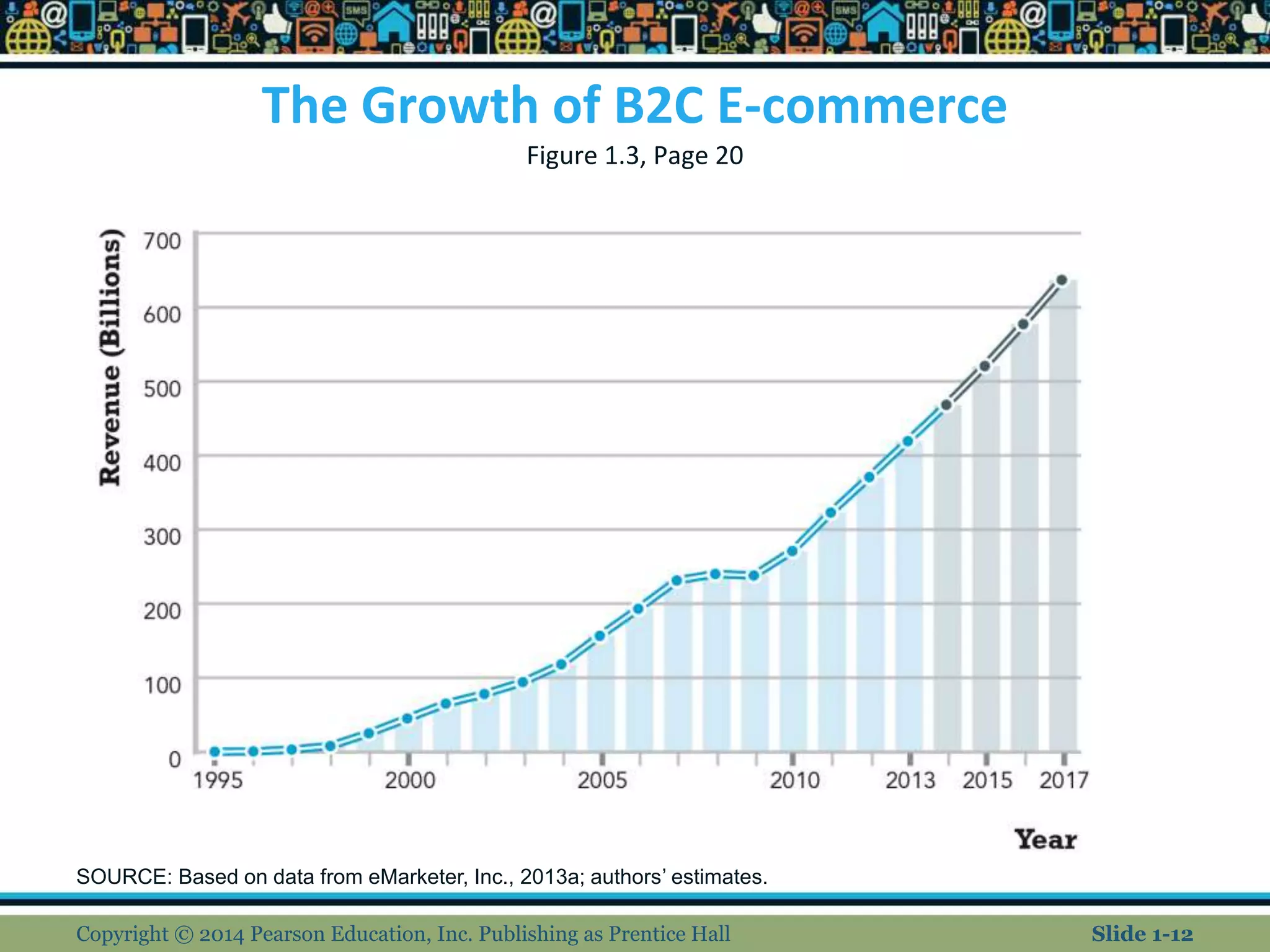
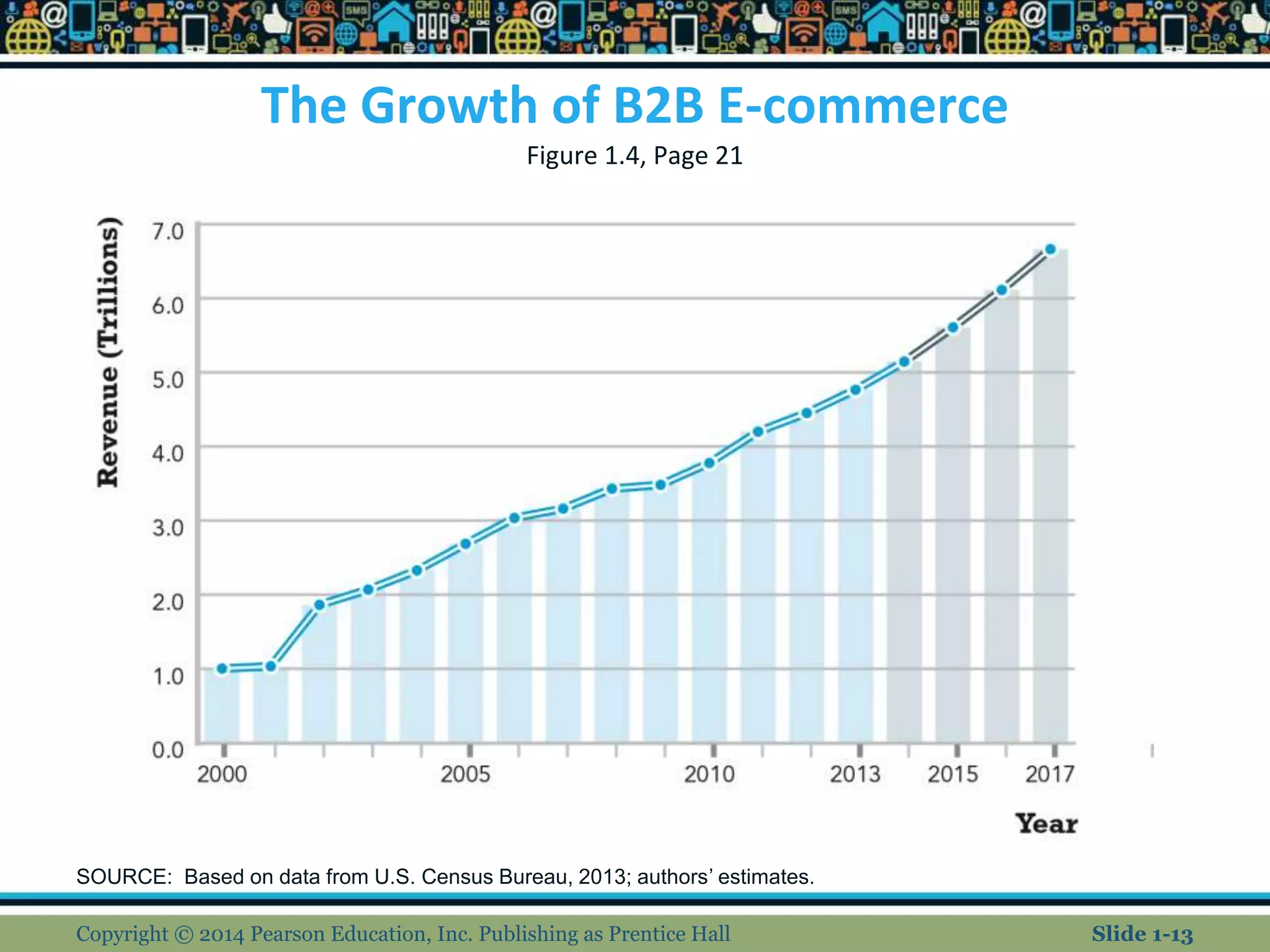
This document provides an overview of e-commerce and discusses key trends. It covers the evolution of e-commerce from its beginnings in the 1990s to present day, highlighting major milestones like the dot-com crash and rise of social media. The document also examines characteristics of e-commerce like ubiquity and personalization. Types of e-commerce like B2C, B2B, and mobile are defined. Future predictions include the continued growth of integrated online and offline companies and potential increased regulation.