1) Ecosystem degradation diminishes species' ability to survive and is caused by deforestation, mining, habitat change, overexploitation, pollution, and climate change.
2) Ecological succession refers to predictable changes in community composition, such as hardwood trees replacing pine forests by outcompeting them for sunlight.
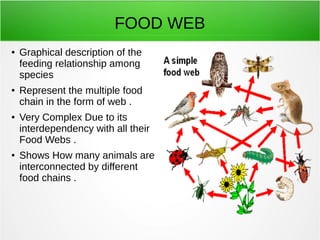
3) A food chain represents the transfer of energy between trophic levels from producers to primary, secondary and tertiary consumers and decomposers. Food webs show the complex interconnected food chains in an ecosystem.