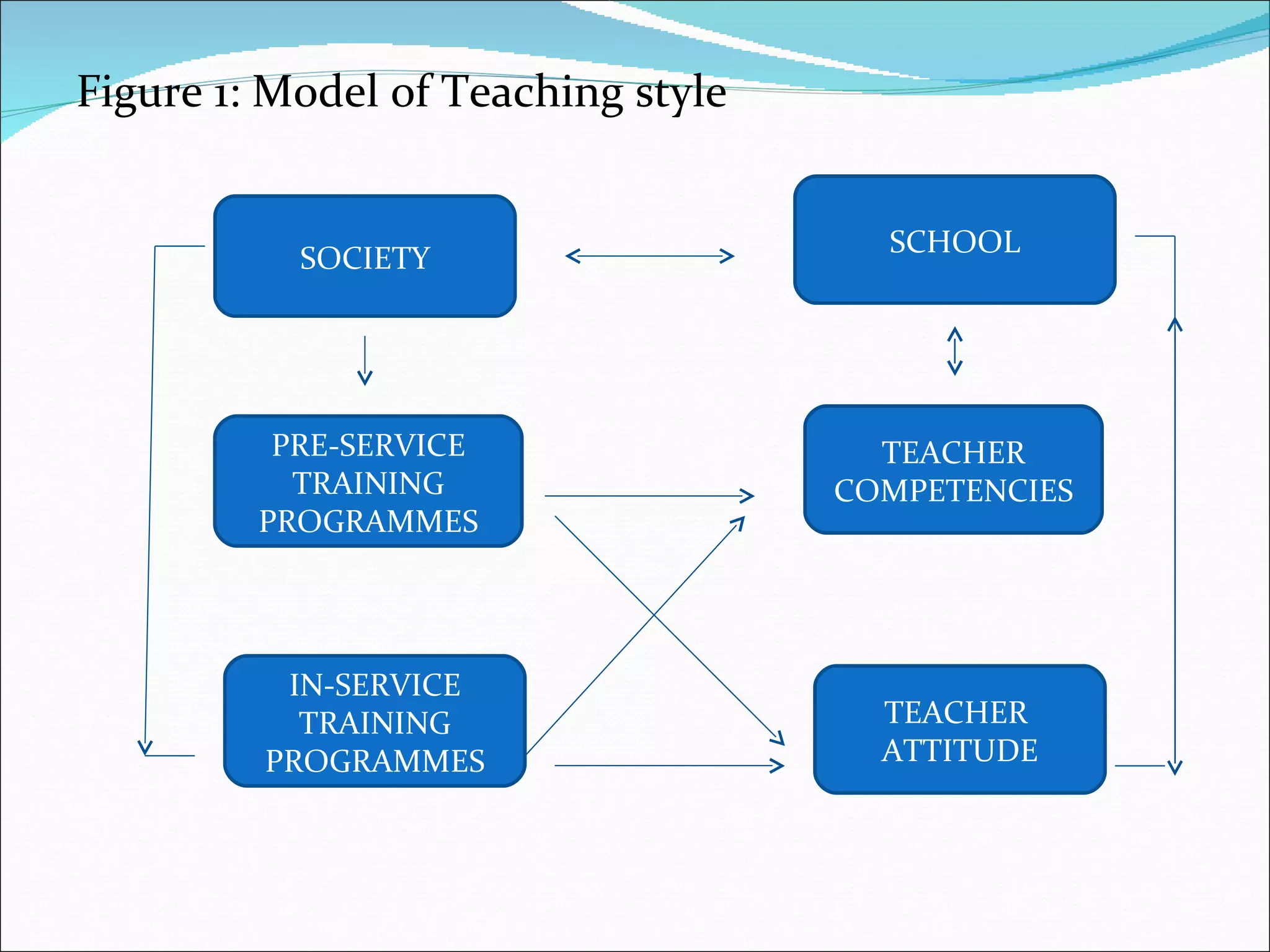
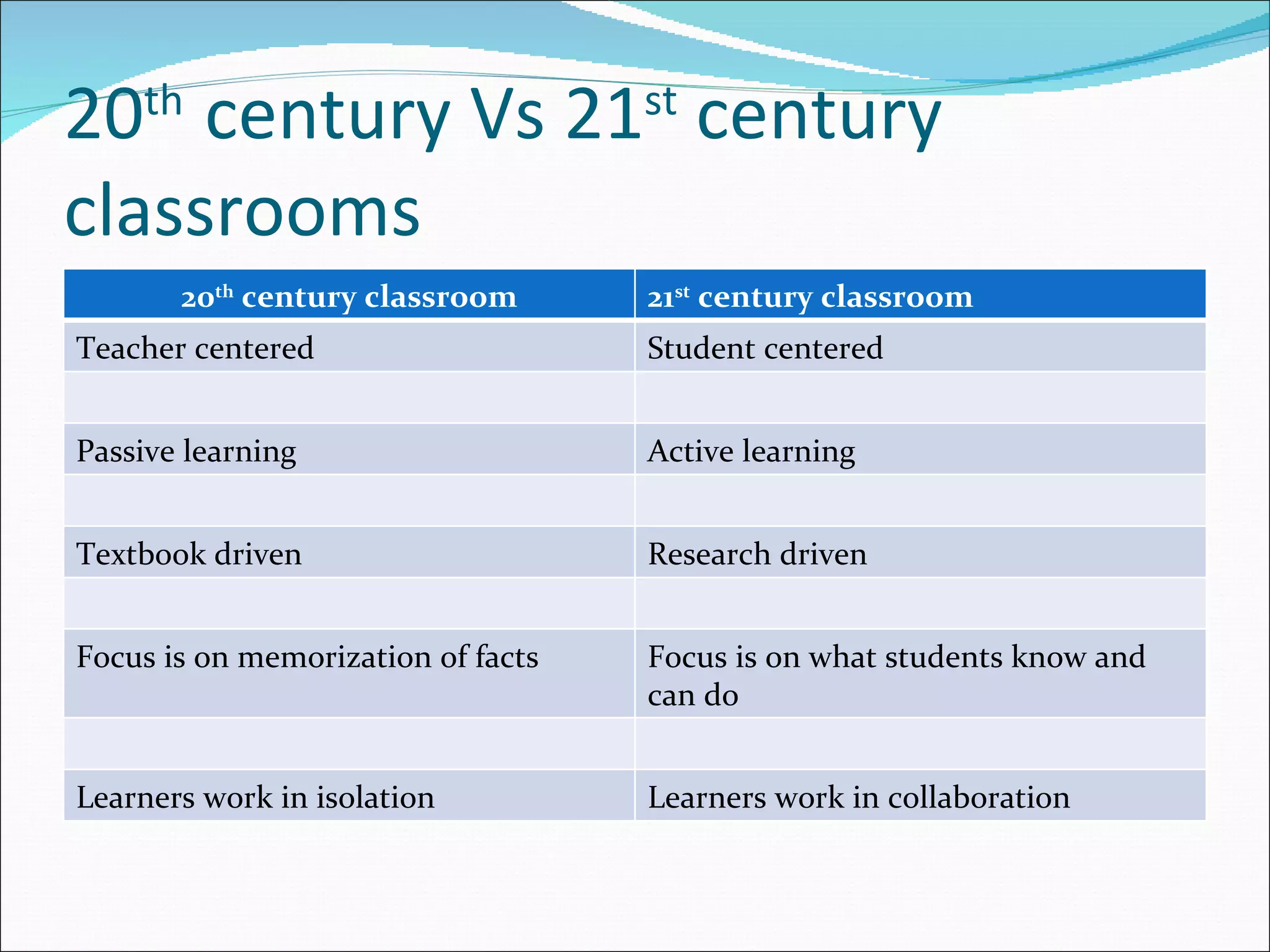
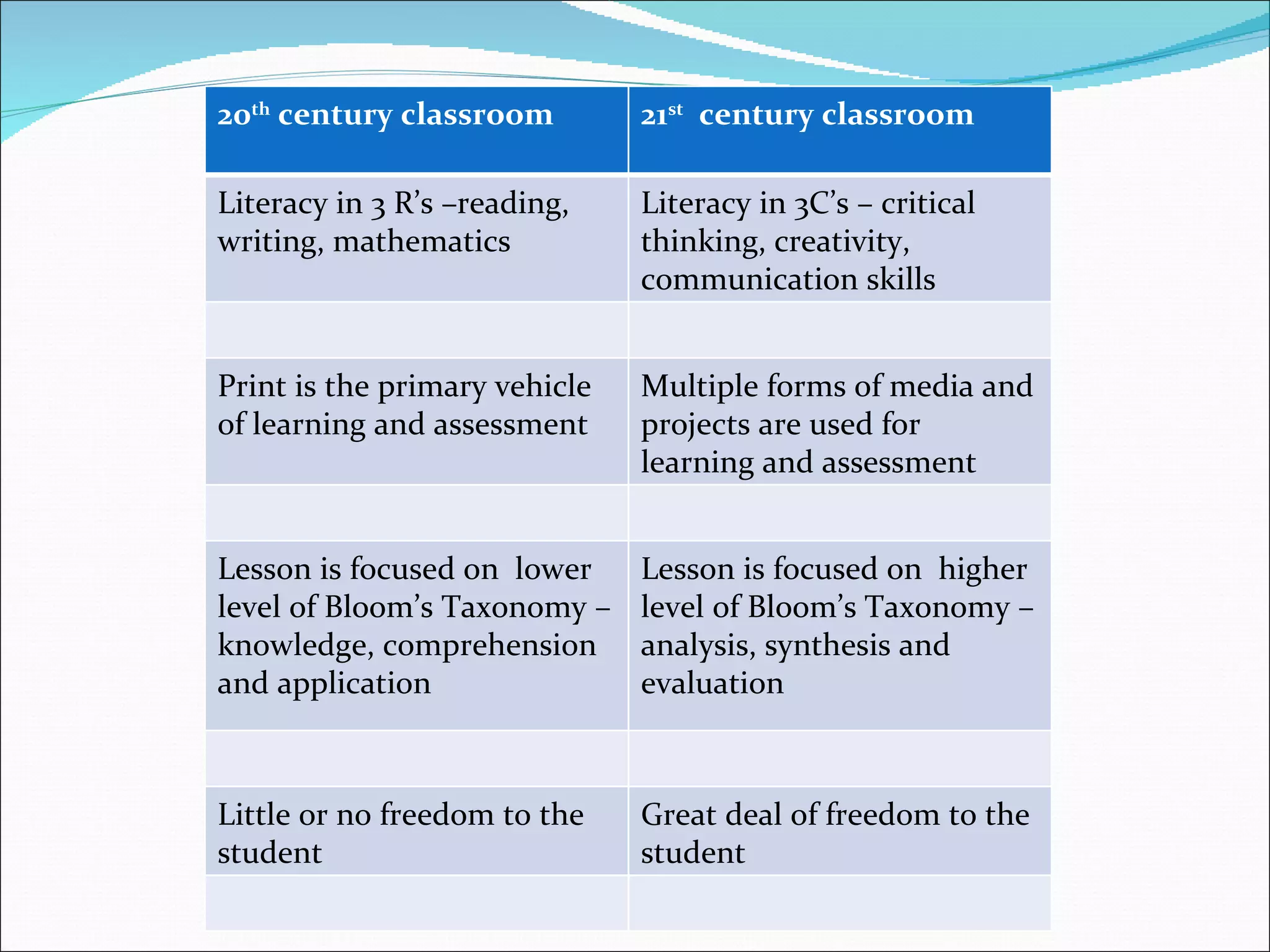
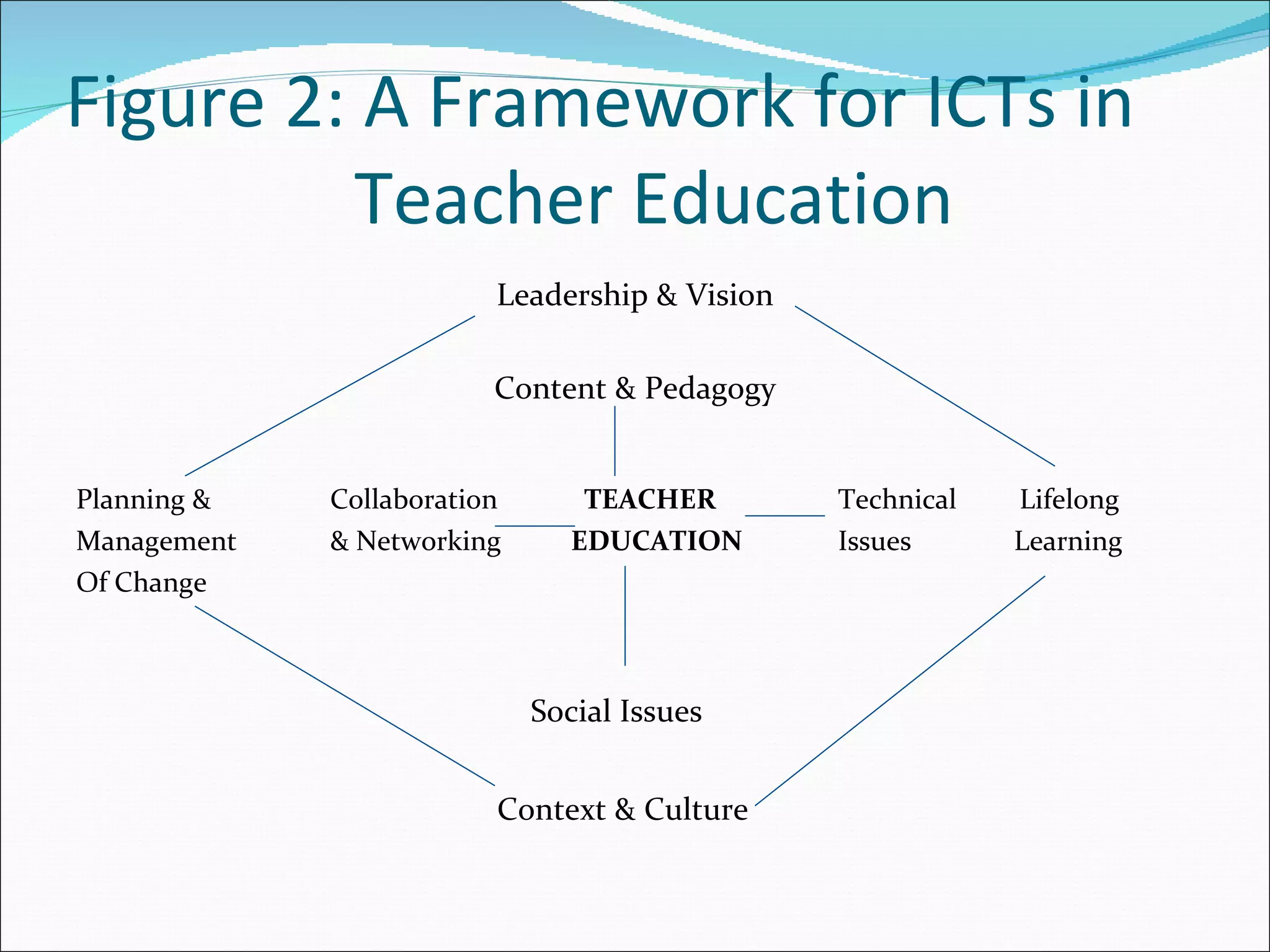
The document discusses the need to integrate information and communication technologies (ICT) into teaching and learning to prepare students for the 21st century. It outlines the skills needed for students to succeed such as knowledge, life skills, media literacy, self-management, and metacognition. New theories of learning focus on students as active learners seeking knowledge within meaningful contexts. Effective ICT integration requires developing teachers' competencies in areas like pedagogy, collaboration, social issues, and technical skills. Barriers to ICT integration include lack of funding, motivation, confidence, and computer literacy. Recommendations include providing digital technologies and internet access in classrooms and schools and ensuring teachers have the skills to use new tools to help students achieve