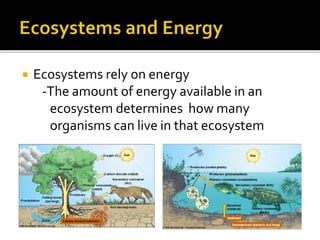
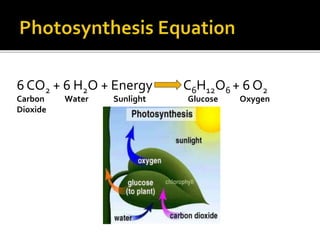
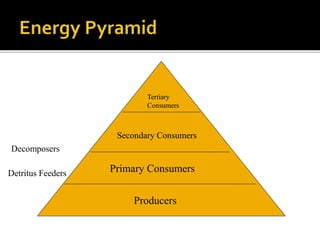
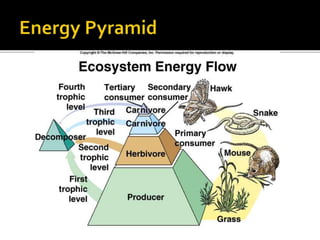
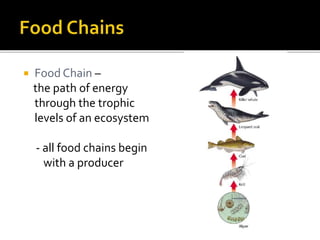
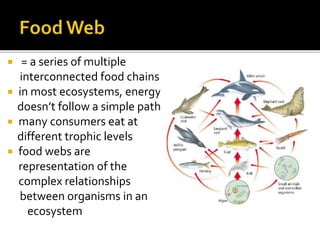
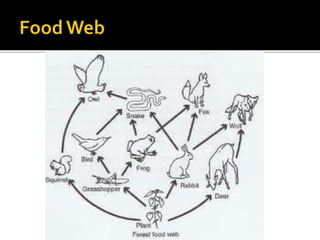
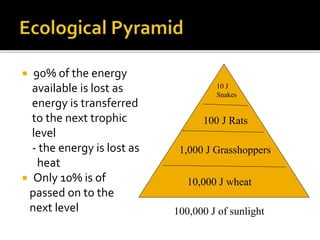
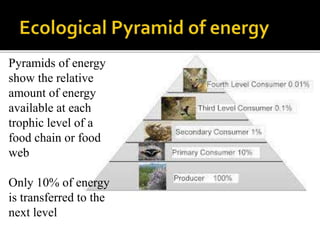
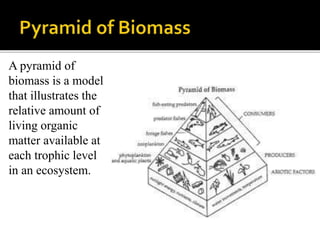
An ecological system consists of a living community and its physical habitat. Energy enters through sunlight and powers primary producers like plants through photosynthesis, generating glucose. Primary consumers then eat producers, and secondary consumers eat primary consumers, forming a food chain that transfers 10% of energy between trophic levels. Decomposers recycle nutrients by breaking down dead organisms.