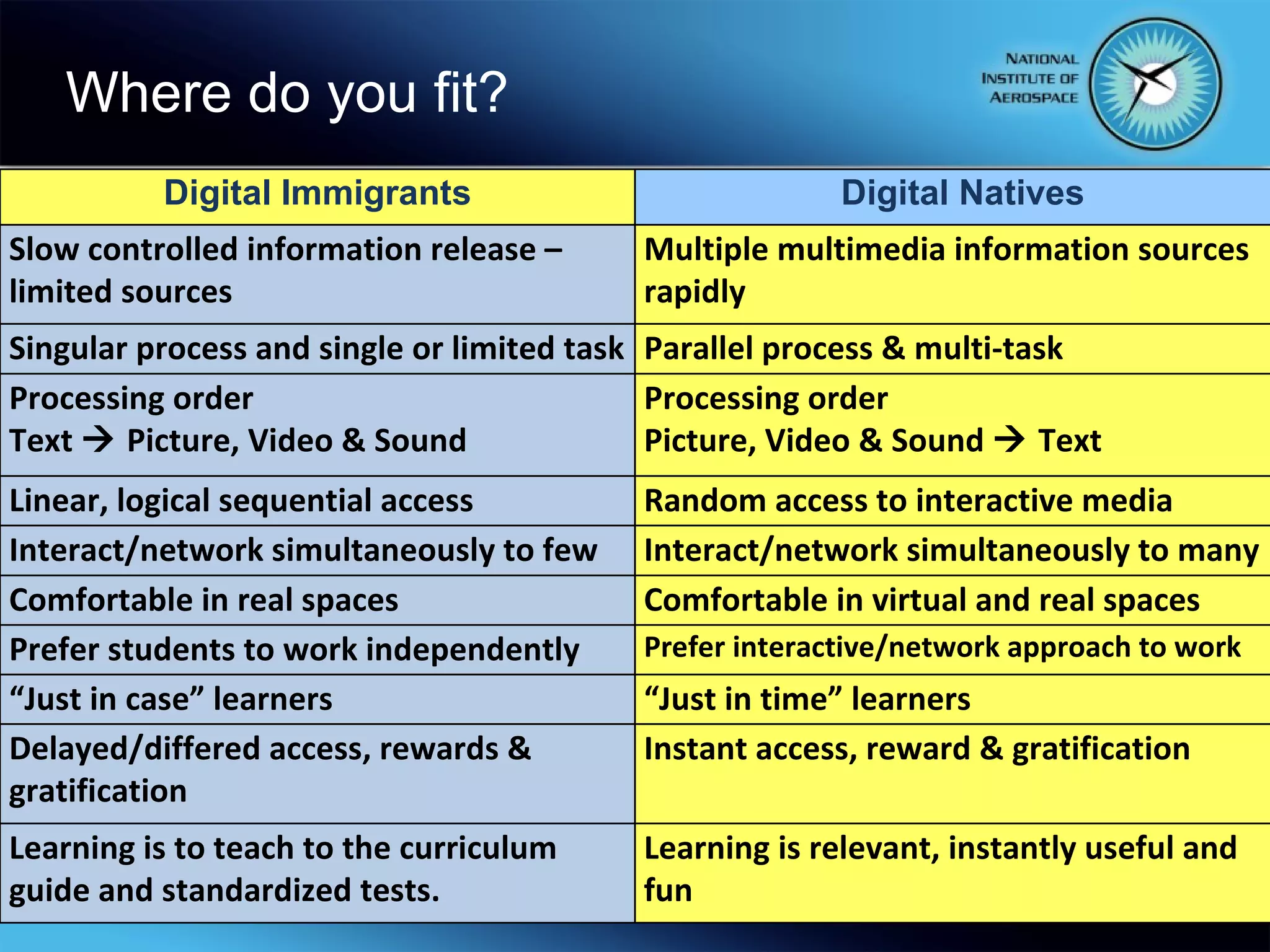
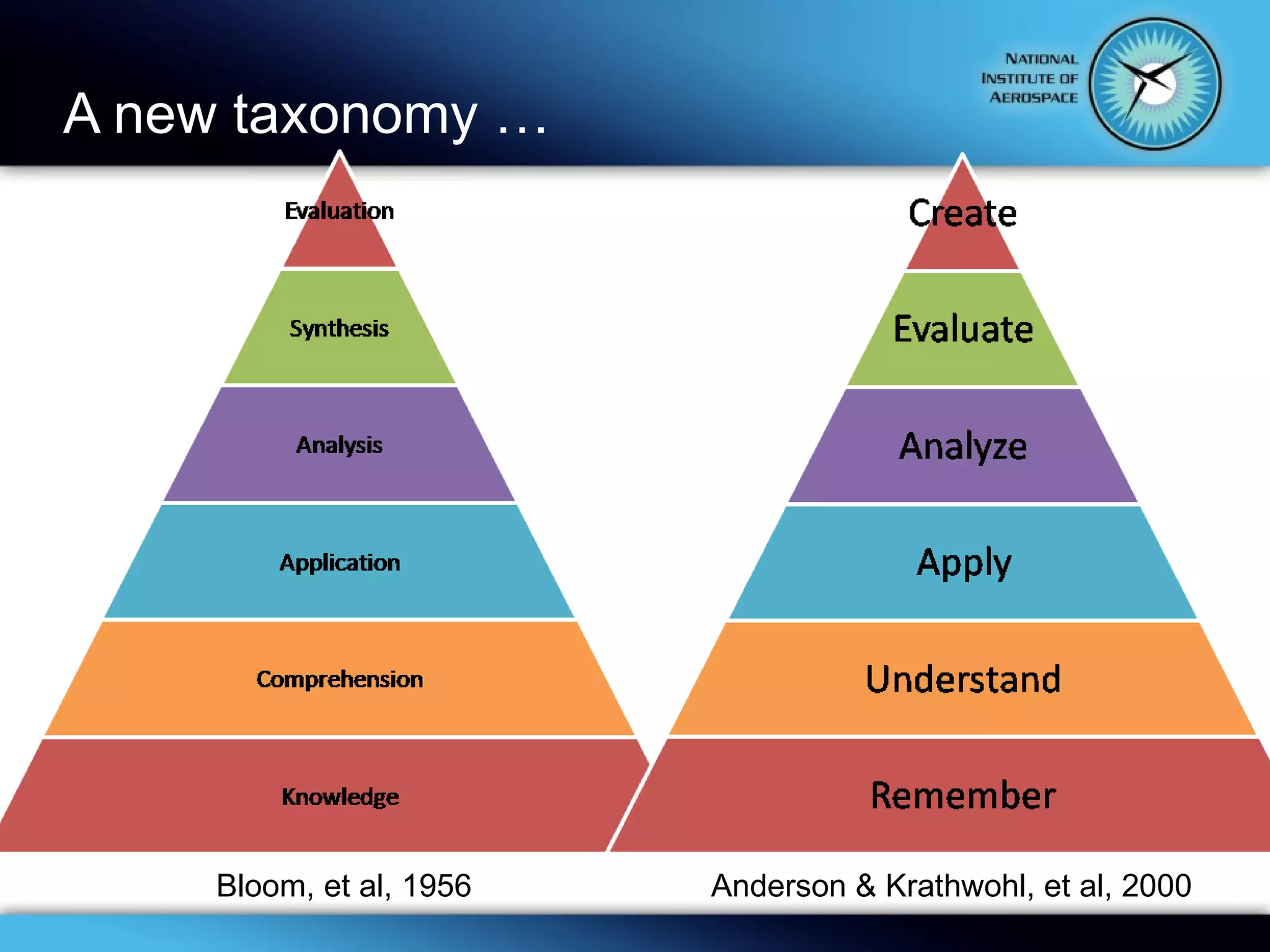
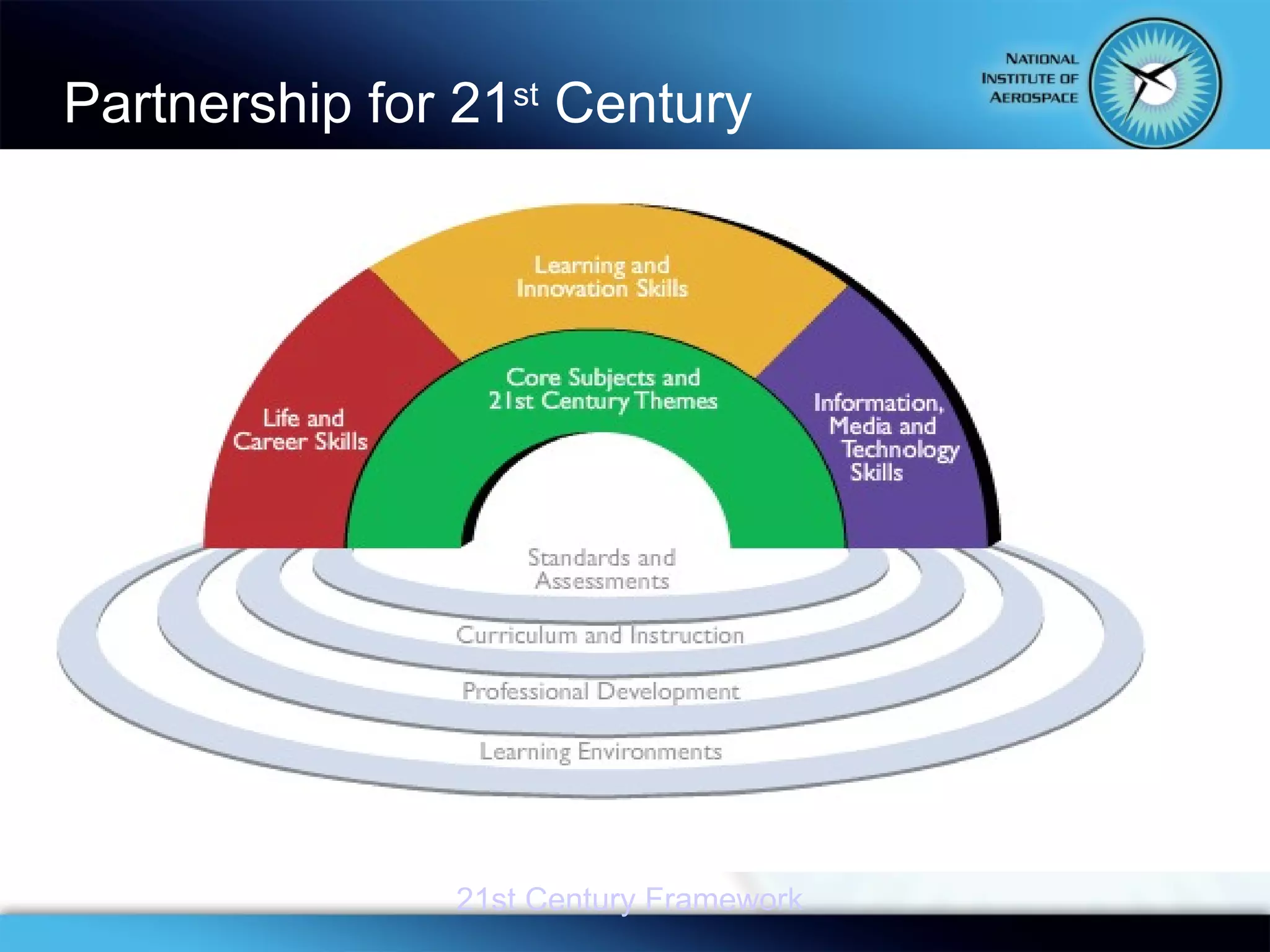
