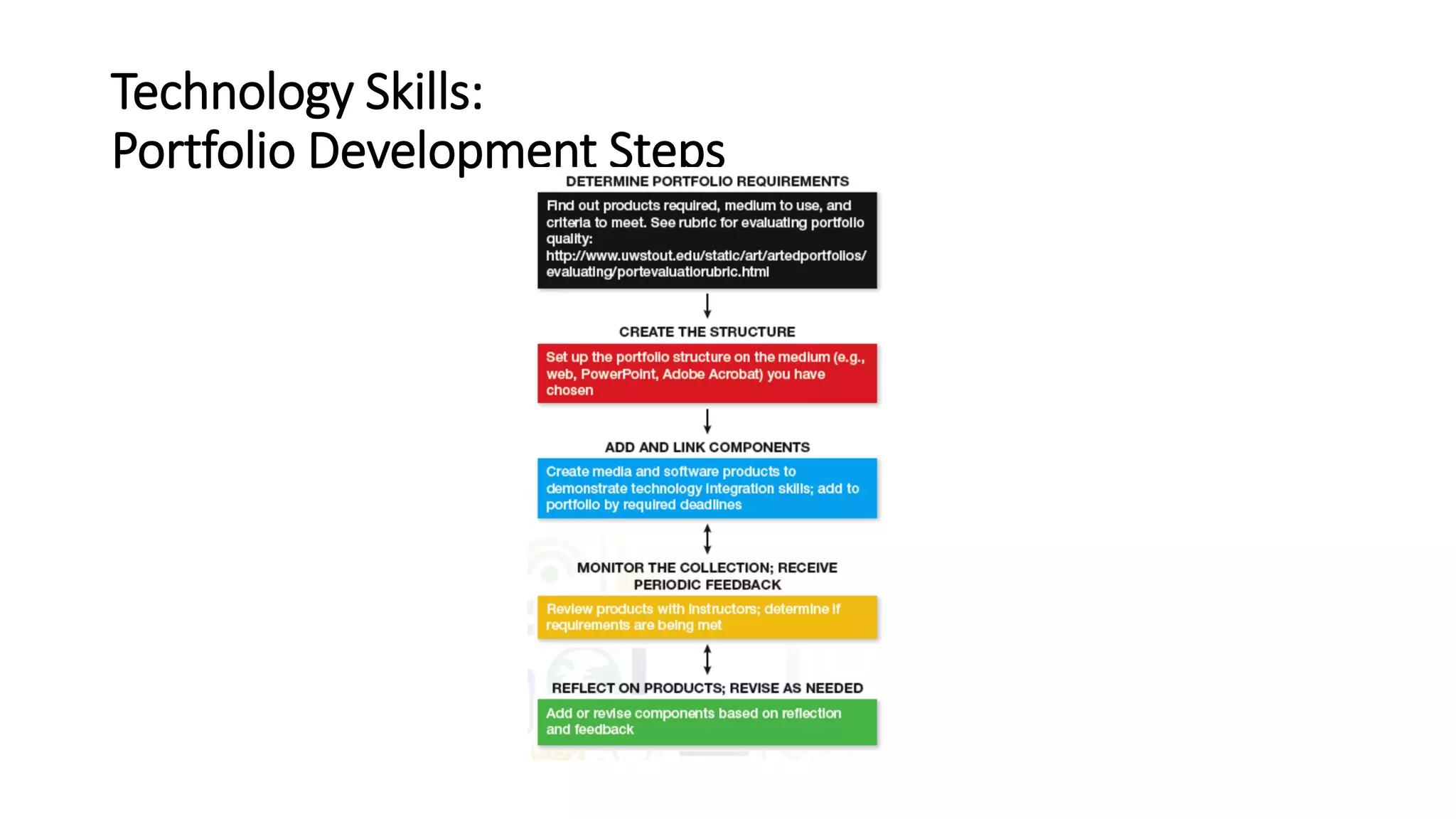
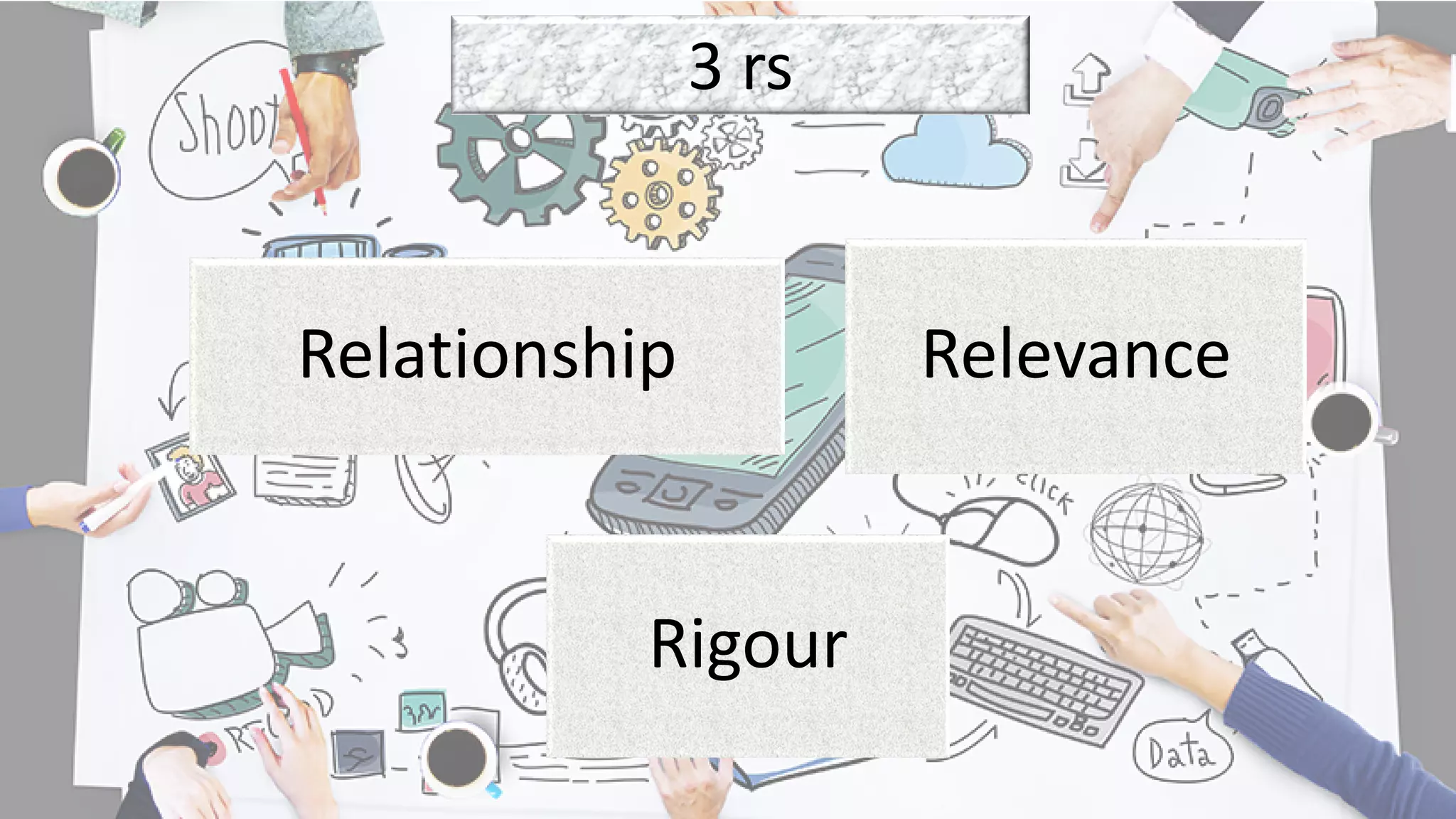
