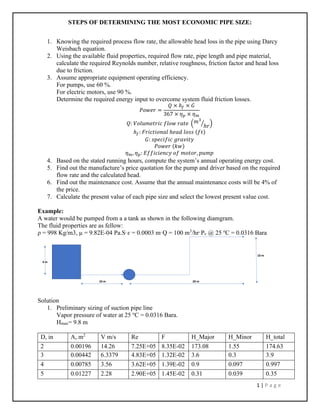
The document outlines steps for determining the most economical pipe size, which includes calculating flow rate, head loss, and energy costs using the Darcy-Weisbach equation. It presents an example analysis comparing 4-inch and 5-inch diameter pipes, indicating that the 5-inch diameter is more economically optimal despite having a higher initial cost. The analysis also includes maintenance costs and break-even calculations to assess overall costs and efficiencies.