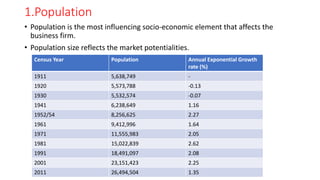
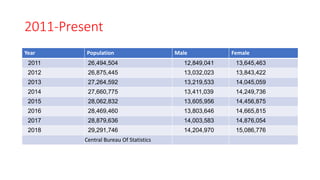
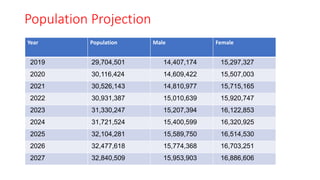
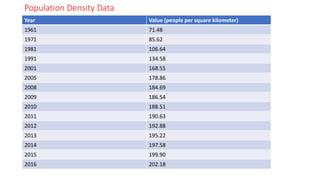
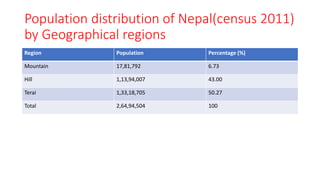
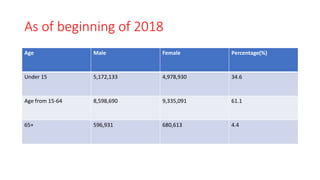
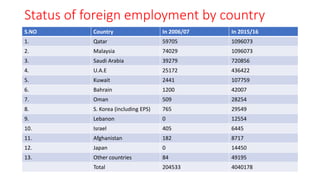
The document discusses various socio-economic dimensions affecting Nepal, focusing on population dynamics, density trends, age and sex structure, employment trends, labor market issues, and migration for foreign employment. Key findings include a growing population, increasing urbanization, a shifting labor force away from agriculture, and significant migration leading to substantial remittance inflows. The demographic factors play a crucial role in influencing business environments and economic development in the country.