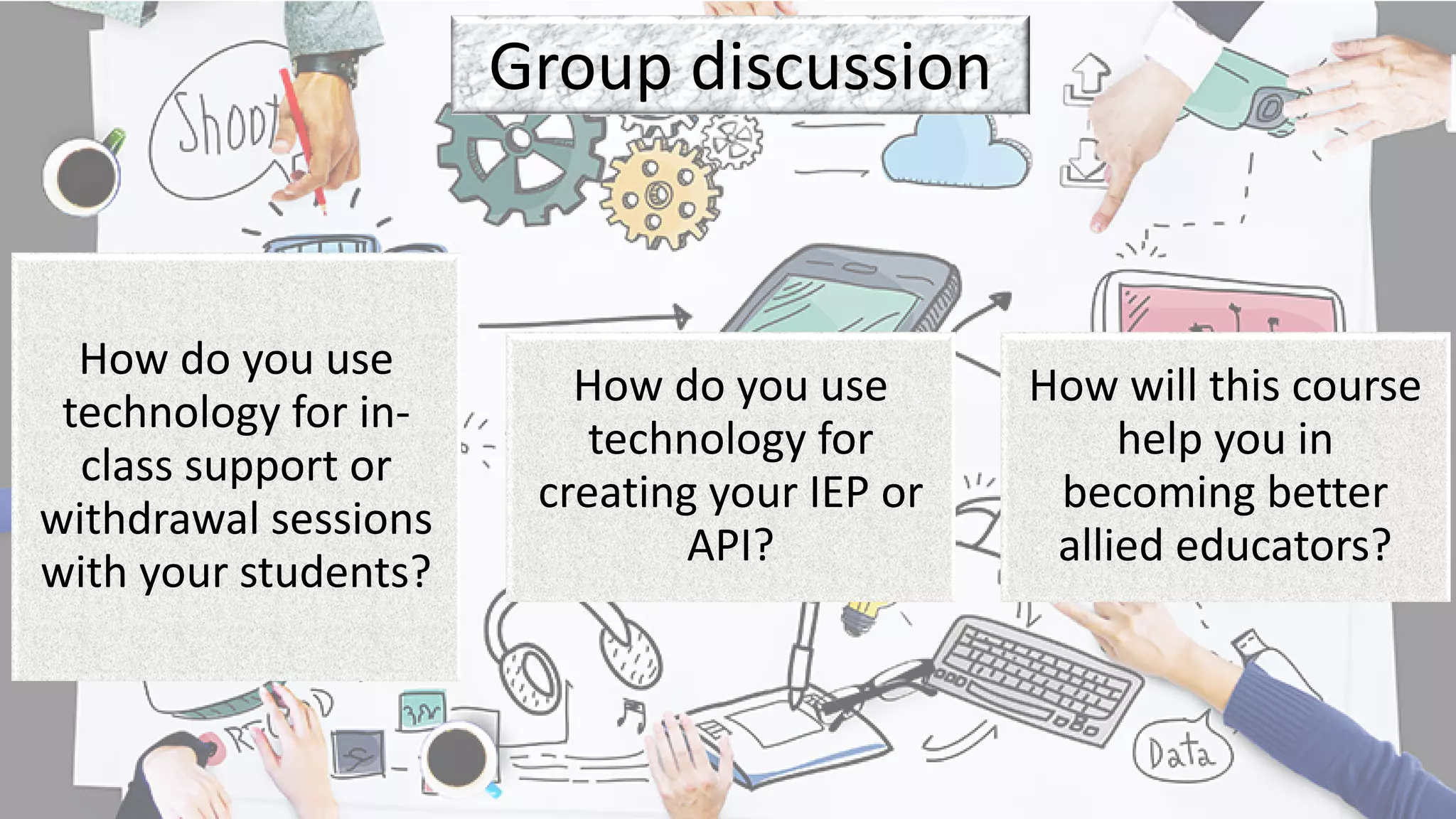
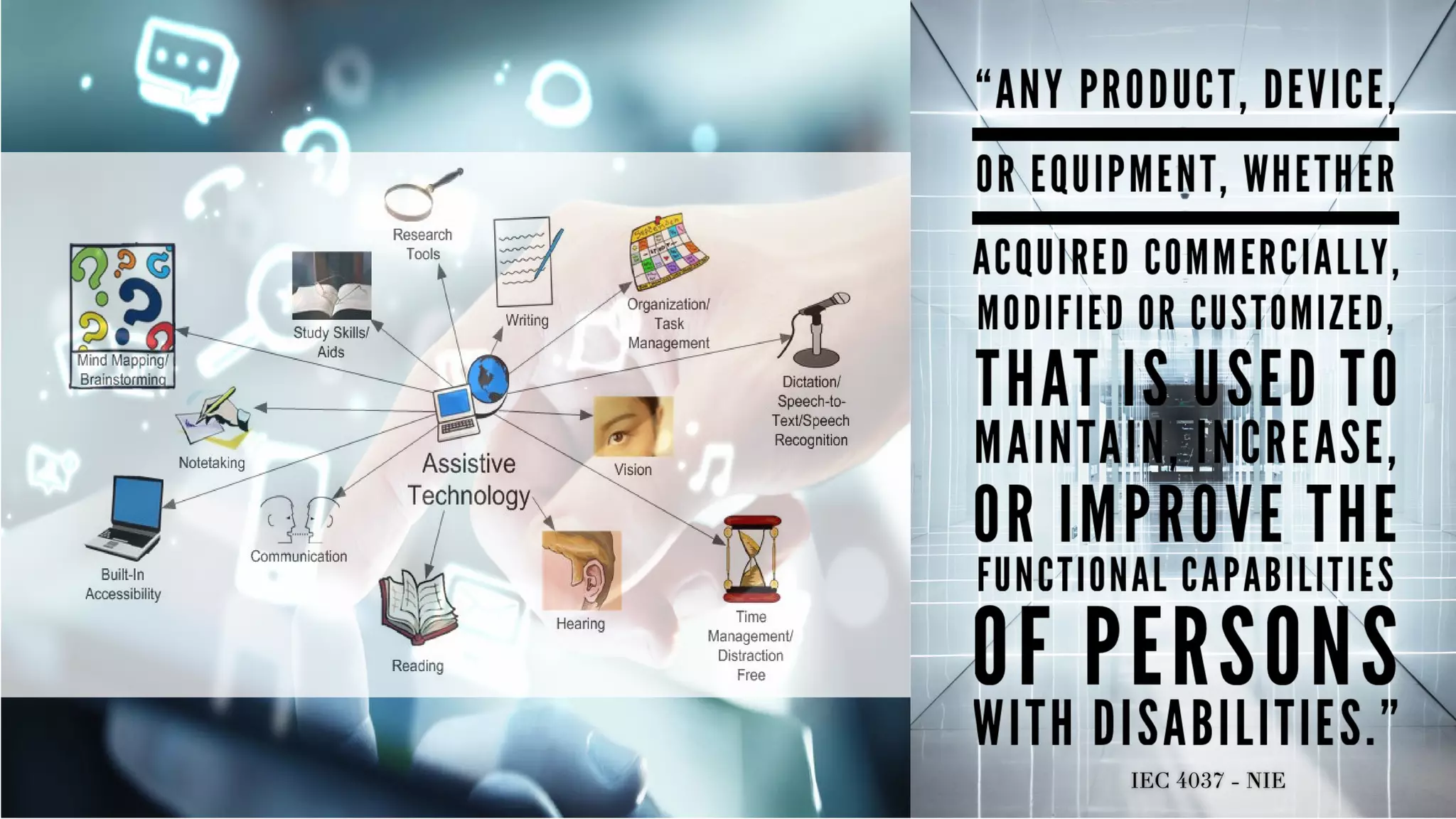
