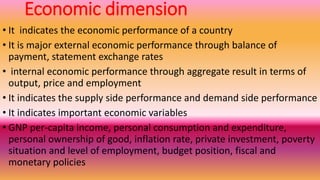
The document discusses the economic environment and dimensions that influence business in Nepal. It outlines key components of Nepal's economic structure, including GDP, GDP per capita, economic policies, inflation rates, and levels of employment. It also examines Nepal's socioeconomic indicators such as population size, density, age distribution, labor force composition, and employment trends. The 14th economic development plan aims to transform agriculture and tourism and expand infrastructure to reach middle income status and a more prosperous, socially just nation.