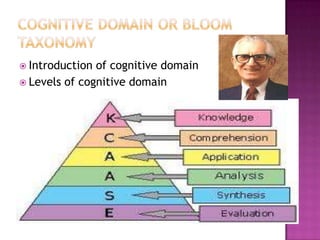
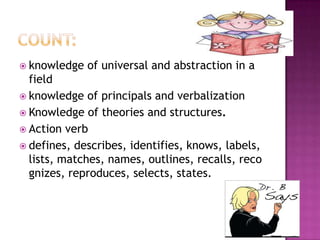
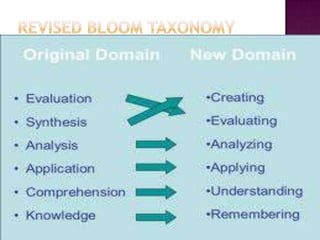
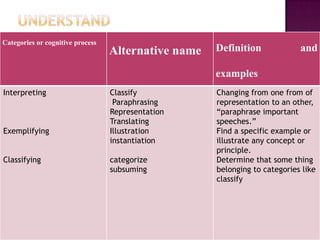
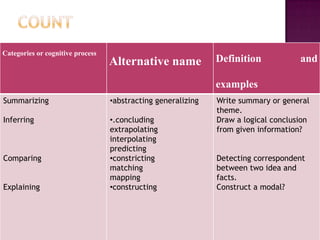
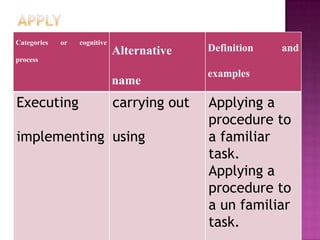
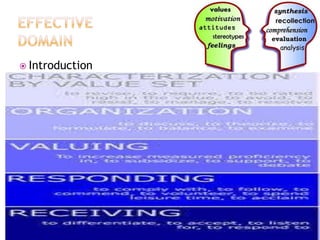
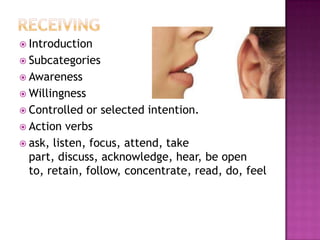
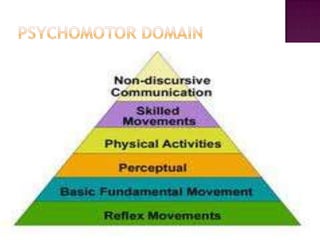
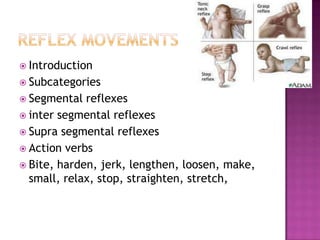
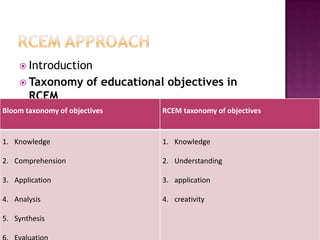
The document discusses the classification of educational objectives into three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. It provides detailed descriptions and examples of levels within the cognitive domain, including knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. Sub-categories and action verbs are provided for each level. The document also discusses objectives related to the affective and psychomotor domains.