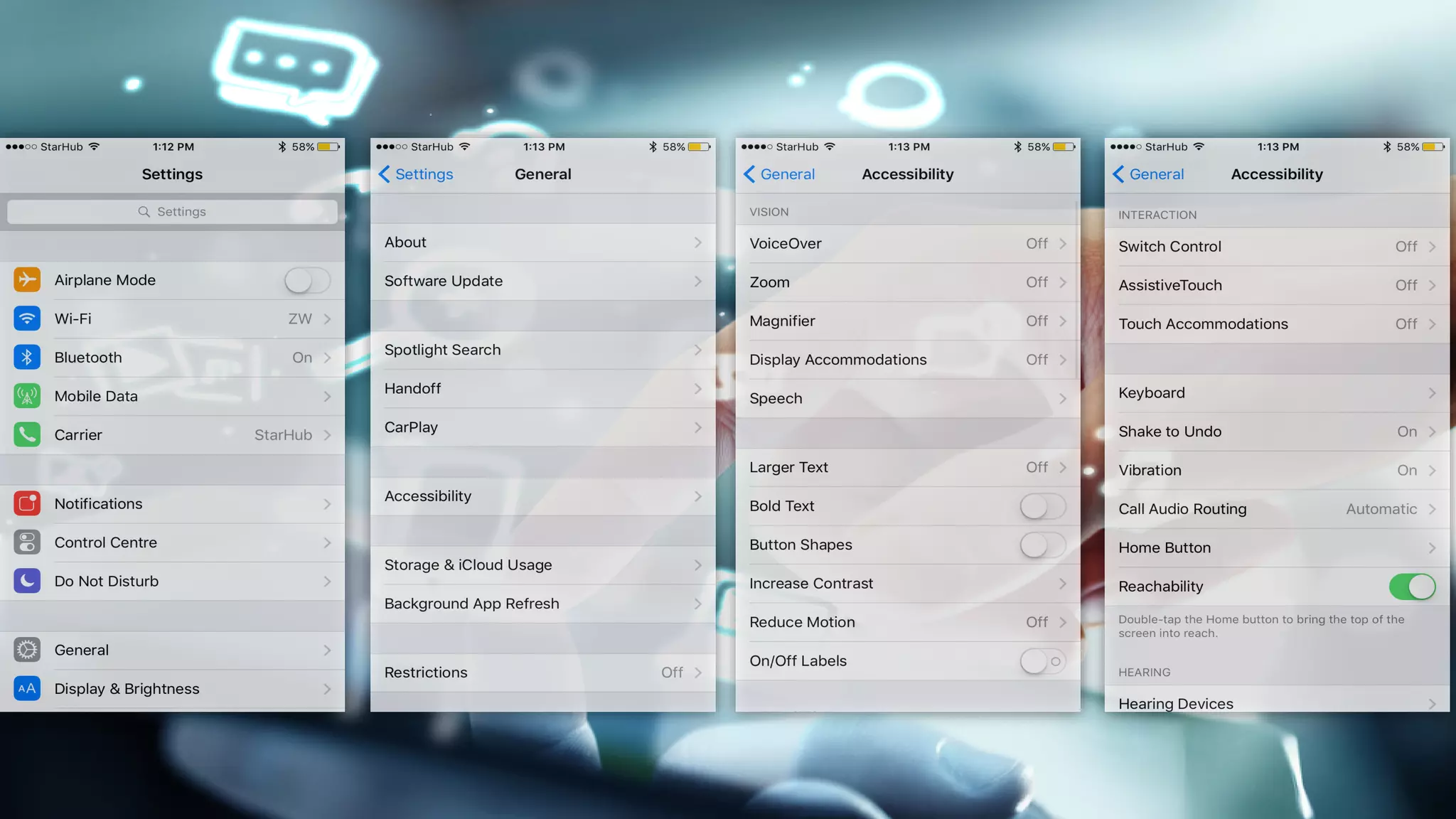
This document provides an overview of an educational technology