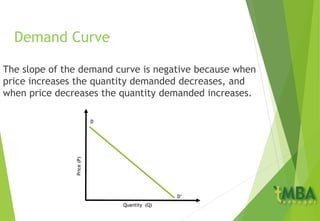
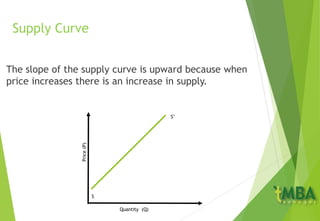
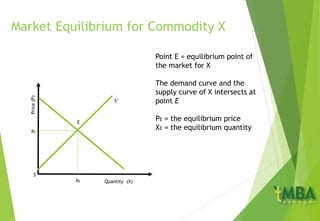
This document outlines the course schedule and content for an economics course. It includes chapters on the subject and aim of economics, the market mechanism of demand and supply determining price, and economic growth and national economic performance. A key section summarizes the market for a commodity X, how demand and supply curves establish an equilibrium price where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied, and how equilibrium is impacted by changes in demand and supply. It also discusses how prices coordinate production and allocation across interdependent markets.