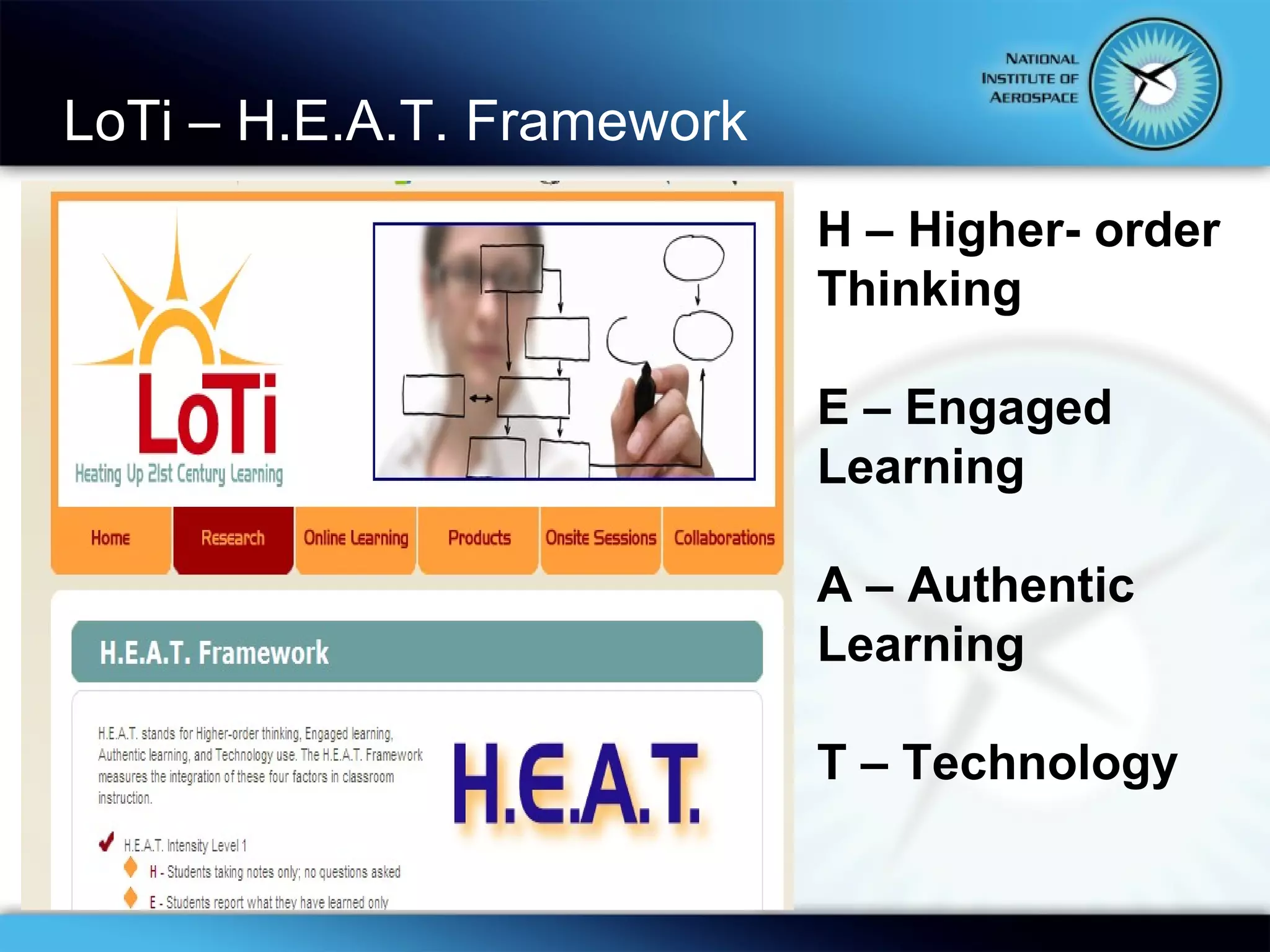
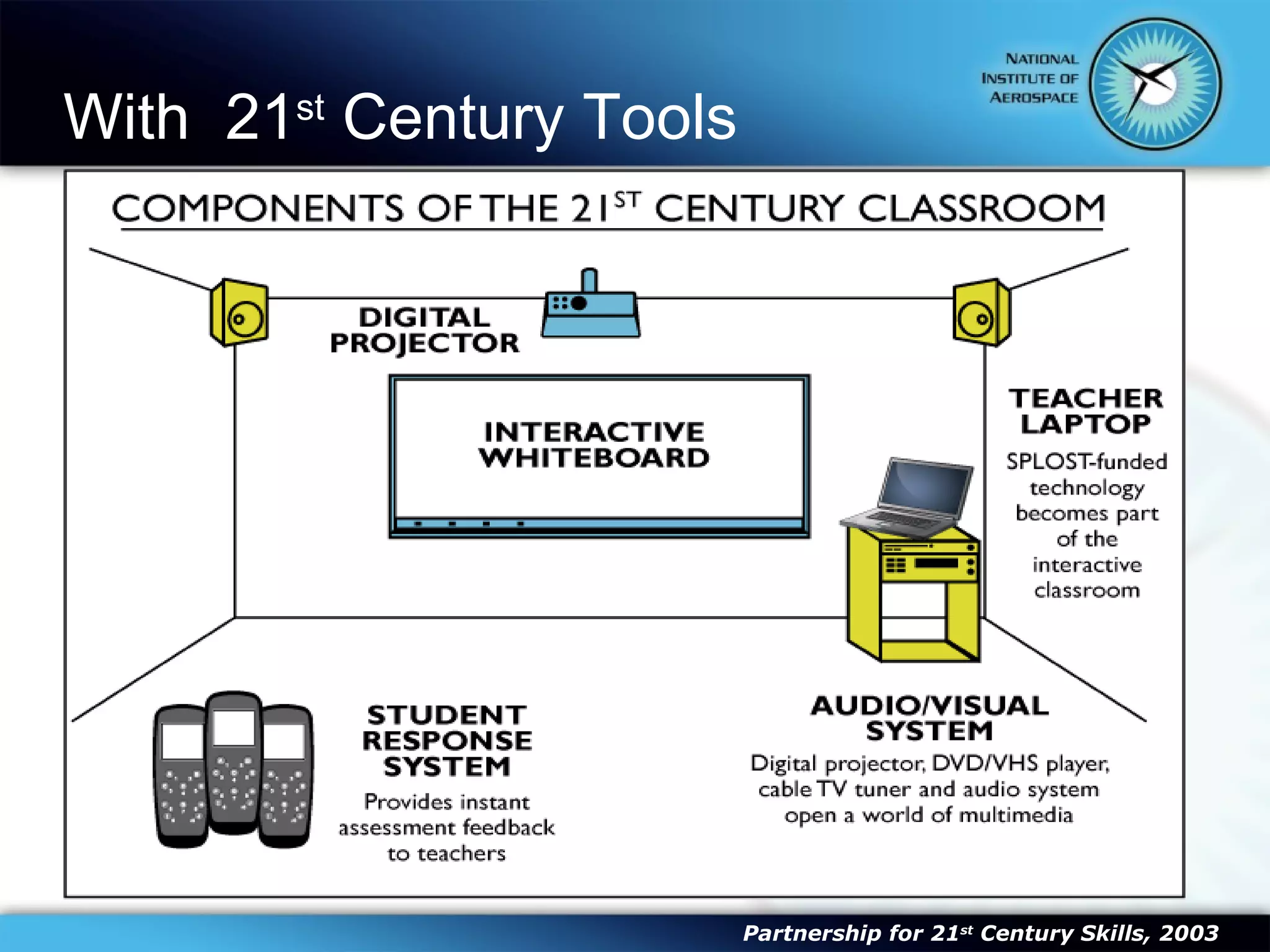