course, including:
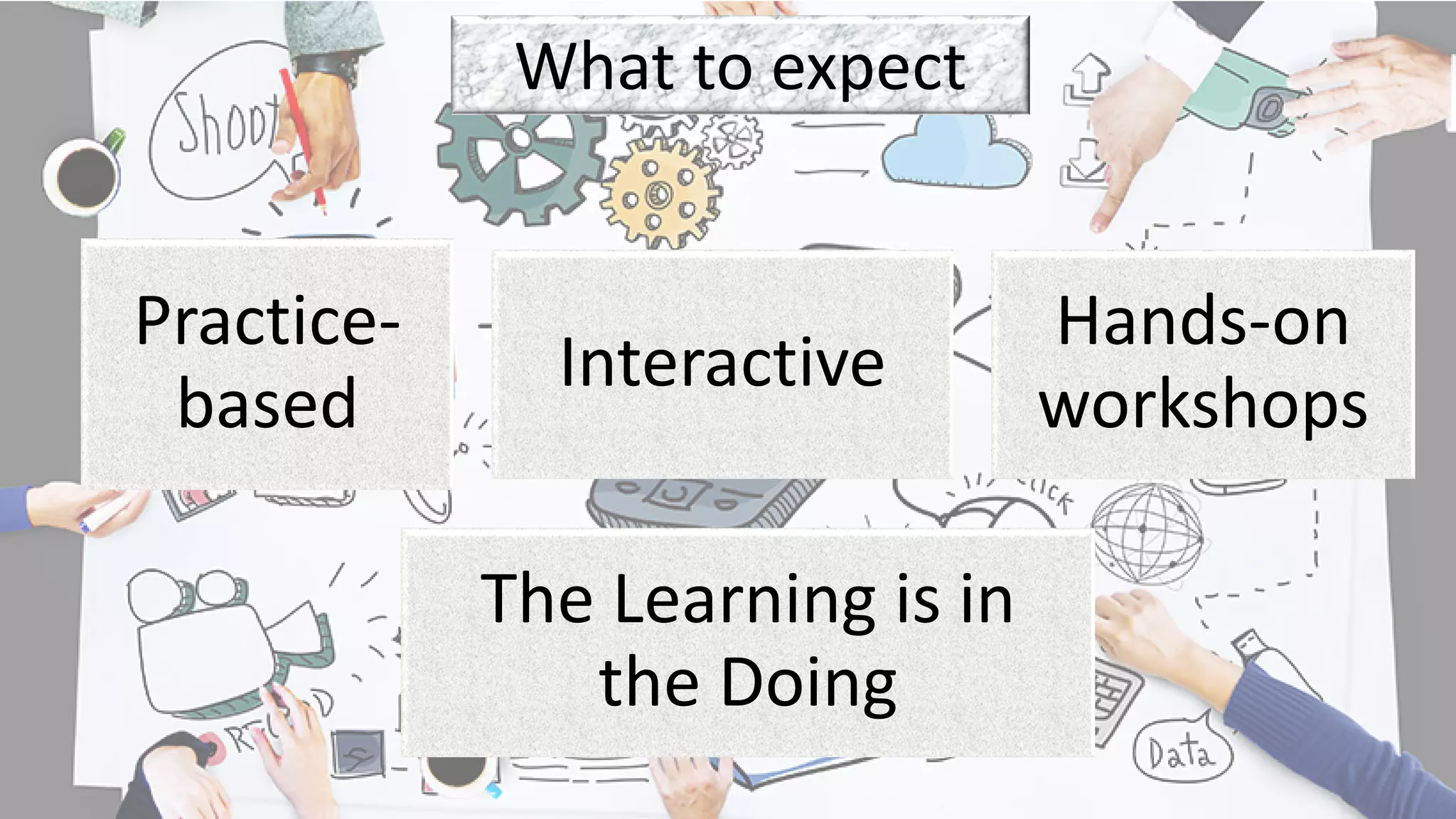
- The course instructors and what to expect from the interactive, hands-on workshops focusing on practical strategies.
