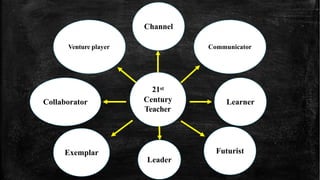
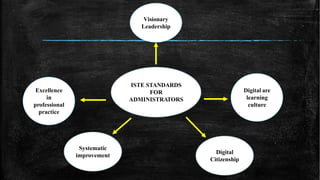
This document discusses the evolution of teachers, students, and instruction from early generations to the 21st century in light of technological advances. It notes that 21st century teachers act as channels, communicators, learners, futurists, leaders, exemplars, collaborators, and venture players. Students are now active creators of knowledge who think critically and collaborate, versus passive receivers of facts. Instruction has shifted from teacher-centered to student-centered, incorporating multimedia, collaboration, and real-world contexts. The document also outlines 21st century skills and elements that foster 21st century learning, including emphasis on core subjects, learning skills, tools, content, context, and assessments. Finally, it discusses standards for technology use in education