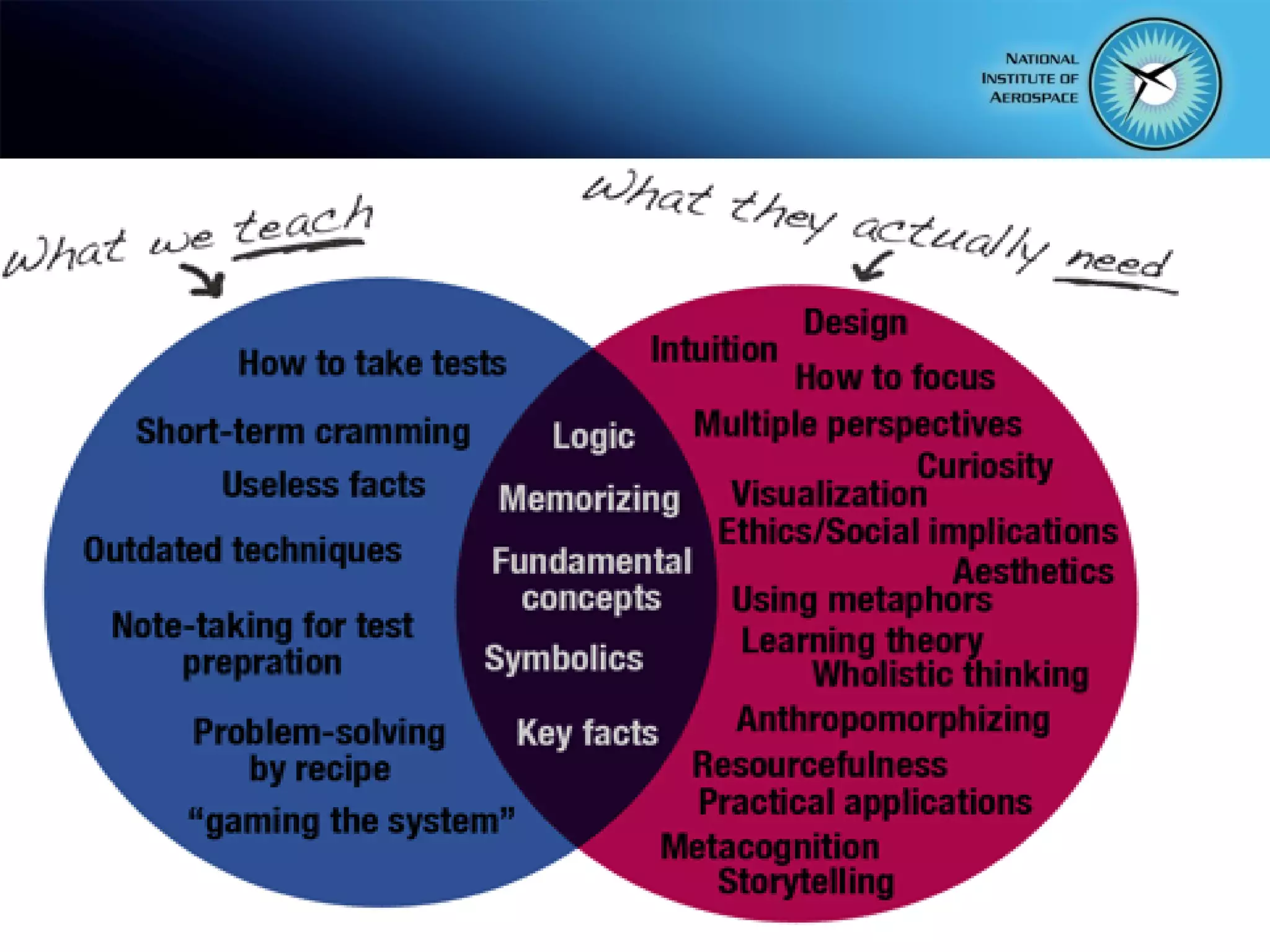
This document summarizes the objectives and content of a presentation on connecting teaching and learning to 21st century skills and tools. The presentation defines characteristics of 21st century students, explores challenges for teachers, and examines how classrooms and professional development can incorporate 21st century topics and digital tools to engage students.