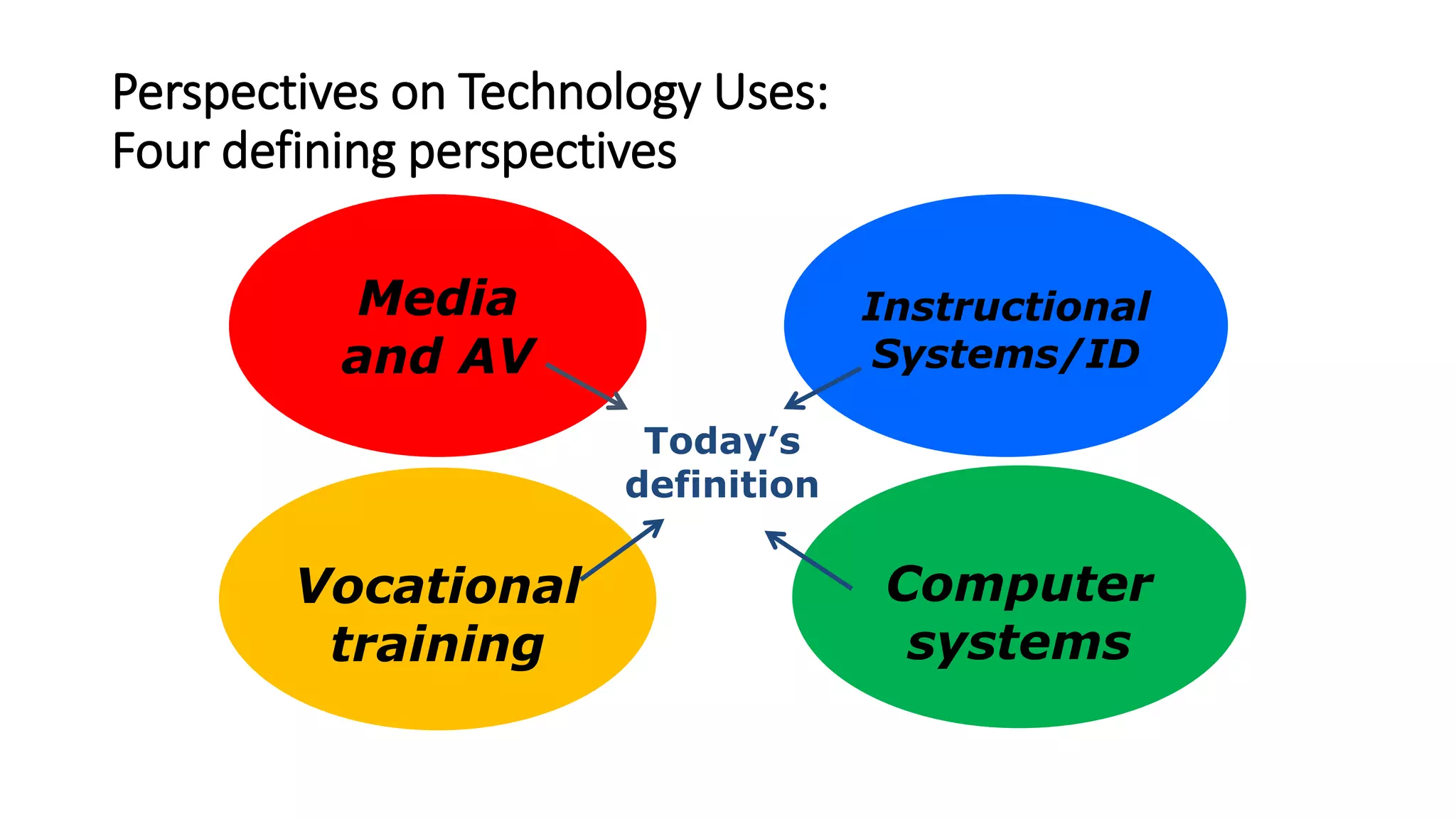
- Key terminology, perspectives, and definitions related to educational technology from various professional organizations are discussed to understand the "big picture".
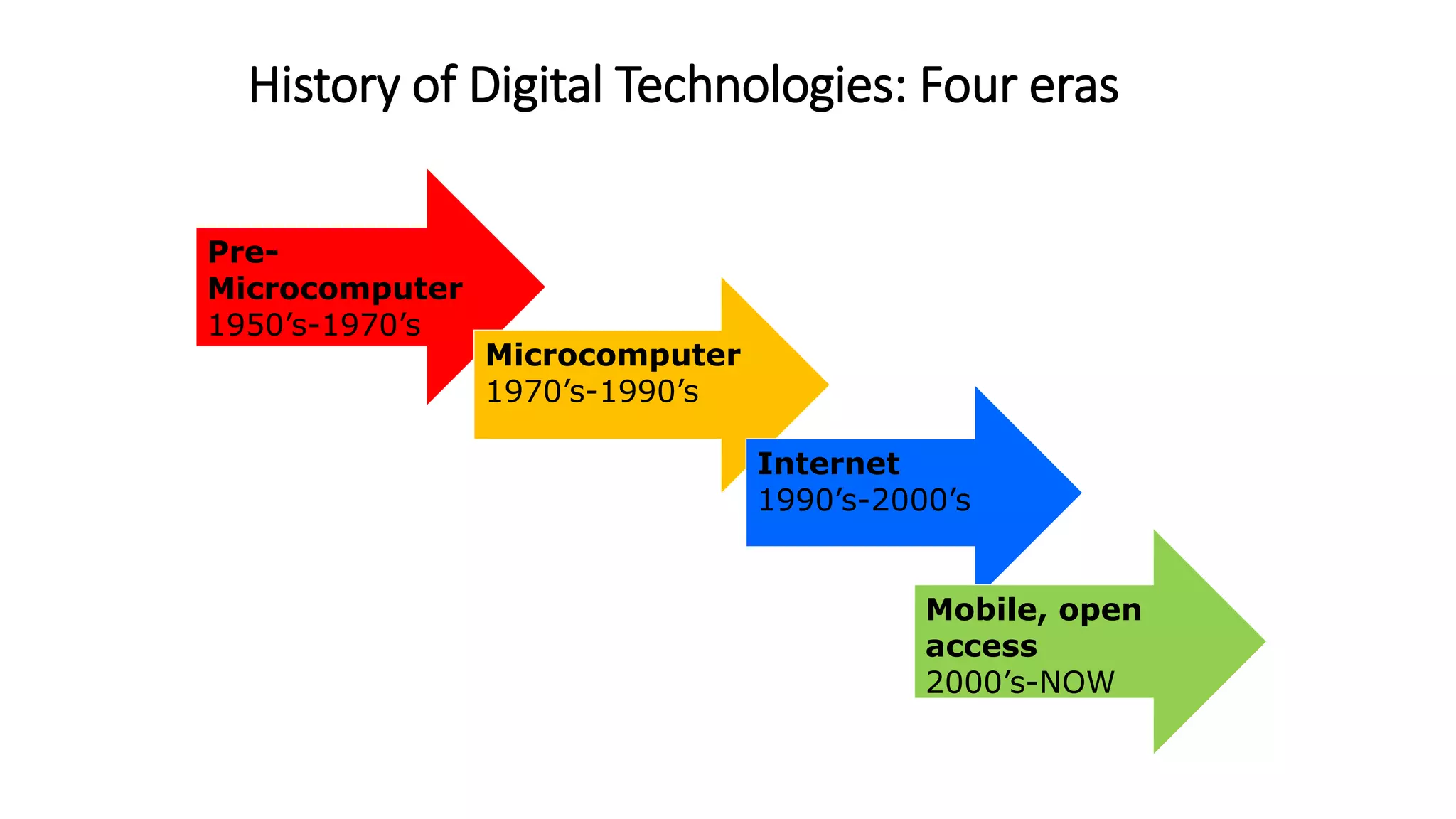
