Embed presentation
Download to read offline


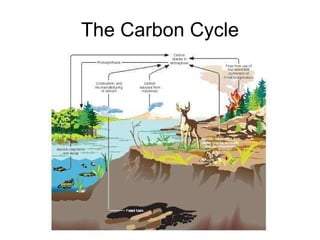




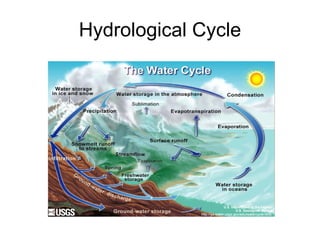

The document summarizes several natural cycles: 1) The carbon cycle involves carbon sinks like plants, forests and soil that absorb carbon, and carbon sources like combustion, respiration and decomposition that release carbon. 2) Nitrogen fixation converts inert nitrogen gas into bio-usable forms through atmospheric fixation by lightning or biological fixation by microbes and plants. Nitrification converts ammonia into nitrites and nitrates which plants can use but are soluble and can leach from soil. 3) The hydrological cycle describes the continuous movement of water above, on and below the Earth's surface, with the same amount of water circulating but individual molecules coming and going quickly.








