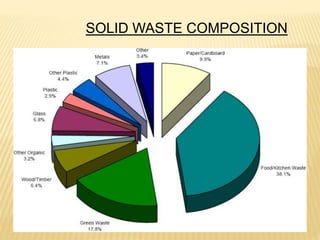
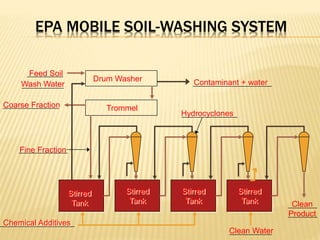
Soil pollution occurs when undesirable materials are added to soil, damaging organisms and reducing land usability. Common pollutants include petroleum, heavy metals, pesticides, and excess fertilizers from industrial, agricultural, and urban activities. Soil pollution affects agriculture, ecosystems, and human health. Methods to control soil pollution include reducing chemical use, recycling waste, reforestation, soil washing, and land farming to stimulate microbial breakdown of contaminants. Long-term effects of unchecked soil pollution include reduced soil fertility, crop yields, and ecosystem changes.