- The history of digital technologies from the pre-microcomputer era to current mobile/open access technologies is examined to understand what was learned from the past.
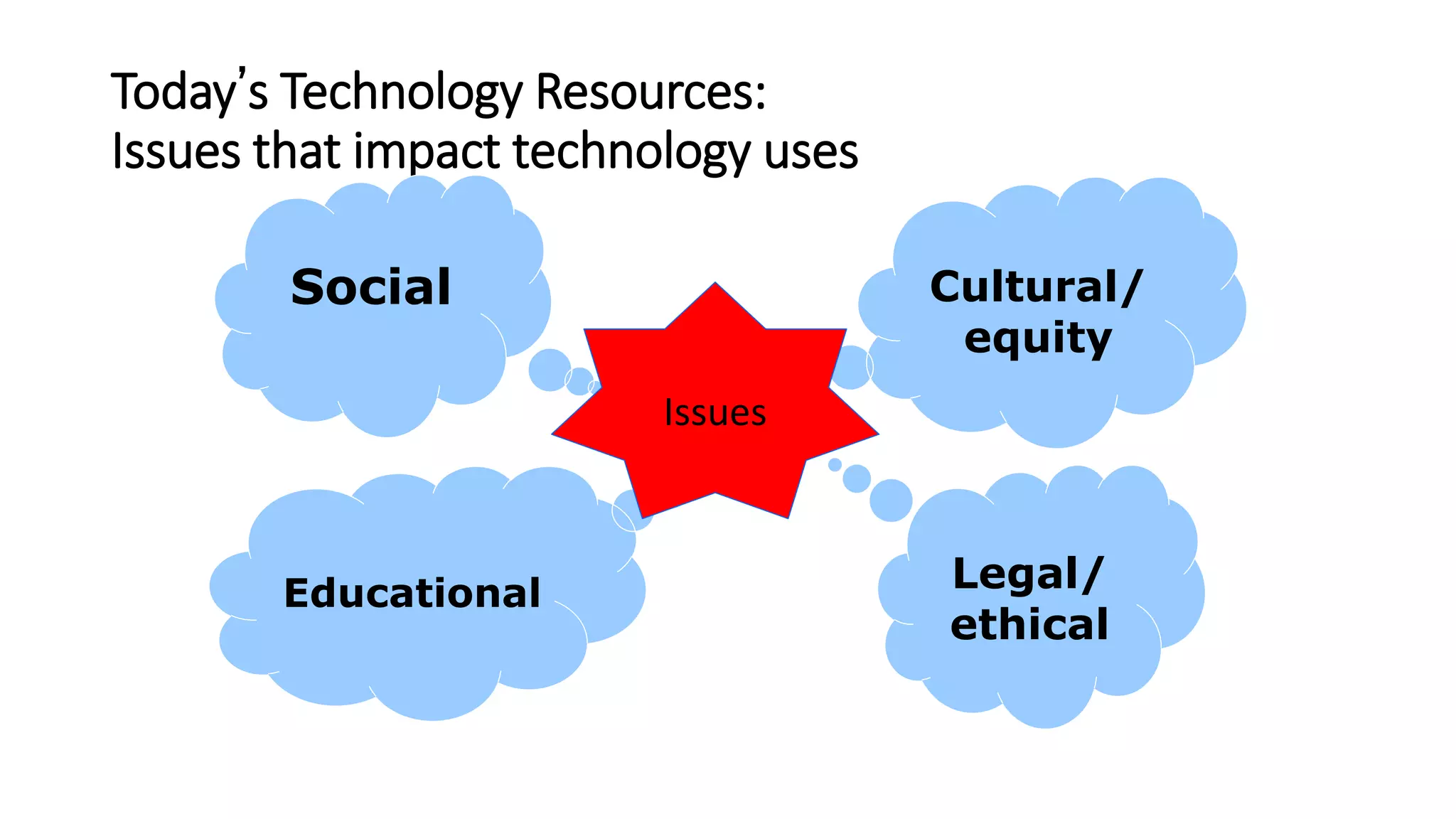
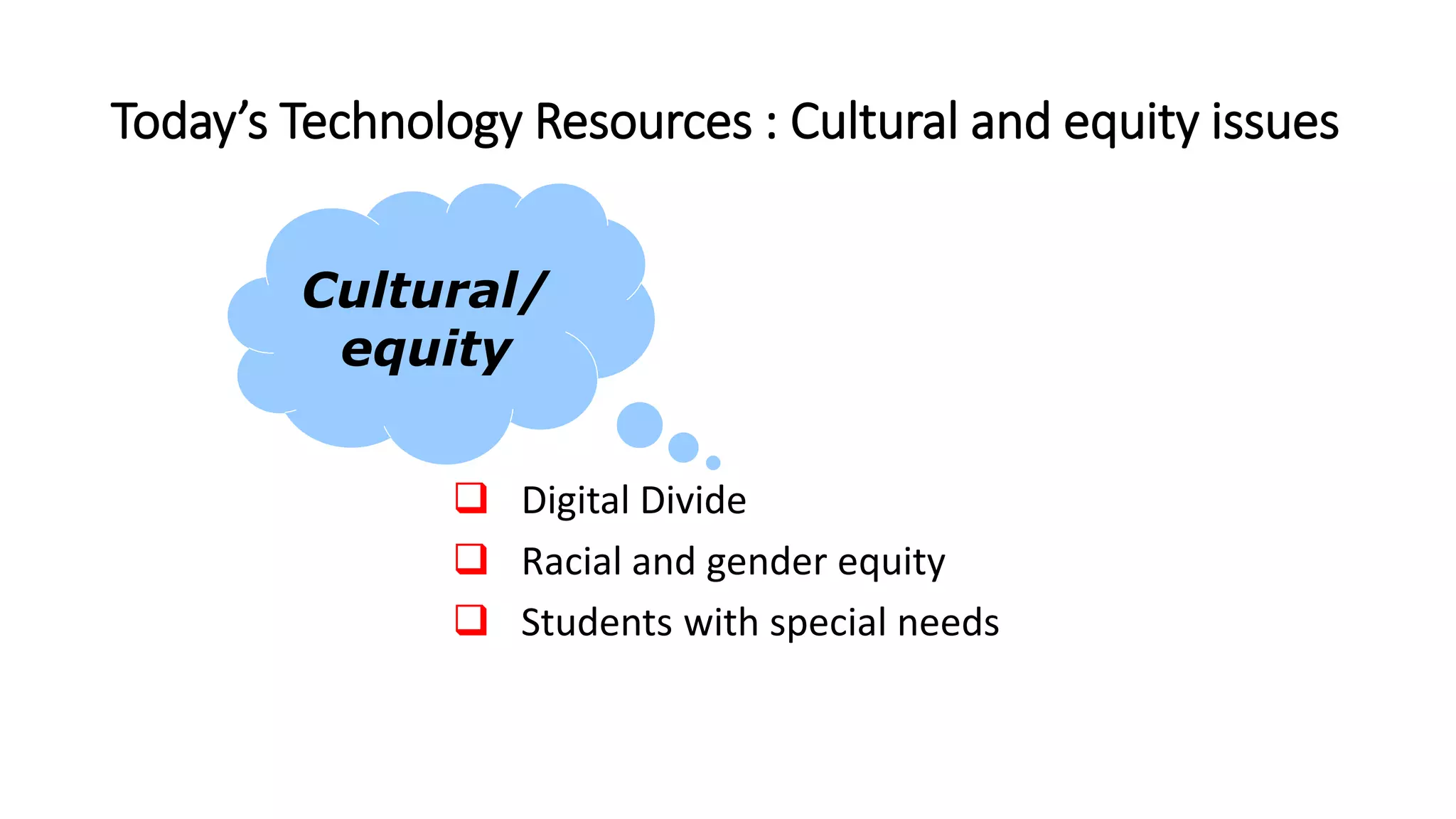
- Issues impacting technology uses such as cultural, social, educational are reviewed to develop a sound rationale for integrating technology.
- Emerging trends in hardware/software and their educational applications are explored to consider the future of educational technology