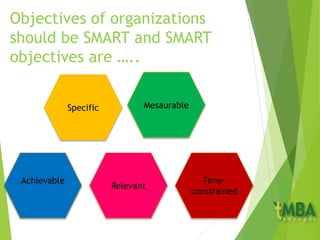
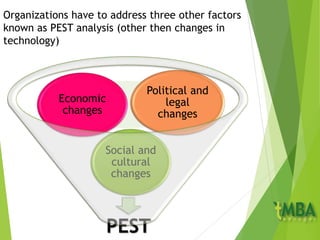
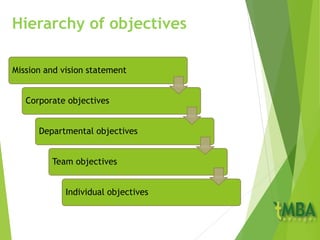
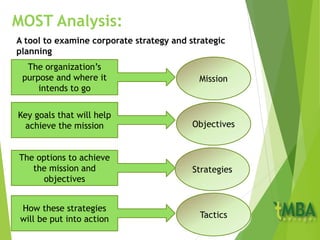
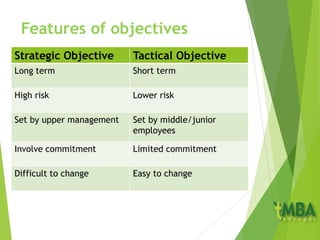
This document outlines the course schedule and key chapters for a business management and organization course. It includes 4 chapters that will be covered: 1) business management and organization, 2) objectives, stakeholders and the external environment, 3) organizational planning and decision making, and 4) growth and the impact of globalization. The document provides further details on chapter 2, describing objectives and how they should be SMART. It also discusses management by objectives, assessing objectives, and analyzing organizations' external environment using PEST analysis.