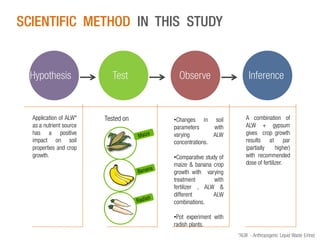
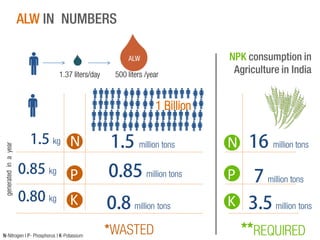
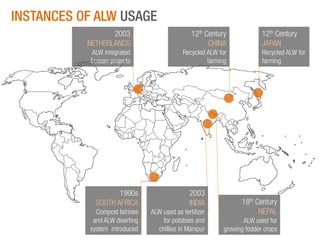
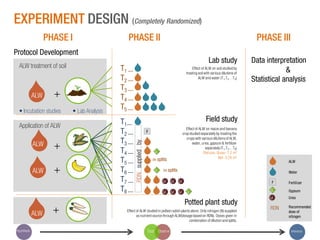
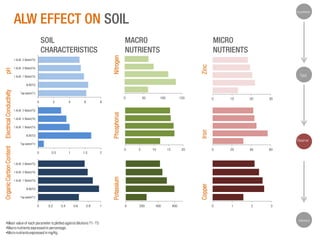
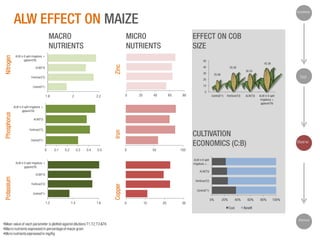
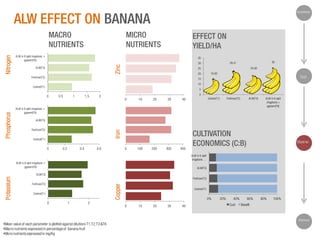
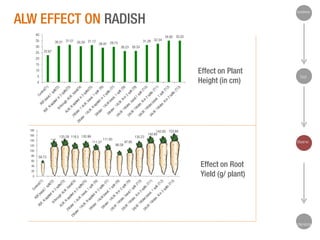
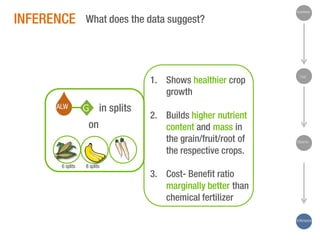
The document discusses a Ph.D. thesis by G. Sridevi on the impact of anthropogenic liquid waste (human urine) on soil properties and crop growth, supported by Arghyam Foundation. The study found that urine can effectively function as a fertilizer, improving crop growth when combined with gypsum, and presents various experiments on maize, banana, and radish plants to validate these findings. Finally, it emphasizes the potential economic benefits of using urine as a sustainable agricultural nutrient source.